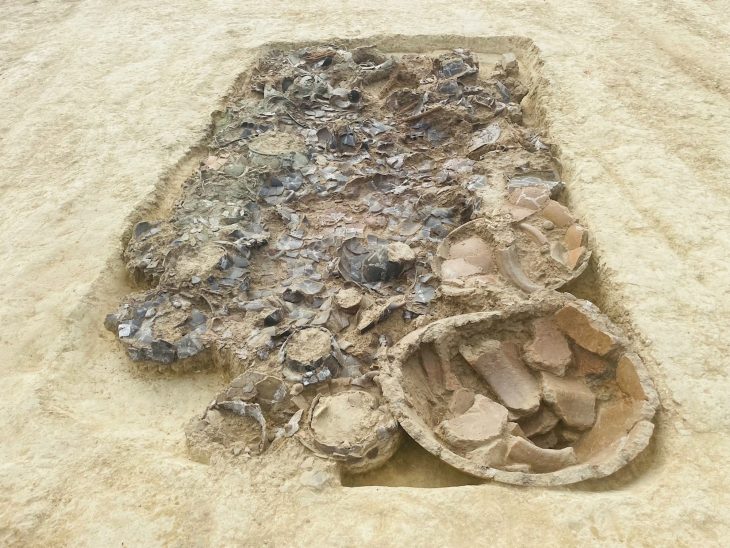
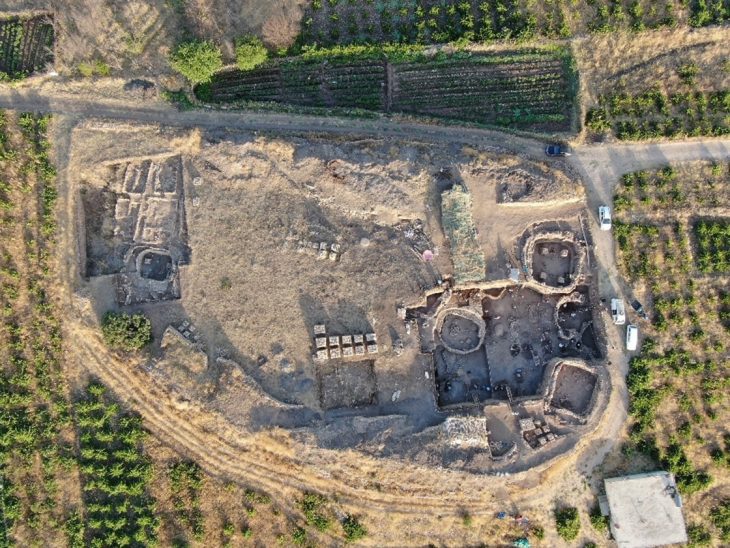
The Tomb of Nestor’s Cup, a burial that contained one of the oldest known Greek inscriptions, was more crowded than expected, scientists discovered.
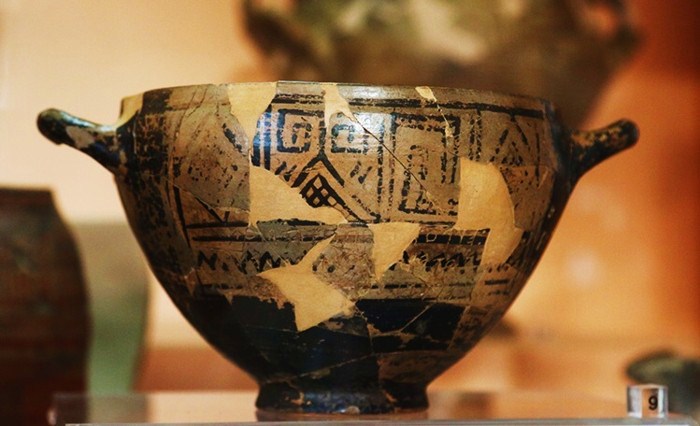
The Tomb of Nestor’s Cup is regarded as one of the most interesting finds in Mediterranean pre-classic archaeology. This tomb, officially known as Cremation 168, dates from the 8th century BCE and is one of the hundreds discovered in the Italian town of Pithekoussai. The burial contained a rich set of grave goods, including a silver brooch and two dozen fragmented pottery vessels. But what captured the attention of the archaeologists was a small ceramic wine cup dated to the second half of the eighth century B.C.E.
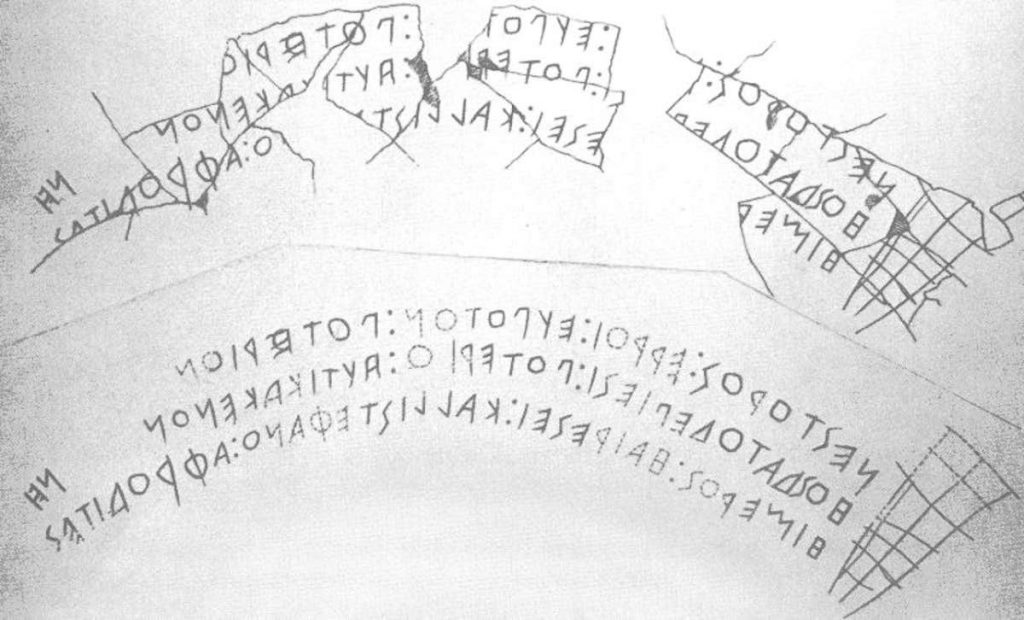
The clay vessel, known as Nestor’s Cup, carries a three-line boast, concluding with a guarantee that whoever drank from the cup will be struck with longing for Aphrodite, goddess of beauty and love.
The cup, which was decorated with simple black geometric motifs, had been brought from the Greek island of Rhodes. Someone wrote the following words on it at some time after it was made: “I am Nestor’s cup, good to drink from. Whoever drinks this cup empty, straightaway desire for beautiful-crowned Aphrodite will seize him.”
Three lines of text in the Greek alphabet are thought to be an allusion to Homer’s poetry.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The tomb was thought to hold a single occupant — a child — but a new analysis of the tomb’s bones revealed that it instead held the remains of at least three adults.
The results of the new study were published in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on October 6, 2021, by Melania Gigante of the University of Padua in Italy.
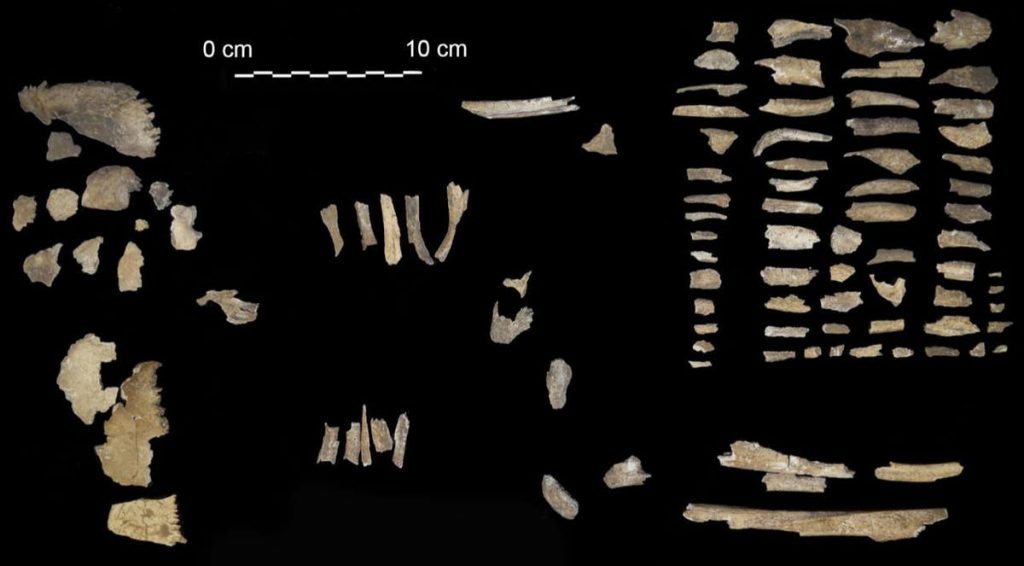
Gigante and colleagues conducted thorough examinations on the shape (morphology) and tissues (histology and histomorphometry) of the 195 burned bone pieces in the tomb for this study. Only around 130 of these fragments are human, with at least 45 belonging to animals such as goats and maybe dogs. The researchers discovered bone tissue from distinct life stages among the human bones, indicating at least three individuals of different ages. This is the first evidence of multiple individuals (and non-humans) among the remains in the Tomb of Nestor’s Cup.
The bone fragments could be grouped into three distinct age groups, the researchers found, meaning that at least three individuals were buried in the tomb. While heat damage from the cremation made it impossible to determine their ages with precision, none of the bones belonged to a child, Gigante and colleagues conclude.
Further research might help to solve the mysteries surrounding the creation of this tomb and its famed cup.
















