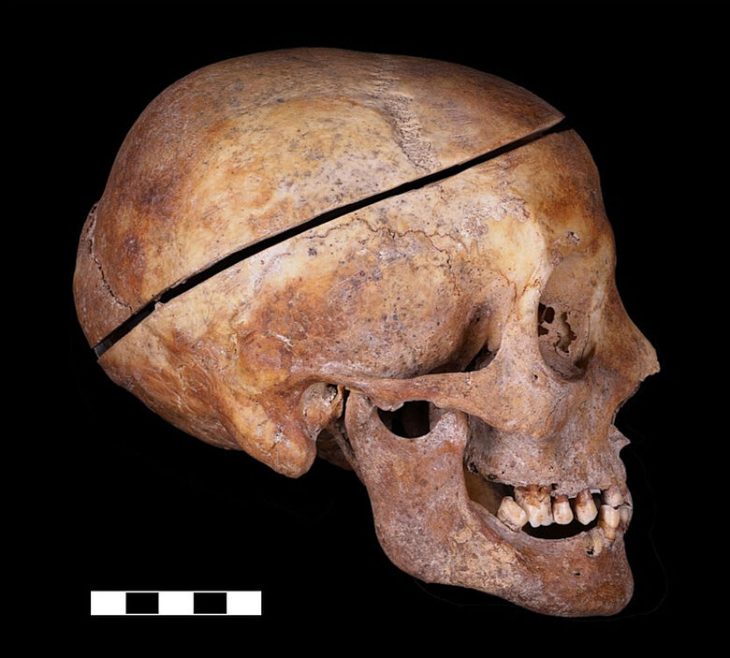
A genetic analysis of bone fragments excavated from an archaeological site in Ranis, Germany provides conclusive evidence that modern humans – Homo sapiens – had reached northern Europe around 45,000 years ago.
This dates modern humans -Homo sapiens- arrival thousands of years earlier than previously thought and shows that they co-existed with Neanderthals for several millennia before the latter went extinct. In addition, during this period, Neanderthals and humans interbred, as evidenced by Neanderthal DNA found in the modern human genome.
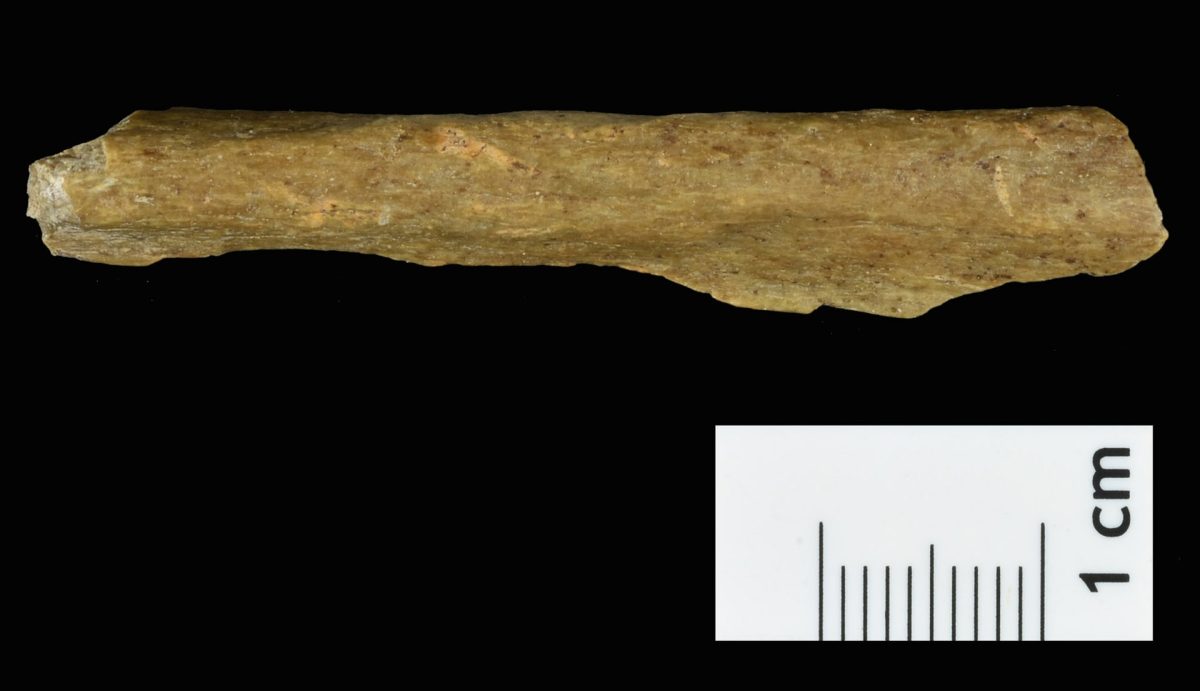
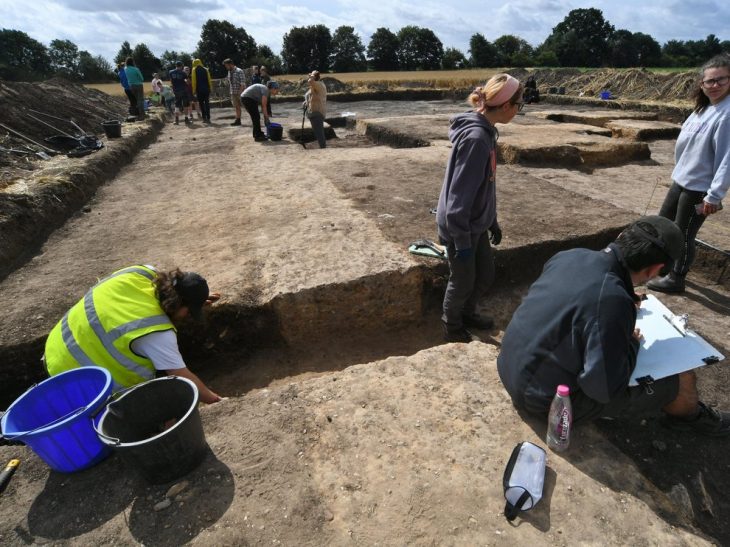
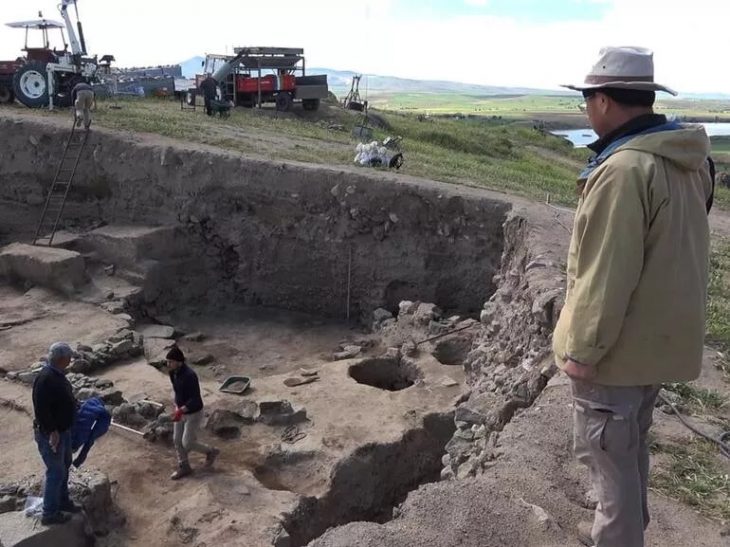
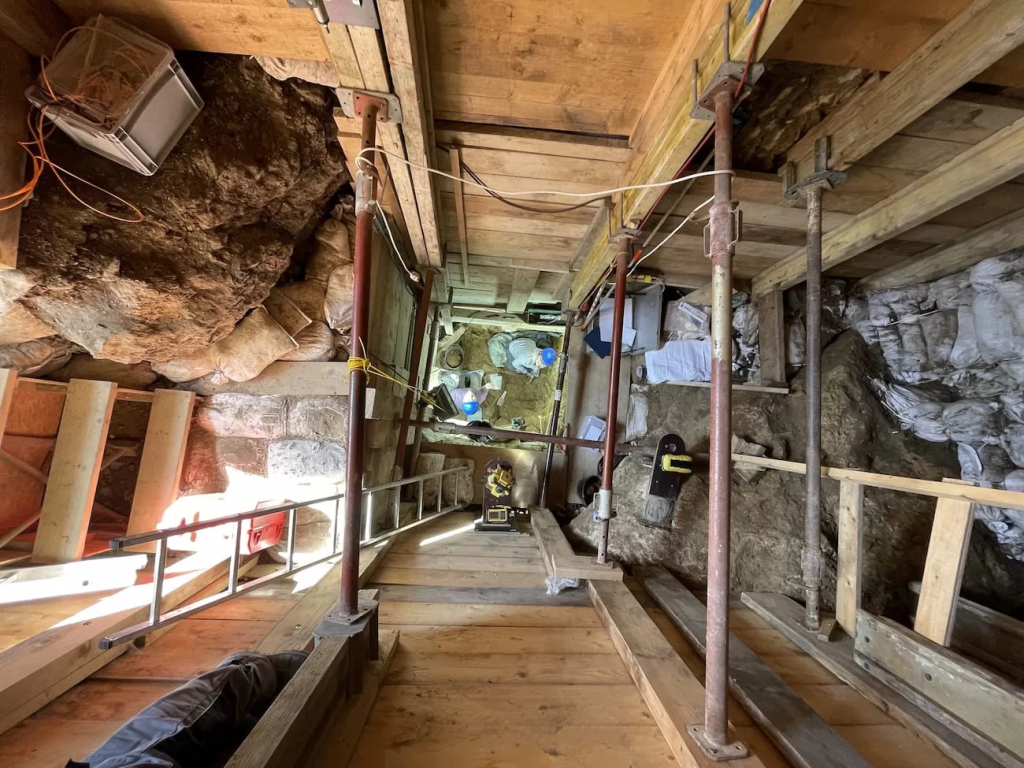
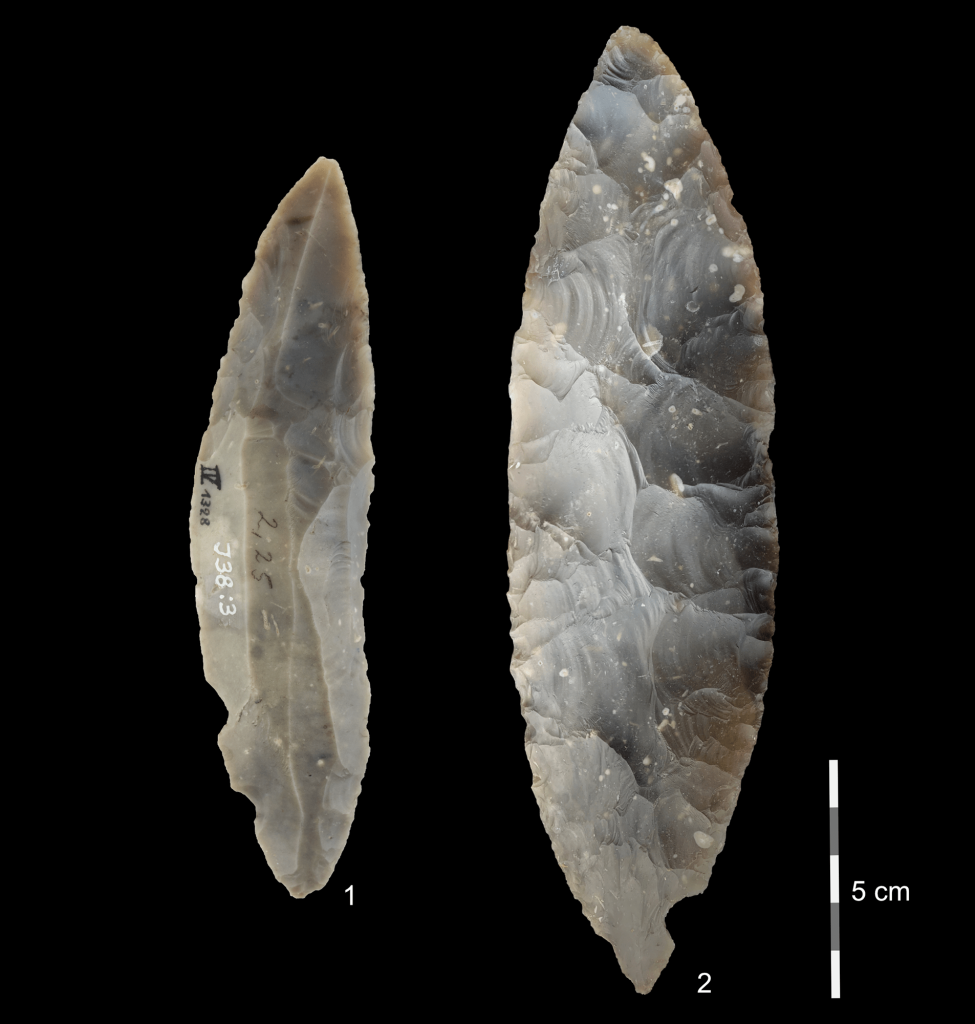
Scientists discovered leaf-shaped spear points, animal remains, and thirteen bone fragments identified as early modern humans at the base of a medieval castle, 24 feet deep into the layered sediment of the Ilsenhöhle cave. These findings provide evidence that Homo sapiens existed in northern Europe 45,000 years ago.
Thirteen bone fragments’ DNA revealed they belonged to Homo sapiens, and their mitochondrial sequences matched those of other European populations. Remarkably, several fragments shared the same maternal lineages, indicating they came from the same individual or close female relatives.
This genetic evidence supports previous discoveries that Homo sapiens and Homo neanderthalensis interbred occasionally as the two species interacted. It also lends weight to the idea that the migration of modern humans into Europe and Asia around 50,000 years ago contributed to the demise of Neanderthals, which had occupied the area for more than 500,000 years, to extinction.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The findings, are detailed in three papers published in the journals Nature and Nature Ecology & Evolution.
The stone blades at Ranis, referred to as leaf points, are similar to stone tools found at several sites in Moravia, Poland, Germany and the United Kingdom. These tools that are thought to have been produced by the same culture, referred to as the Lincombian–Ranisian–Jerzmanowician (LRJ) culture or technocomplex.
Because of previous dating, the Ranis site was known to be 40,000 years old or older, but without recognizable bones to indicate who made the tools, it was unclear whether they were the product of Neanderthals or Homo sapiens.
The Ranis cave provides evidence of the earliest dispersal of Homo sapiens into northern latitudes of Europe. It turns out that stone artifacts that were thought to be produced by Neanderthals were, in fact, part of the early Homo sapiens toolkit,” says Jean-Jacques Hublin, a study co-author and paleoanthropologist at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, in a statement.

Inspection of nearby animal teeth and bones revealed that these early humans existed amid a harsh, tundra landscape populated by reindeer, cave bears, horses, and woolly rhinoceros in conditions comparable to modern Siberia or northern Scandinavia.
Through the use of contemporary methods for the re-excavation of Ranis and the extraction of mitochondrial DNA from bones, the team was able to reconstruct the history of early settlements throughout northern Europe.
Their multidisciplinary analysis creates a new chronology, demonstrating that, contrary to popular belief, Homo sapiens did not arrive after the extinction of Neanderthals, but rather coexisted with them for millennia and intermittently occupied the Ranis site as early as 47,500 years ago.
University of California, Berkeley
Cover Photo: © Tim Schüler TLDA