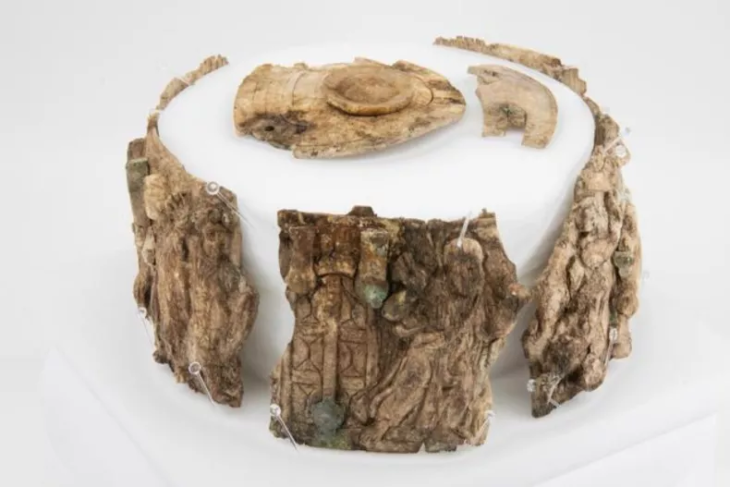
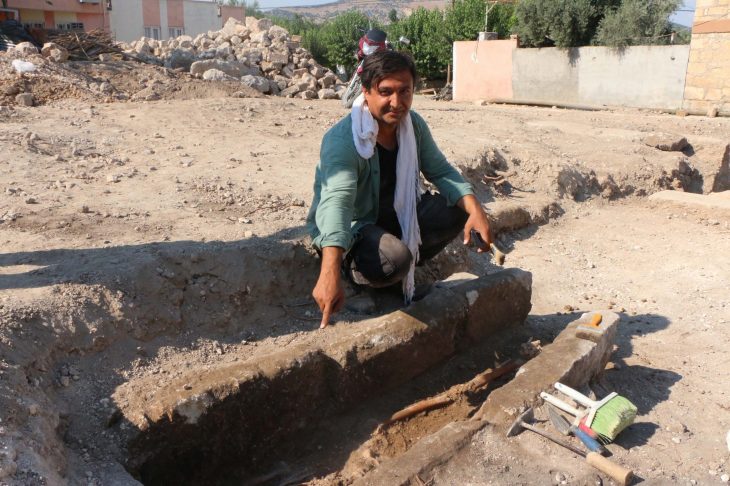
A medieval necropolis was discovered during excavations at the construction site of a bus station in the old seaside town of Sozopol, 35 km south of Burgas on Bulgaria’s southern Black Sea coast.
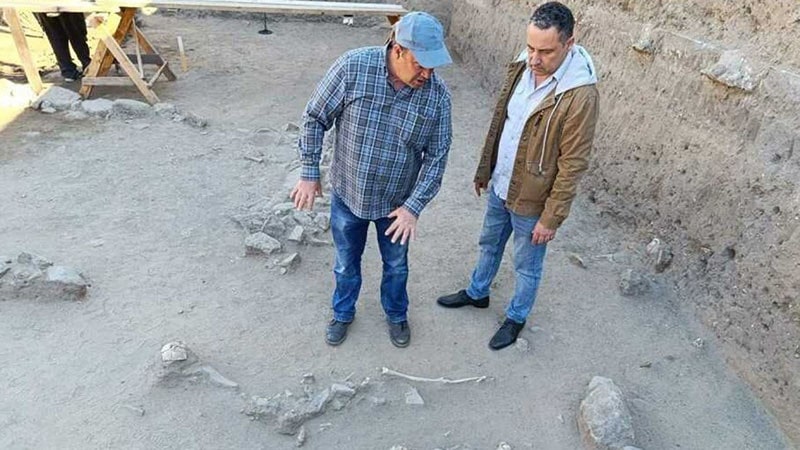
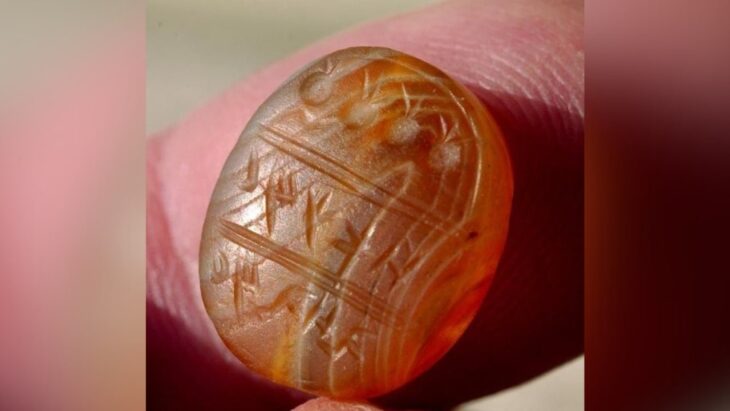
Early on in the rescue excavations on the site of the future Sozopol bus station, Yavor Ivanov, the head of the archaeological excavations, and Dimitar Nedev, the director of the Archaeological Museum in Sozopol, made some interesting discoveries. The layer above it contained two 13th-century lead seals. with images of saints and inscriptions referring to correspondence, most likely between high clergy.
Ten burials and reburials have been uncovered south of this site.
“As in the modern world, when a close relative dies, he is buried in the grave of a previously deceased family member. There may be a layering of 10-15 burials on top of each other,” explains Yavor Ivanov.
So far, during the excavations, they have discovered several skeletons of children, including a baby. Probably buried above one of its parents.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
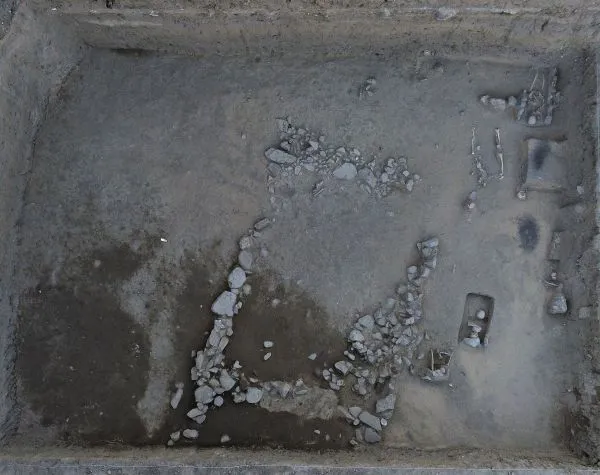

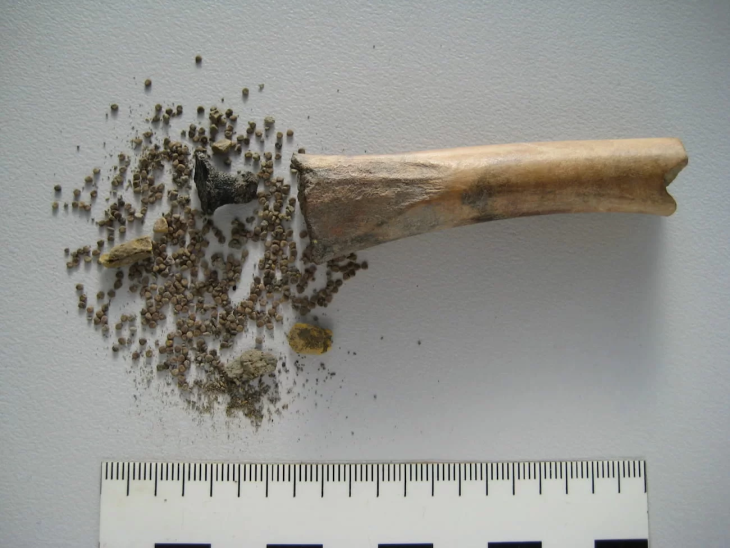
Human remains are well-preserved. According to Christian tradition, they face west. The ceramics discovered date from the eleventh to the early thirteenth centuries. Except for coins and ceramics, no grave goods have been discovered thus far. More iron nails were discovered, but there was no evidence of a wooden structure into which they were driven. Burials are in burial pits.
A structure made up of small and medium-sized rubble stones is visible south of this sector. Its purpose is unknown, but it could be a deep building or a route to other structures. It will provide a broader overview of the area situated on the isthmus dividing Sozopol’s old and new towns. A single-nave church was opened in front of the municipal building and other burial structures, and studies were conducted there during the 2012–2013 water cycle construction.
The depth that the archaeologists have reached in the current excavations is roughly three meters. The extensive work is expected to result in a high saturation of burials and reburials in the medieval necropolis. Archaeologists hope to study the burial customs of local people during the Middle Ages.
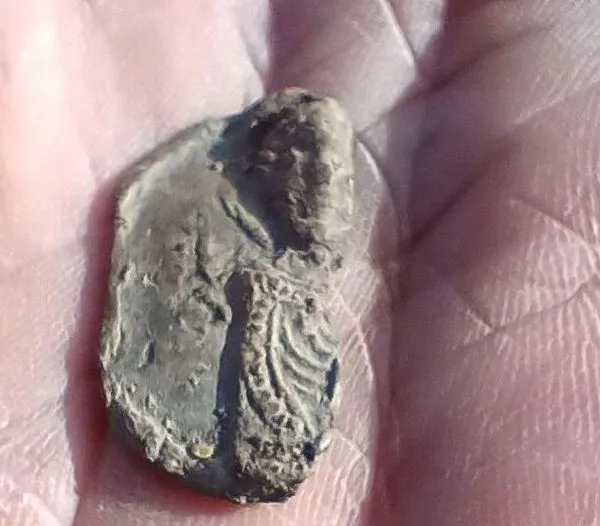

In the southwest corner was a large pithos, which was occasionally used for funerals in addition to storing cereals. The vessel discovered at the site was empty, but it will be checked for organic remains.
Yavor Ivanov states that further burials from the 4th century are anticipated to be discovered at the bottom, in a deeper location, and from the Late Hellenistic period, similar to those discovered nearby during earlier excavations.
Cover Photo: Dimitar Nedev and the Director of the “Culture” Directorate in the Municipality of Sozopol Yordan Petkov. BTA