An enigmatic Anglo-Saxon object has been unearthed in a captivating discovery near Langham, Norfolk, East of England.
This gilded silver artifact, which dates from the late eighth or early ninth century, is both a testament to the sophistication of ancient artisanship and a mystery that has yet to be solved.
Despite the skill that would have been required to make it, the roughly 1,200-year-old object has no apparent purpose and remains a mystery to archaeologists.
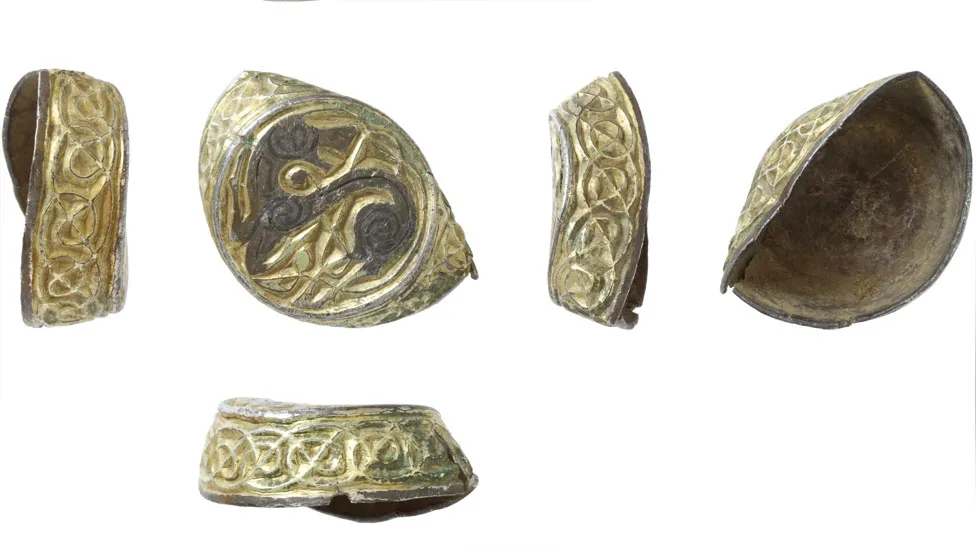
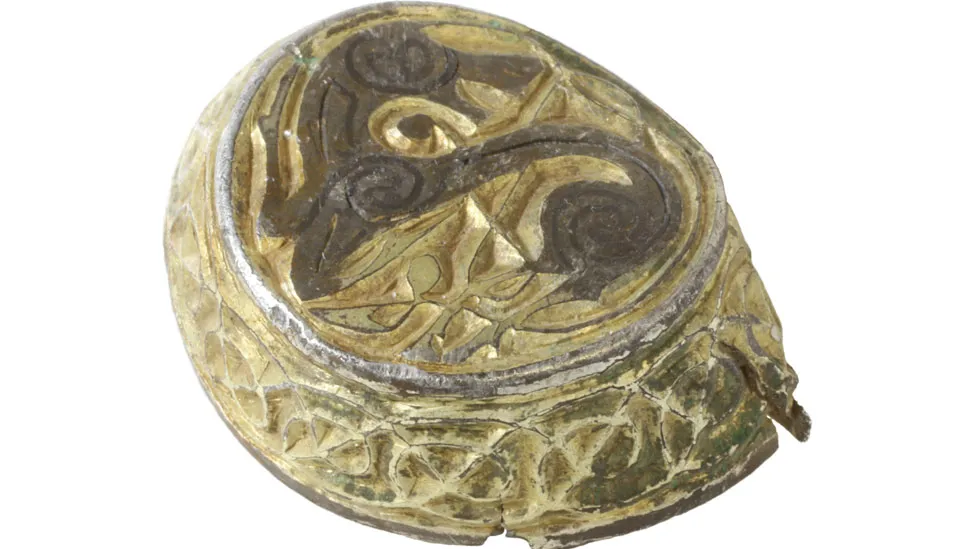
Detectorists in Norfolk found the gilded silver relic, which is 19.4mm (0.7in) in diameter with intricate designs depicting a stylized animal looking over its shoulder.
The artifact boasts a meticulous design with a flat, circular top and short, straight sides forming a shallow, hollow cylinder. The object is adorned with a meticulously crafted spiral pattern and a backward-looking animal, possibly a horse. This design bears a striking resemblance to the style found in the Book of Kells or the Lindisfarne Gospel, both renowned for their intricate illustrations.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
This piece was created using a sophisticated technique known as gilding, in which mercury was mixed with powdered gold to accentuate the design – a process indicative of the period’s high level of craftsmanship.

Helen Geake, the Norfolk Finds Liaison Officer and a respected historian commented on the artefact. She believes the ornate trinket reveals the skill of Anglo-Saxon craftsmen.
She told the BBC: “It was made by someone with a real eye for loveliness.
“It’s so tiny and yet it was created just as carefully as something like a Bible or piece of jewellery.”
It is believed the design would have been created using gold and mercury imported from Spain. While the skill and expense suggest the object was as important as personal jewelry and the ornaments added to sacred texts, experts do not know what the artifact was used for.
Dr. Helen Geake speculates that it might have been part of a staff, the rest of which has decayed over the centuries.
The discovery of this Anglo-Saxon object not only adds to our understanding of historical artisanship, but it also piques the interest of experts and history buffs alike. As we delve deeper into the mysteries of the past, such discoveries provide fascinating glimpses into our forefathers’ creative prowess and technical skills.
Adding to its mystique, the object has been officially declared a treasure by a coroner. The Norwich Castle Museum has expressed an interest in acquiring this extraordinary piece for its collection.
Cover Photo: ANDREW WILLIAMS/NORFOLK COUNTY COUNCIL