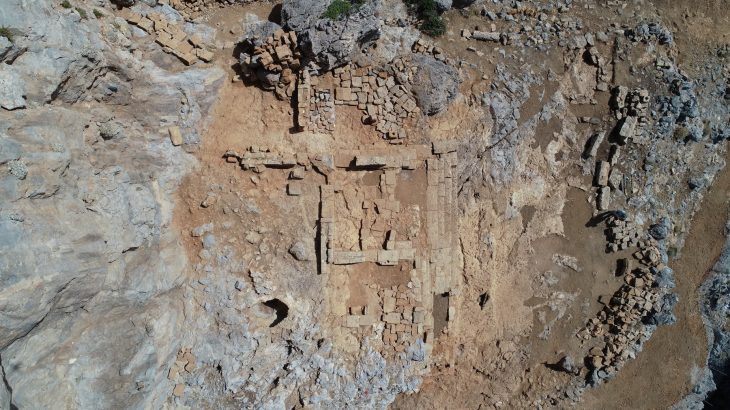
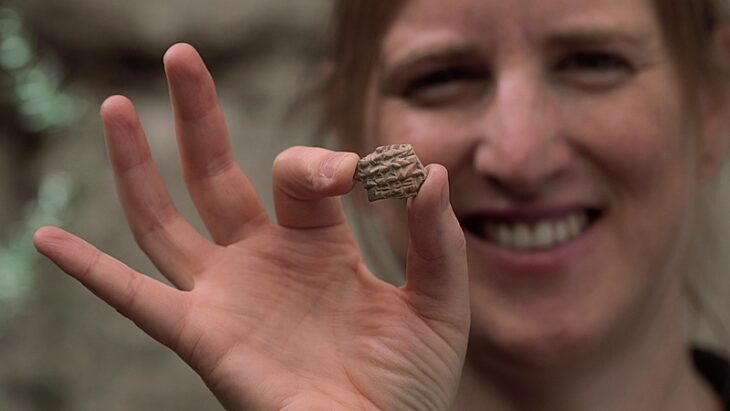Archaeologists discovered a Gulf-type seal made of soft stone dating to the end of the third millennium BC at Kalba, a prehistoric coastal site in the Gulf of Oman.
Since 2019, excavations have been carried out on the south-eastern Arabian Peninsula by the Austrian Academy of Sciences (OeAW) to investigate. As a result of this research, researchers can be detected for the first time the extensive trade networks extending from the Indus region to the Aegean Sea about 4500 years ago. According to researchers, presumably, the Gulf region already served as a nexus between East and West about 4500 years ago.
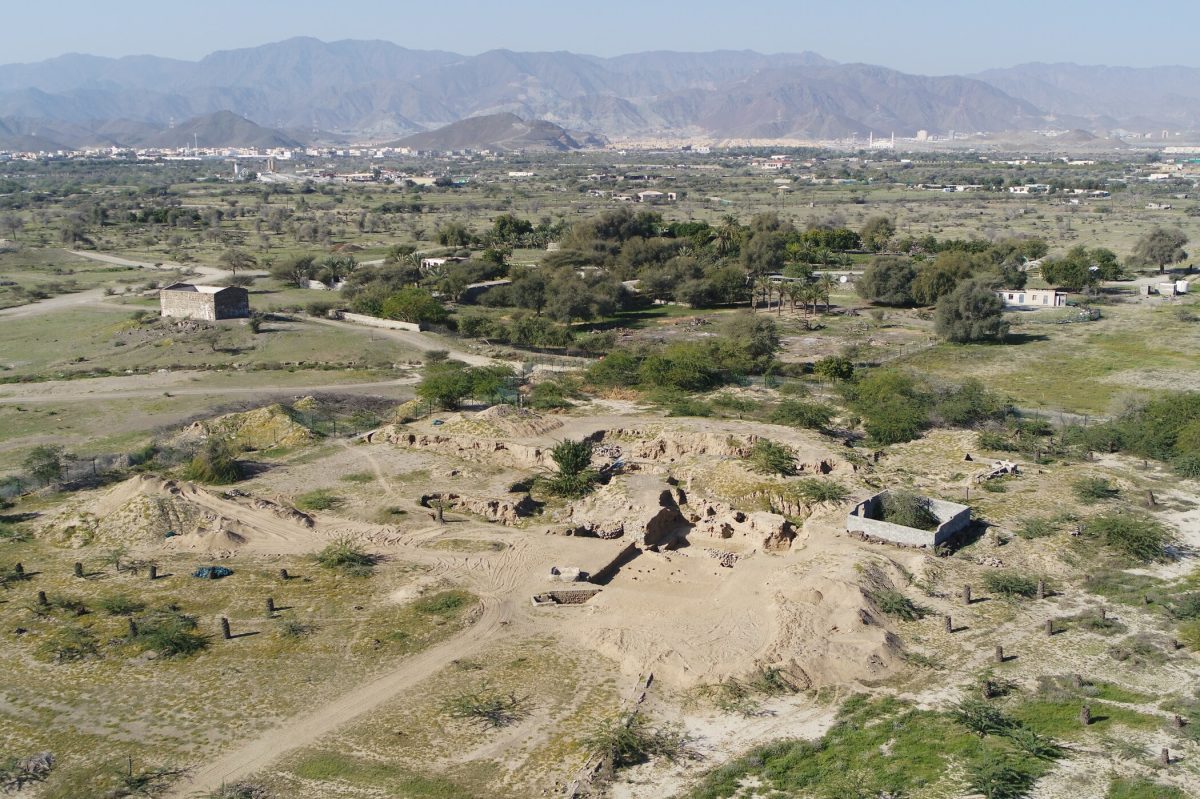
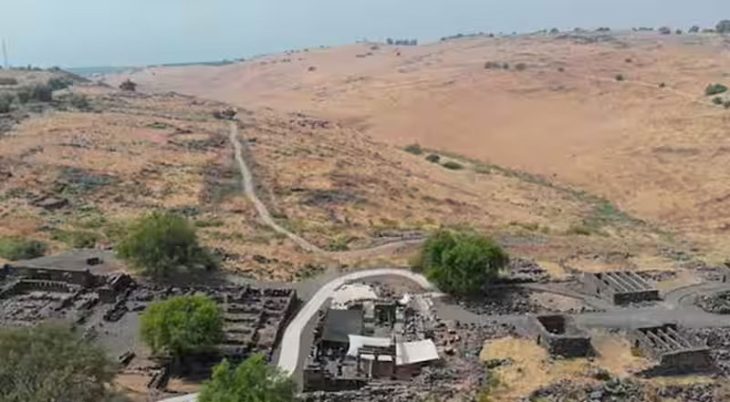
Kalba is a multi-period site situated in the Emirate of Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, on the Gulf of Oman, and it is one of the sites under investigation as a hub for these early commercial networks in the southeastern Arabian Peninsula.
Kalba was continuously inhabited from the Early Bronze Age to the Iron Age (c. 2500–600 BC), despite environmental changes that made the area more arid.
In addition to providing favorable weather, Kalba’s strategic location made it an excellent entry point for caravan routes connecting land and sea. The Hajar Mountains can still be crossed via this route, which also makes it possible to trade goods with the southeast of the Arabian Peninsula.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
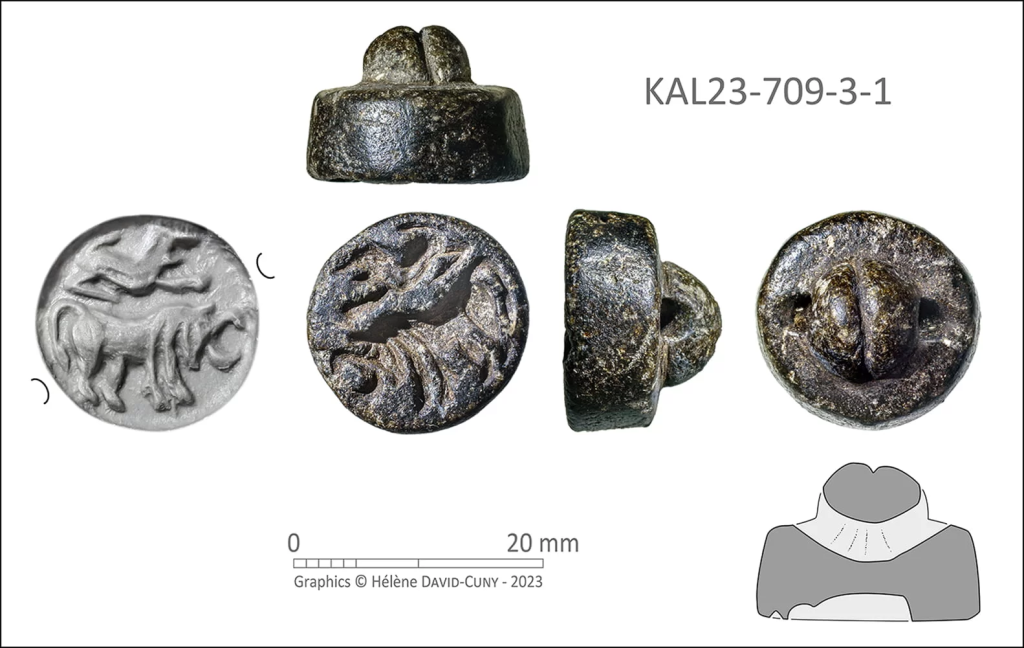

However, the researchers emphasize the importance of considering the question of what objects or raw materials were brought to Kalba, produced and used at the site, and which presumably served as trade goods. All indications point to a special relevance of mineral resources.
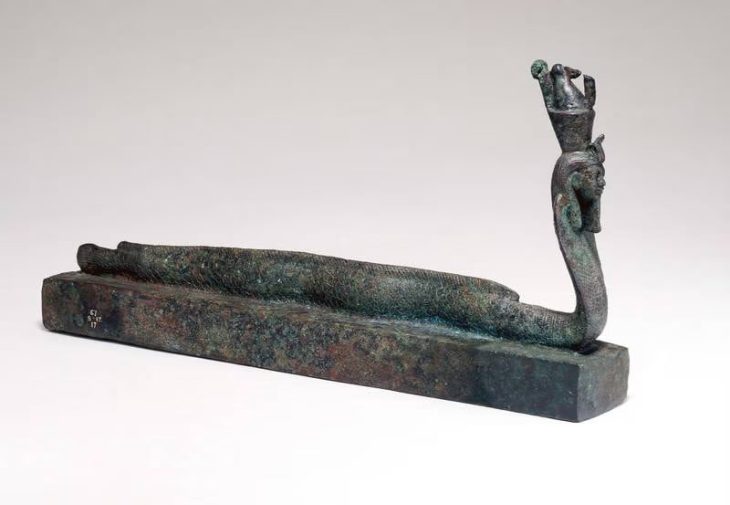
The research findings show that a multi-crafting coastal community not only occupies a favorable ecological niche but also employs sophisticated and adaptable raw-material procurement strategies. Moreover, a “Gulf-type” seal attests to Kalba’s involvement in extensive networks of trade and exchange.
According to archaeologists, this type of seal, originally produced in the Dilmun region, can be dated to the late third millennium BCE. The seal depicts a bull and possibly a lion in an attacking posture. The bull motif, widely recognized in similar seals, is influenced by the iconography of the Indus Valley seals. The lion, however, is intriguing, as it is not represented in Indus seals, but is rather known as a motif in the cylinder seals of the westernmost Mesopotamian region.
The motifs on the “Gulf-type” seal from Kalba, they conclude, seem to represent a potential synthesis of Eastern and Western motif traditions within a distinct local seal type in the southeastern Arabian Peninsula, emphasizing the cohesive nature of this coastal trading hub.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.15184/aqy.2024.45
Cover Photo: Aerial photograph of the excavations in Kalba. Photo: SAA/K. Kamyab