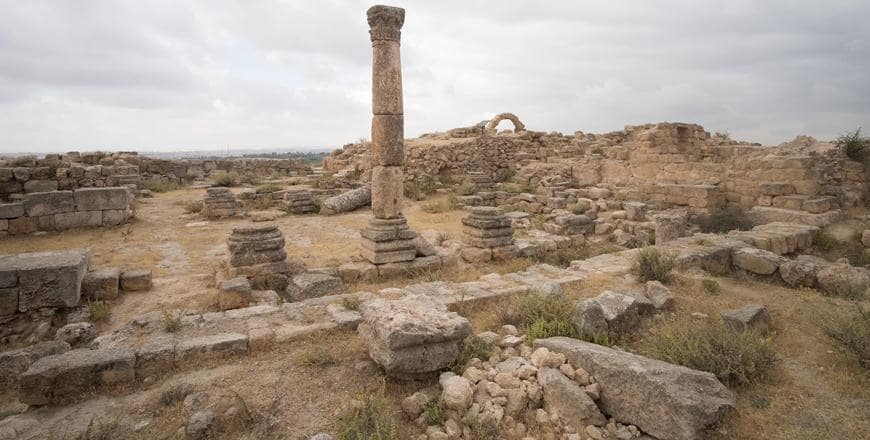
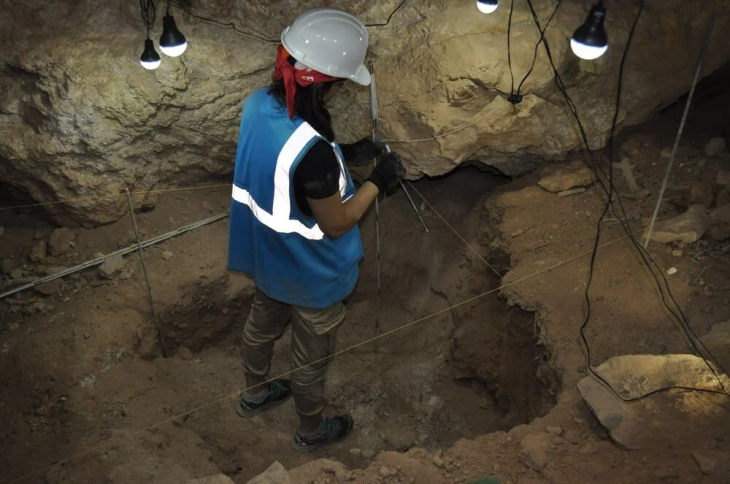
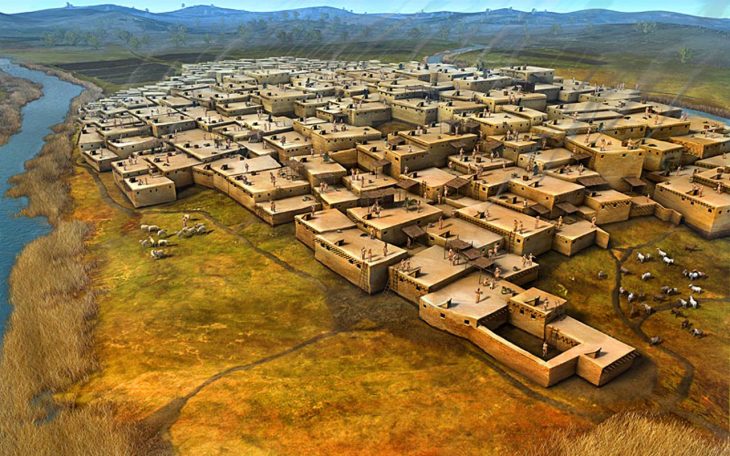
The American archaeologist stated that Tell Hisban, located on the Madaba plains of Jordan, represents the “granary of the empires”.
The first person to conduct Tell Hisban’s research on the period from 1968 to 1976 was Siegfried H. Horn, Professor of Old Testament and the History of Antiquity at the Seventh-day Adventist Theological Seminary at Andrews University in Michigan, USA.
The primary search of this first phase was the quest for the site’s biblical connections—hence the name of the expedition, which attests to the excavator’s pre-occupation with finding biblical Heshbon at Tall Hisban.
Heshbon is referenced 35 times in the Old Testament, and there is near full agreement among 18th and 19th-century explorers that Tall Hisban is, in fact, the location of ancient Heshbon. Biblical Heshbon plays a prominent role in the story of the Israelite conquest and settlement of the land of Canaan. It was the fortress of Sihon, king of the Amorites, that the Israelites captured on their way north through Moab and Ammon (Numbers 21:23-31). Numerous Old Testament writings also mention the tribe of Reuben rebuilding and settling the town.
At the same time, Tell Hisban is a market town that developed from the time of the Assyrians, Babylonians, and Persians and continued its importance in the Middle Ages by becoming a district capital with a military garrison during the reign of Sultan Al Nasir Muhammed (1310-1340).
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The site, covering some eight hectares, had significant cereal production, Bethany Walker, a professor at the University of Bonn, Germany, said.
A Mamluk citadel occupies the hilltop and under the hill was a densely populated village comprised of clusters of one–room farmhouses with shared courtyards and cisterns, Walker continued, adding that the site reached political and social prominence during the 14th century.
She noted that state investment helped the urbanization of the village and the souk in Tell Hisban, providing agricultural products for the central highlands of Transjordan. Tell Hisban’s participation in the interregional markets was primarily based on its cereal production.
Walker, “These decisions were made by cultivators themselves not by any state imperative or policy. Even the economic pressure of taxation would not account for the selection of specific cereals,” Walker said, noting that the size of cereal production is suggested by the size and number of storage facilities.
Cereal production was the most taxable commodity at Tell Hisban in the 16th century, although by the end of the century nobody lived in the village, she highlighted, adding that these storage facilities were, therefore, most likely from the Mamluk period.
“Large quantities of grain were stored in the fortress of Tell Hisban in 18th and 19th centuries, and with the grain boom in the mid-19th century, cereal was massively produced and transported to Palestinian ports,” Walker said.
The 16th century represents “a turning point” in the relationship between the local community and the large-scale commercialization of agriculture, the professor said.