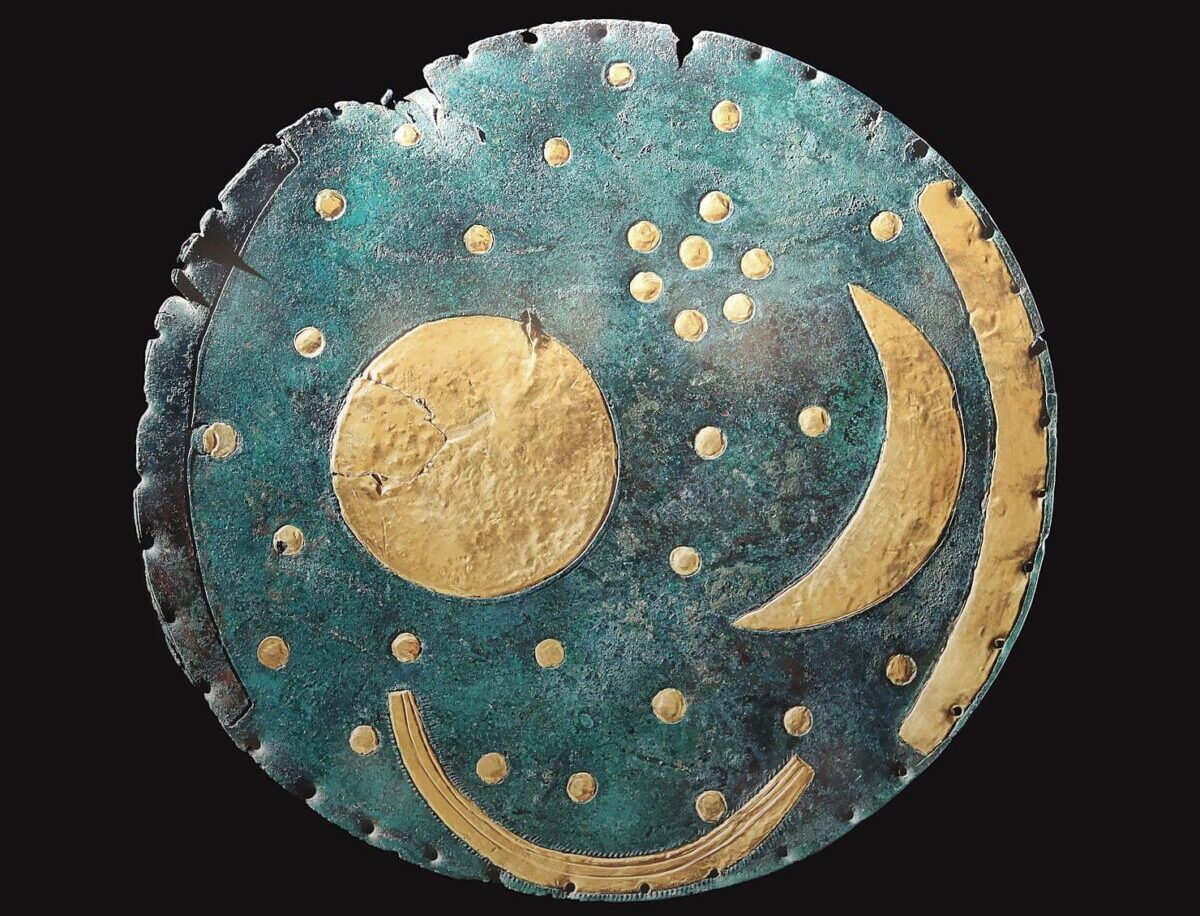
Discovered in 1999 in Germany, the Nebra Sky Disc is the oldest known depiction of the cosmos. A recent examination of the Bronze Age artifact revealed the intricate methods used in its creation, which UNESCO described as “one of the most important archaeological finds of the twentieth century.”
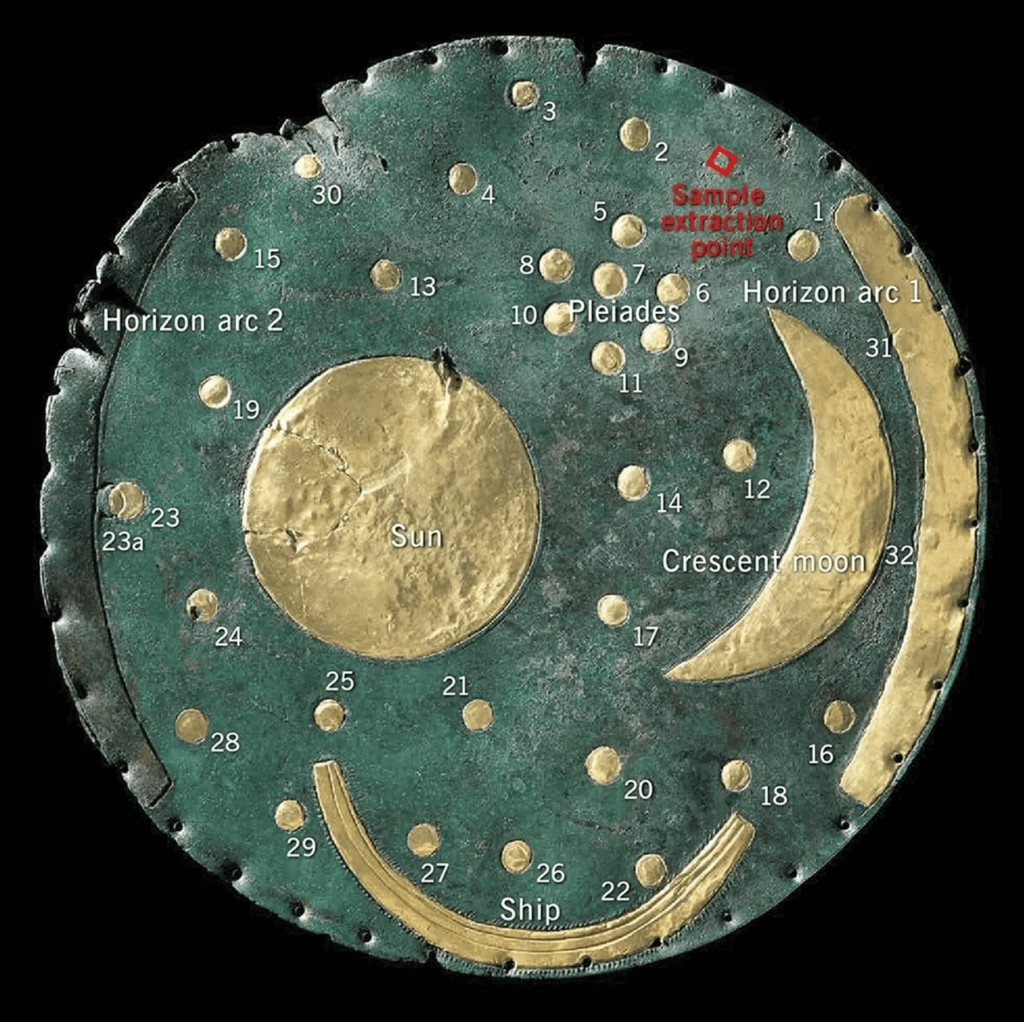
The Nebra Sky Disc is a product of the Únětice culture, which originated in the Bronze Age of Central Europe. It reflects a sophisticated ancient understanding of both metalworking and astronomy and was created sometime between 1800 and 1600 BCE. Clusters of stars, a sun, and a crescent moon are among the celestial bodies depicted by golden inlays covering the blue-green patina of the Nebra Sky Disc. The angle between the solstices is thought to be indicated by two golden arcs that run along the sides of the disc, one of which is now absent. It is thought that a boat is represented by another arc at the composition’s base. Only a few millimeters thick, the disc has a diameter of around 12 inches.
The Nebra Sky Disc is one of the best-investigated archaeological objects. The origin of the raw materials it is made of is well known The disc is made from copper, tin, and gold—materials whose origins have been traced to Cornwall, England. The rich blue-green patina of the disc’s bronze today results from chemical changes over time. Originally, it would have been a deep bronze hue.
The design and astronomical significance of this bronze disc are astounding, but so are the technical mysteries that surrounded its creation. The intricate processes that shaped this artifact have been revealed in fascinating detail by recent metallographic analyses.
Previous studies determined that the disc could not have been made simply by casting due to its material composition and physical structure. The most recent discovery confirms that the disc was made using an extremely complex hot-forging process, which adds yet another level of complexity.
The new research, published in the scientific journal Scientific Reports, utilized modern metallographic analyses to reveal that the disk was produced using an elaborate warm forging process.
The research team used light microscopy and more sophisticated techniques like energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and electron backscatter diffraction to perform microstructural analyses on color-etched surfaces. These investigations focused on how the finished bronze disk was made from a cast piece, shedding light on techniques that had not been completely clarified until now.
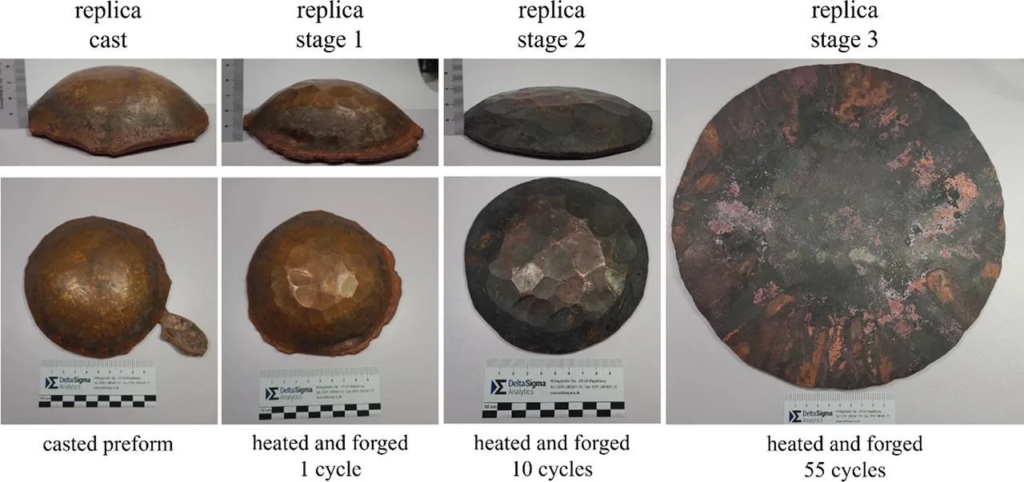
The results show that Early Bronze Age artisans were not only exceptional casters but also highly skilled in intricate bronze processing methods. About ten work cycles were required to produce the disc, each of which included heating the metal to roughly 700 degrees Celsius, shaping it with a hammer, and then annealing it to relax the material’s internal structure. With a final diameter of about 31 centimeters and a thickness of only a few millimeters, this technique enabled the disc to attain the necessary strength and thinness.
Famous coppersmith Herbert Bauer used a cast blank to make a replica of the Sky Disc in order to better understand the craftsmanship. According to Bauer’s experiments, the original artifact needed fewer forging cycles than the replica, indicating that it was both thinner and larger. These discoveries highlight the extraordinary abilities of Bronze Age metalworkers, who were skilled in both sophisticated processes like hot forging and casting.

The fact that, more than 20 years after the recovery of the Sky Disc, research has yielded such significant new findings once again underscores the extraordinary nature of this unique discovery of the century and the advanced level of metallurgical knowledge already developed in the Early Bronze Age, stated state archaeologist Prof. Dr. Harald Meller.
The Nebra Sky Disc is also an impressive testament to how important it is for the advancement of knowledge to reexamine even well-known and supposedly well-researched discoveries when new methods become available, said Meller.
A group of experts from Saxony-Anhalt’s Landesamt für Denkmalpflege und Archäologie (LDA) joined forces with the Otto-von-Guericke University of Magdeburg and DeltaSigma Analytics GmbH to look into these procedures.
State Office for Monument Preservation and Archaeology Saxony-Anhalt
Dieck, S., Michael, O., Wilke, M. et al. Archaeometallurgical investigation of the Nebra Sky Disc. Sci Rep 14, 28868 (2024). doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-80545-5
Cover Image Credit: Wikipedia Commons
















