Petroglyphs are among the world’s oldest practiced art forms and are as diverse as the wide-ranging cultures and civilizations that have produced them. One of these places of immense historical importance is Teymareh in the heart of Iran.
A petroglyph, also known as rock art, refers to images that are etched or carved into stone surfaces. In ancient times, pictures served as mnemonic devices to help recall data and this early use of visualization led to the development of systems of symbolic pictographs and ideographs, the precursors of alphabets.
Petroglyphs are powerful cultural symbols that reflect the complex societies and religions of the surrounding tribes.
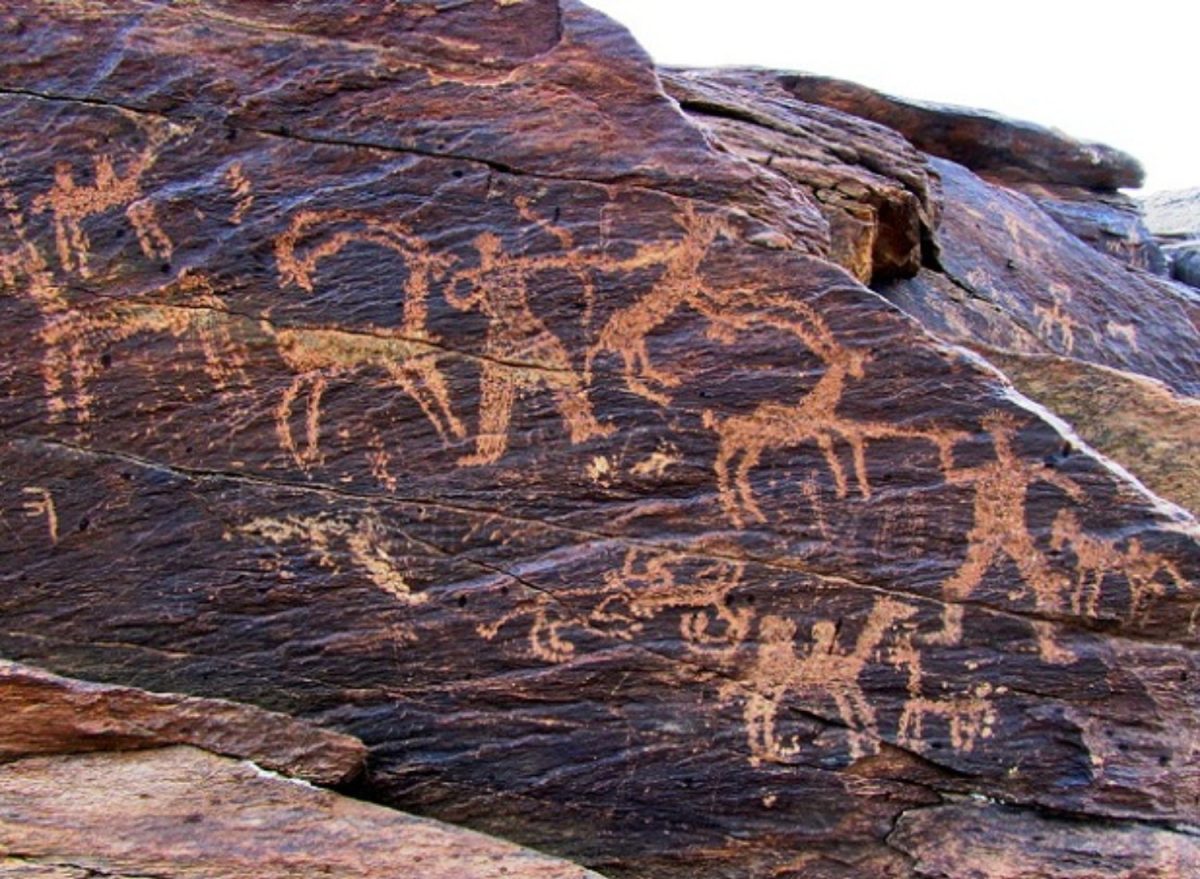
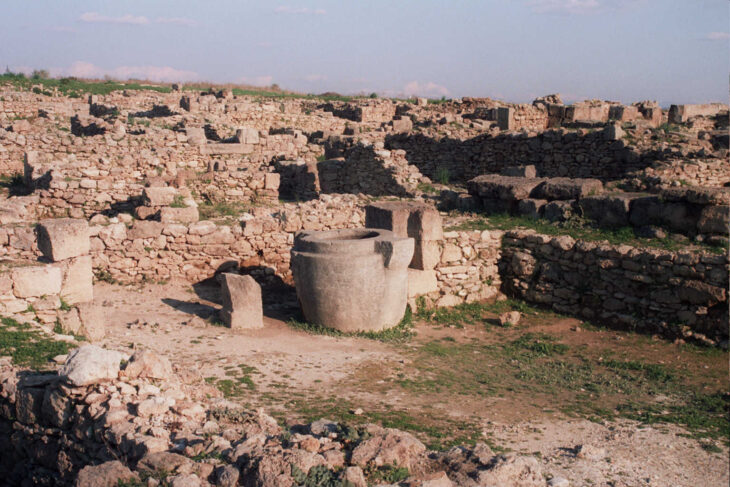
The ancient rocks of Teymareh symbolize the long past of human existence and art throughout the ages. Some of Iran’s prehistoric habitats can be seen in the valleys and mountainous regions that surround Khomeini and Golpayegan. Teymareh is an ancient and rocky region in the city of Khomein, which holds 21,000 petroglyphs with amazing secrets.
The placement of these Petroglyphs in 31 archaeological sites with an area of over 50 square kilometers has brought an unmatched museum in the heart of the region. Qeydu and Mazayen are the oldest remains of the petroglyphs in Teymareh.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
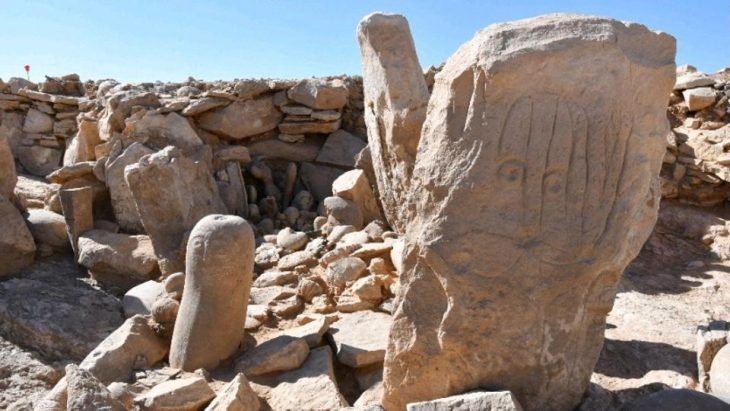
Teymareh carvings feature representations of plants and animals in a variety of styles, from realistic to abstract. There are lots of animal representations, particularly of goats with big, pointed horns. Feline species, canids, horses, dromedaries, owls, fish, tigers, cows, and birds like partridges, storks, and hoopoes are among the other animals portrayed. Figures of plants include wheat, pine, and cedar. Martial arts, magic dances, pregnant ladies, camel caravans, and people with big hands are among the other images.
The petroglyphs found in Teymareht are some estimated to be as old as 40,000 years. However, these invaluable artifacts have been left unprotected and neglected.
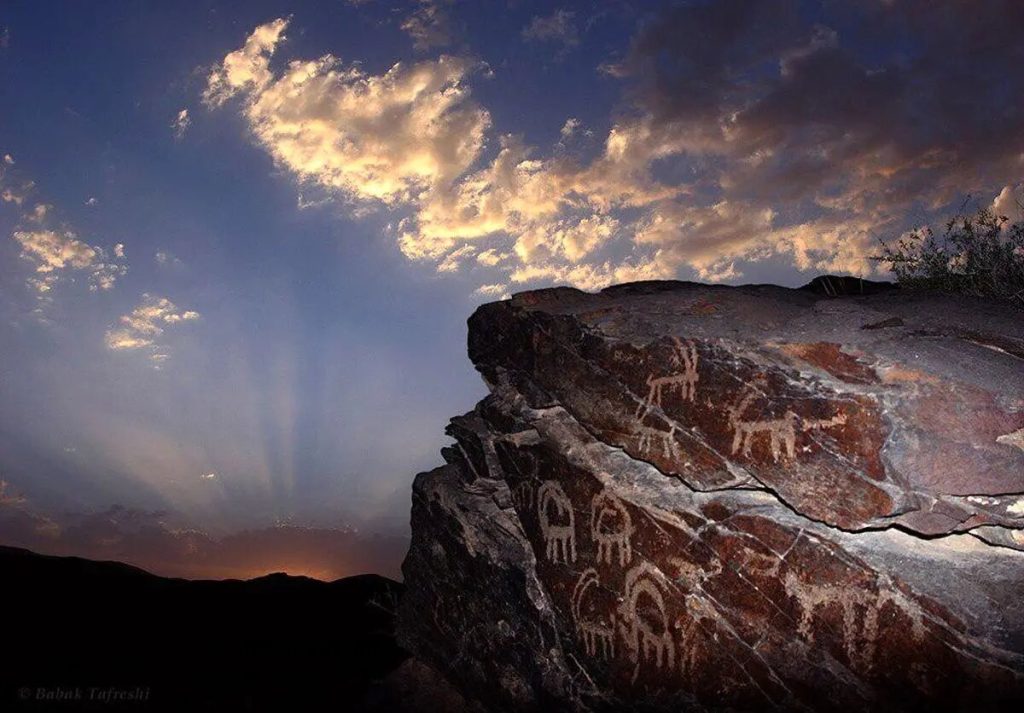

Today, Teymareh stands as one of the largest repositories of such prehistoric art, yet it receives minimal attention from authorities and lacks adequate protective measures.
Teymareh has been neglected to such an extent, according to ILNA, that no national foundation has been established to safeguard this cultural heritage, leaving these antiquated relics exposed and unprotected. With thousands of petroglyphs and rock canvases, Teymareh is undoubtedly the largest open-air museum in the world, according to the report.
For years, the Teymareh petroglyphs went unnoticed and unappreciated. Local organizations such as the Teymareh Friends Association were recognized for the efforts of communities coming together to raise awareness.
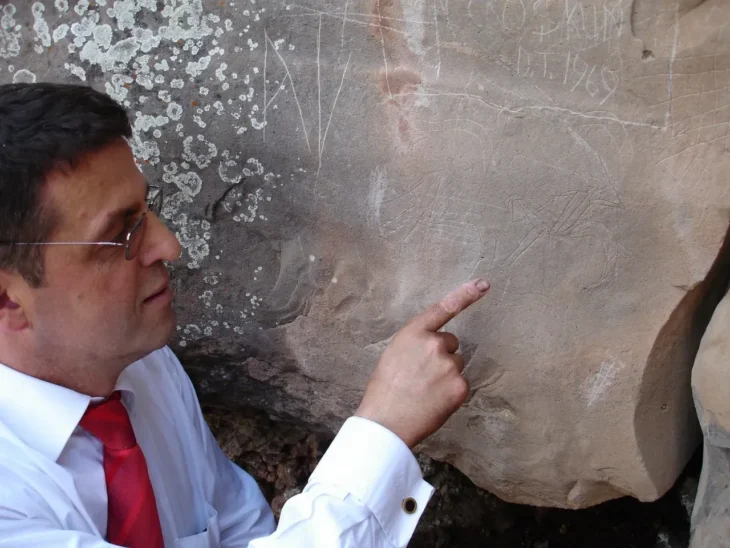
Talking to ILNA, Rasoul Majidi, the director of the Teymareh Friends Association and a leading researcher and guide on Teymareh petroglyphs, has provided insights into the current condition of this vast archaeological site.
“Teymareh was completely unknown until a few decades ago,” Majidi explained. It was only in the early 1990s that Dr. Morteza Farhadi introduced Teymareh to Iranians and the world through his book, titled Museums in the Wind.
Following this publication, more scholars began writing books and articles about Teymareh, slowly bringing its petroglyphs to light. However, Teymareh still hasn’t received the recognition it truly deserves.”
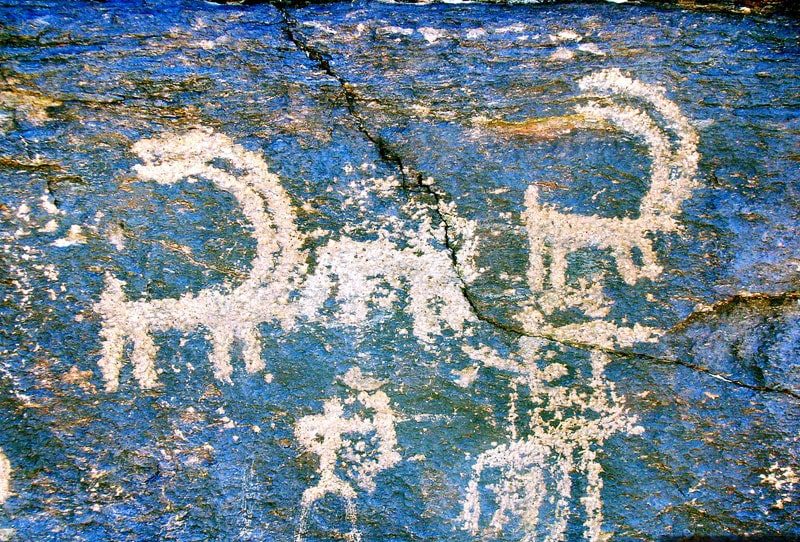

Four Italian travelers and scholars who had read Farhadi’s book made the trip to the region in 2005. Until Majidi, their guide, showed them the extensive rock carvings, they had no idea where to find the petroglyphs. The sheer quantity of petroglyphs astounded the visitors, who, upon their return, urged the site’s preservation, highlighting the invaluable value of these artifacts.
“Until then, we were unaware of Teymareh’s significance and value,” Majidi admitted. “It was the comments from these Italian researchers that changed the course of our lives and inspired us to delve into historical studies and tourism training.”
The locals weren’t initially convinced that Majidi could keep the site intact. A lot of people made fun of the association’s efforts, calling the petroglyphs simple illustrations made by shepherds or, worse, claiming the association had drawn the images themselves. But following in-depth research and international comparisons, the community came to understand that the petroglyphs were a part of a global phenomenon that other countries fervently guard and exploit for tourism.
Elsewhere in his remarks, Majidi recounted how the efforts to attract tourists and archaeologists to Teymareh gradually shifted public perception, but this progress met with a new obstacle: mining activities. These activities threaten the integrity of Teymareh’s petroglyphs.
“The world’s largest open-air museum is now at the mercy of miners,” Majidi lamented. “Five major mining operations extracting silica for the glass and steel industries are active in the area. These mining activities posed a severe threat to this ancient collection until our persistent advocacy managed to halt three of the operations. However, two mines are still operational.”
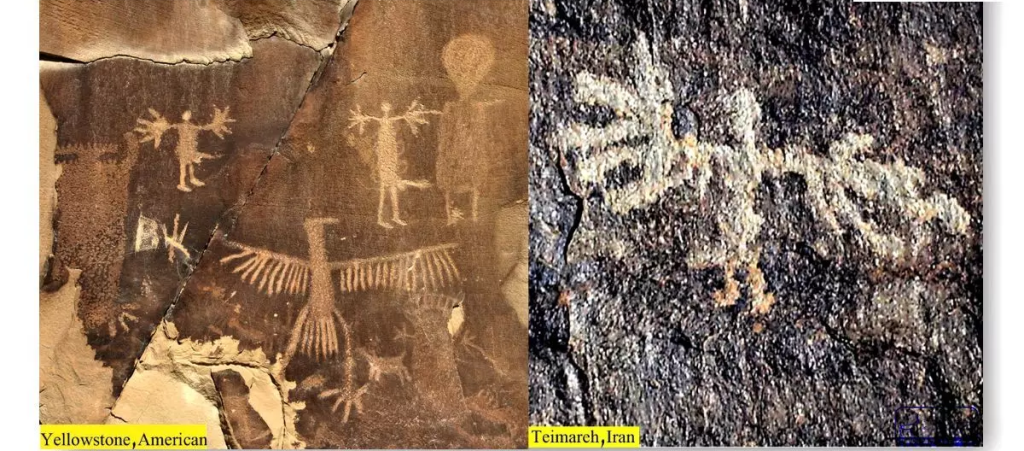

Moreover, Majidi highlighted that all conservation efforts for Teymareh’s petroglyphs have been spearheaded by non-governmental organizations and the local community. Despite these efforts, the national heritage authorities have only managed to register three regions in Teymareh as national heritage sites, with no substantial protective measures implemented.
He further highlighted the contrasting situation in Saudi Arabia, where the government has invested heavily in safeguarding and promoting their 400 rock canvases. “Meanwhile, Iran, with its thousands of rock canvases, lacks any strategic plan for their protection and introduction to the world,” Majidi noted with concern.
Majidi stressed the need for a national base dedicated to Teymareh’s preservation. Despite the influx of archaeologists who recognize the area’s potential, tangible conservation efforts remain lacking.
“We have not seen any foreign tourists in three years. While archaeologists who visit Teymareh acknowledge its uniqueness and potential, these insights remain merely observational and do not translate into action.”
Cover Image: CC BY-SA 4.0