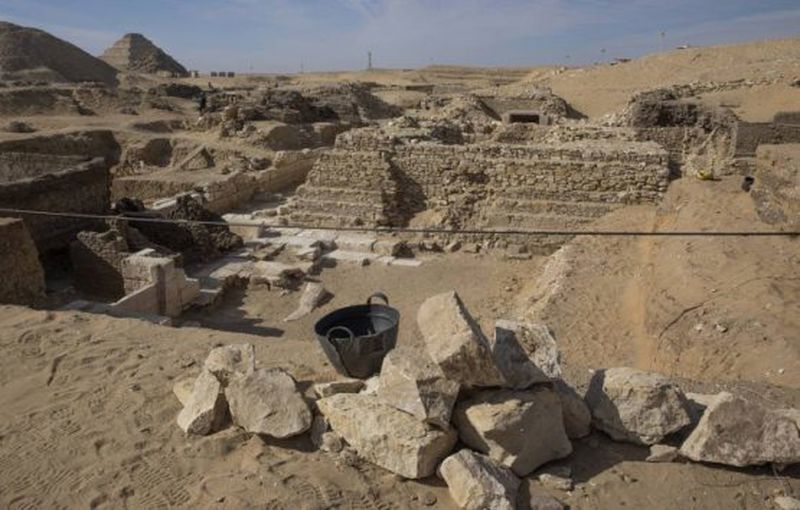
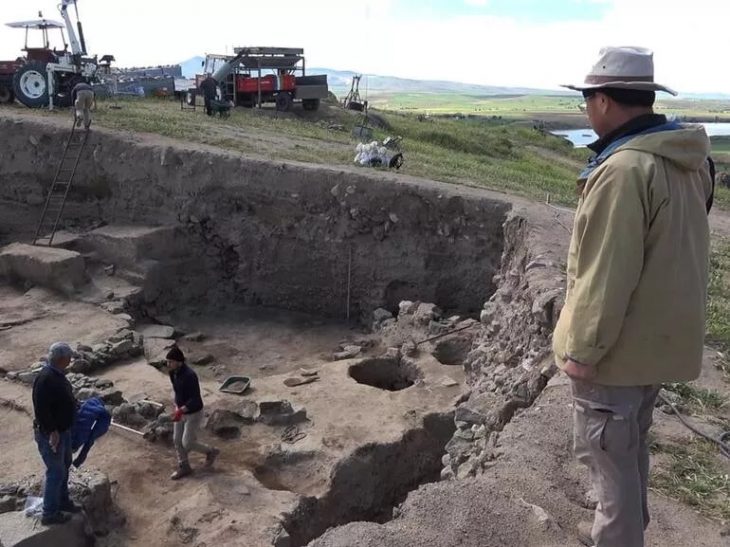
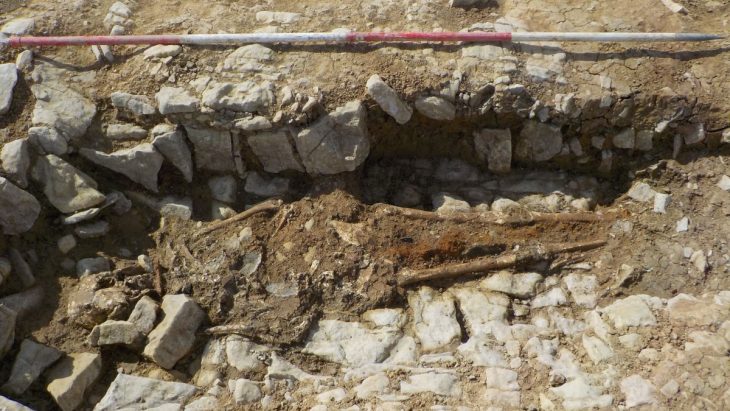
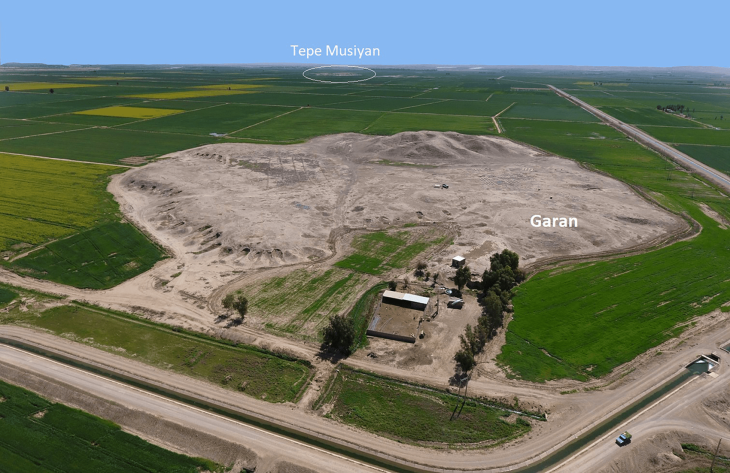
A team of Chinese and Uzbek archaeologists discovered an ancient settlement dating back to the 8th century BC in Uzbekistan, near the country’s Surxondaryo River, also known as Surkhandarya.
A square-shaped architectural structure with several rooms, including a kiln and waste pits, is present at the recently excavated site, offering insight into the ancient civilization that once flourished there. Numerous smaller square rooms within the ruins were discovered; based on the abundance of pottery wares discovered nearby, archaeologists believe these rooms served as living quarters or kitchens.
Utensils made of stone such as millstone, mortars, and pestles were discovered, revealing the “food processing history of ancient people in the region,” Archaeologist He Jierao told the Global Times.
“It reveals the evolution of ancient people’s community lifestyles and how they developed more civilized lifestyles,” He emphasized.
Beginning in April, the excavation project was led by Northwest University archaeologist Ma Jian and his team in Xi’an, Shaanxi Province, China. Three major discoveries were made in Uzbekistan between April and June by experts from China and Uzbekistan.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
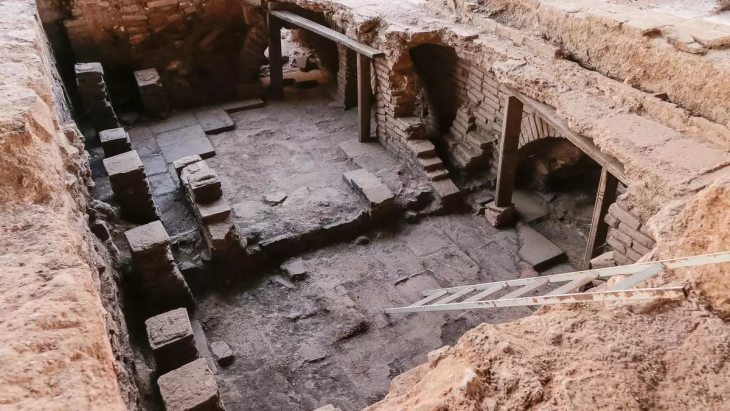
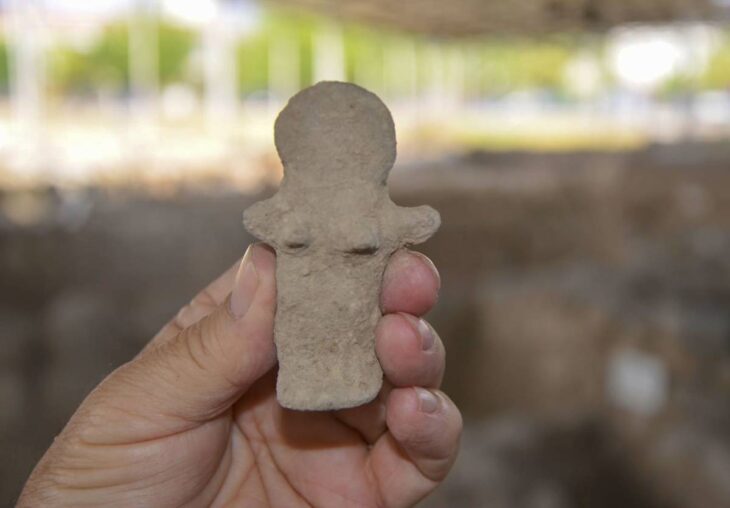
In addition to the 8th-century BC settlement, another major project involved the investigation of the ancient Kushan Empire. Twenty-five old tombs and six buildings from the Kushan Empire were found as a result of the combined efforts. The Kushan Empire was a powerful political system that ruled over what is now Uzbekistan, Afghanistan, and Pakistan. It was founded in the first century AD by the nomadic Yuezhi people.
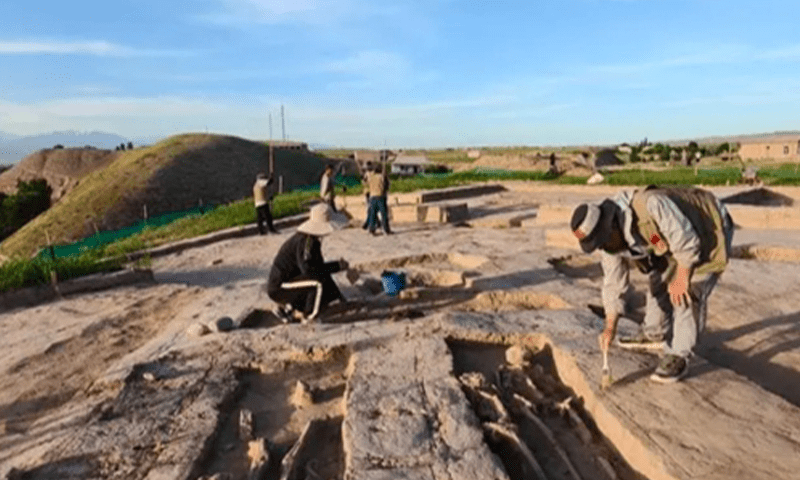

Archaeologist Wang Meng noted that such discoveries are crucial for establishing a chronological timeline of the Kushan culture in the region, helping to trace the development of civilization around the Surkhandarya area.
In the third project, archaeologists focused on the Fergana Valley in eastern Uzbekistan, where they explored and reviewed 84 ruins between April and May. A precious cliff painting was also discovered during the research, which helped paint a picture of the ancient culture of the Namangan Region of Uzbekistan.
These discoveries mark the latest milestones in a longstanding archaeological partnership between Northwest University and Uzbekistan, which began in 2009. By 2024, more than 70 joint projects had been conducted in Central Asia, aiming to study the historical exchanges along the ancient Silk Road.
Wang Jianxin, a pioneering archaeologist who began working in Uzbekistan 15 years ago, highlighted that these collaborations have challenged Western-centric interpretations of Silk Road history and enhanced global understanding of China’s contributions to ancient Silk Road civilization.
Cover Photo: Aniq