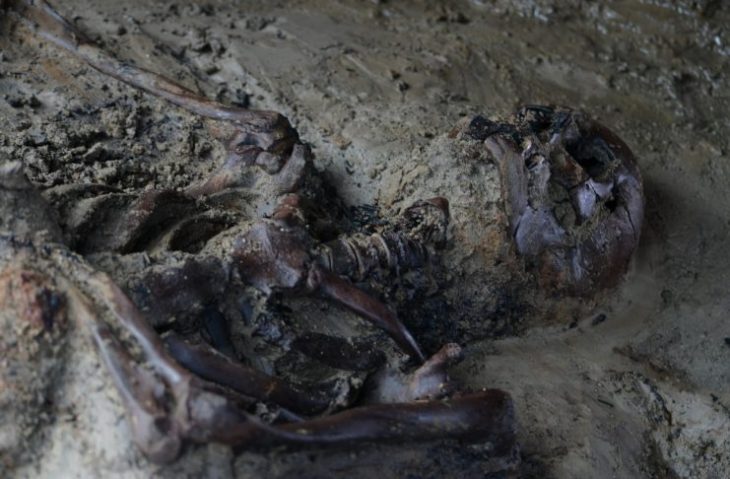
Archaeologists have unearthed a luxurious 2,200-year-old tomb in eastern China, the largest, highest-ranking, and most structurally complex ever unearthed, which may have belonged to an emperor of the state of Chu during a critical period in Chinese history.
Chu was one of the seven Warring States, along with Qin, Han, Wei, Zhao, Qi, and Yan. The unification of these states is recognized as the start of modern China.
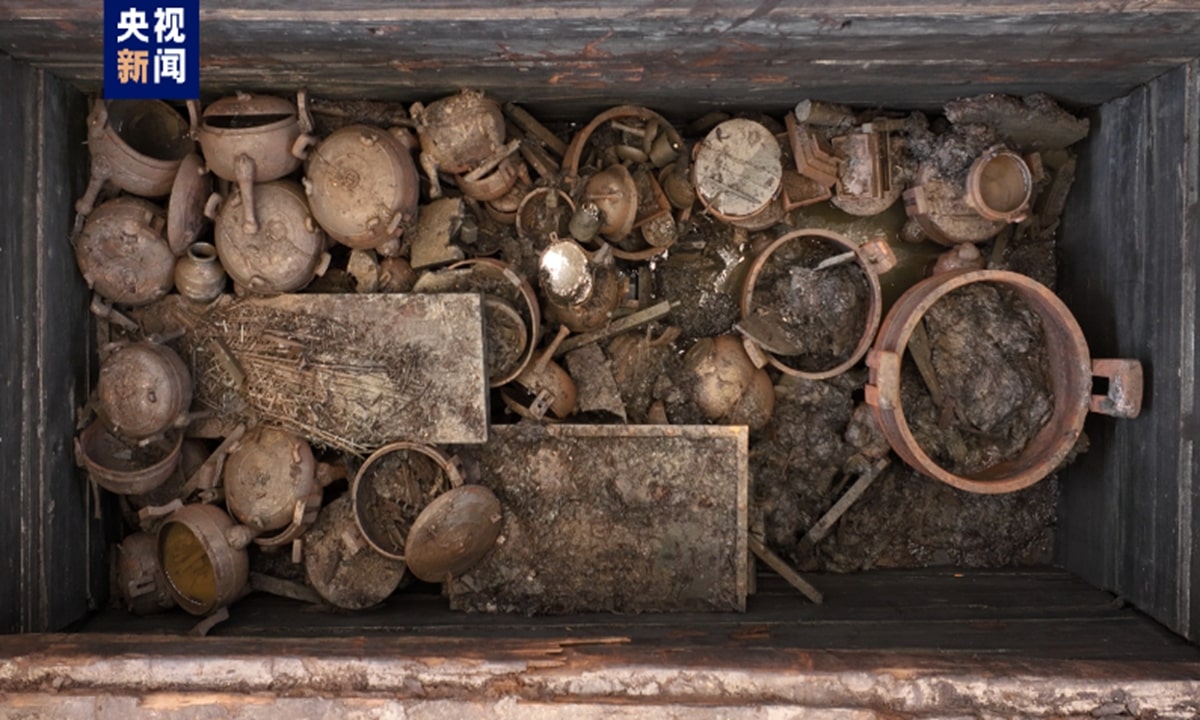
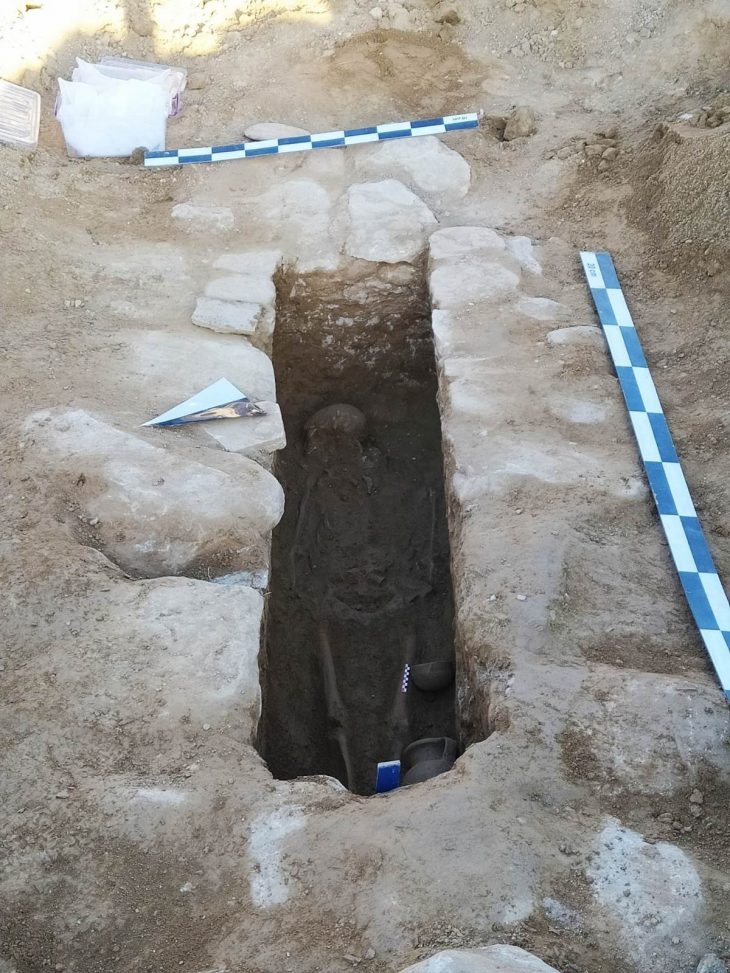
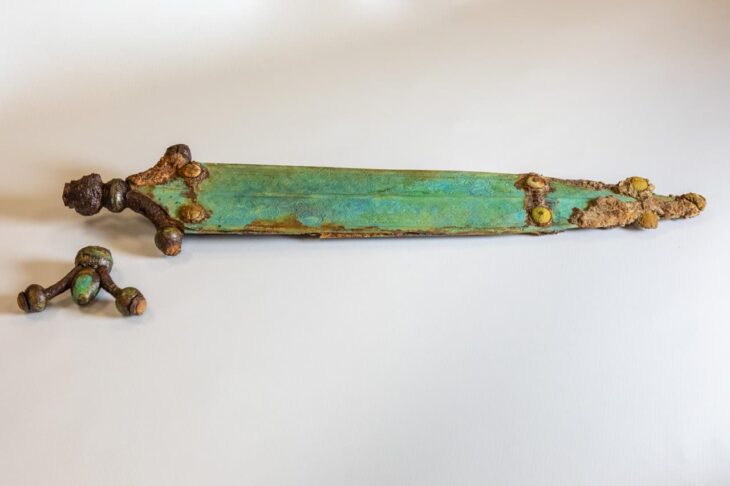
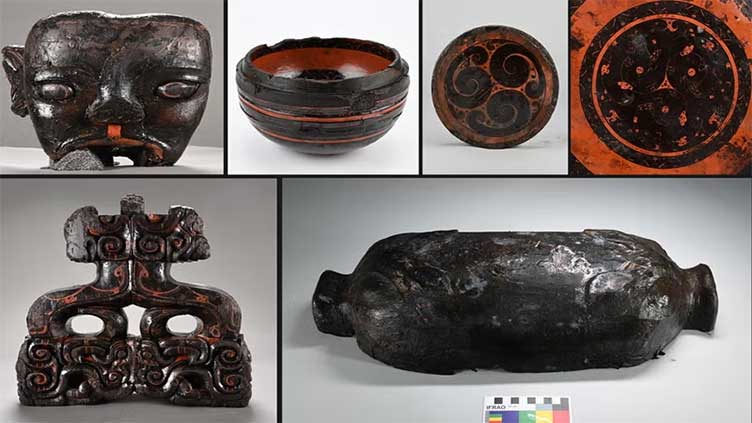
The 2,200-year-old Wuwangdun tomb, which is situated in the Anhui Province of East China’s city of Huainan, has yielded over 1,000 artifacts, including figurines, musical instruments, bronze goods, and everyday utensils and lacquerware artifacts, dating to about 220 BC.
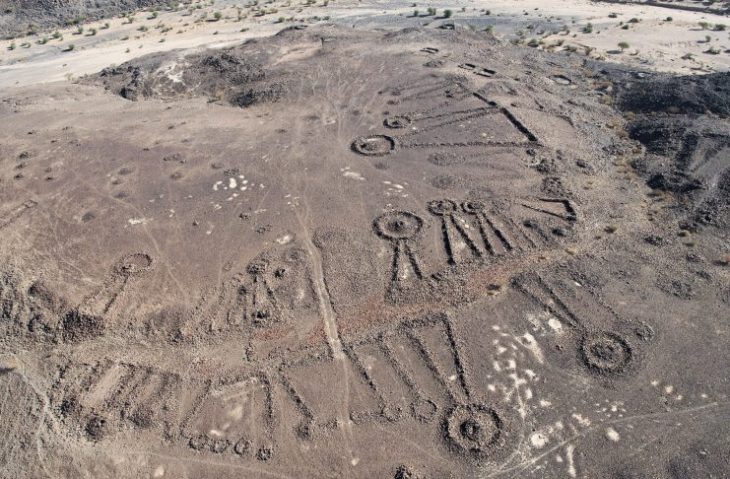
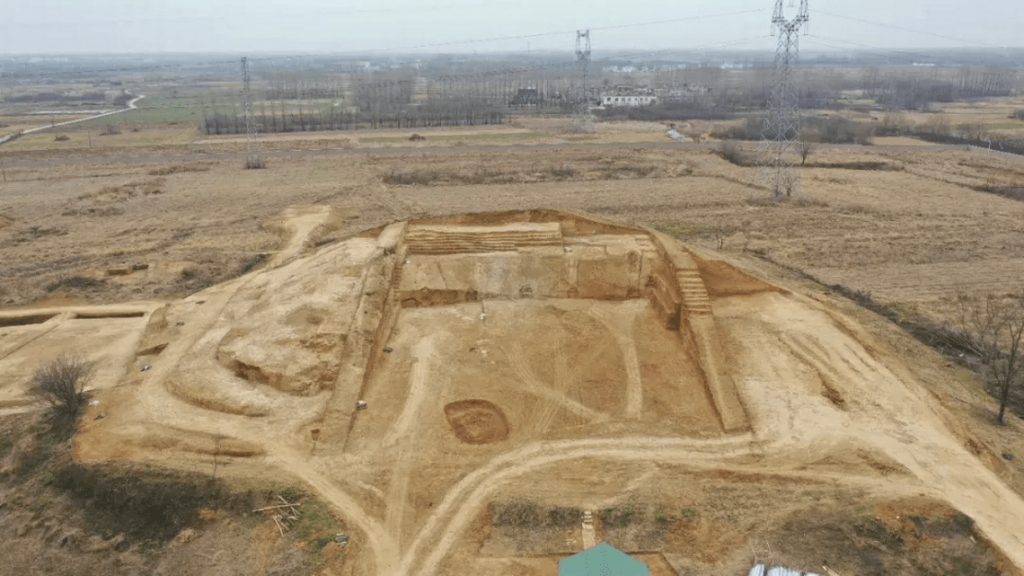
At Wuwangdun, one of the largest-scale Chu state archaeological sites, researchers previously uncovered a cemetery spanning 1.5sqkm, with a chariot and sacrifice pits and a tomb, believed to be that of the cemetery’s owner.
The tomb is thought to be the highest-level ancient Chu state tomb ever excavated, and its vast scale, intricate structure, and rich contents suggest it belonged to the state’s emperor.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

According to information obtained by the Global Times newspaper from the Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology of Anhui Province, based on the size and scale of the tomb, as well as historical records, it is estimated that the owner of the tomb may be King Kaolie of Chu. However, a more accurate determination of the tomb’s occupant will require further extraction of artifacts and analyses of textual evidence.
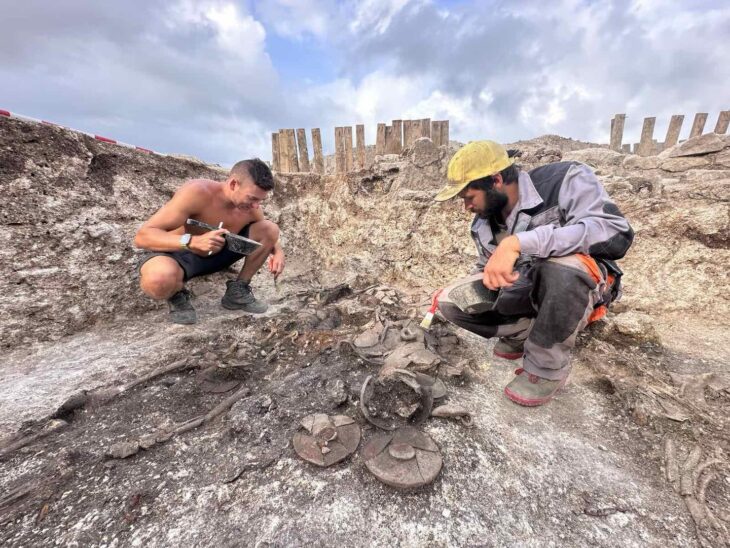
Meanwhile, the tomb had been looted multiple times throughout history. Anhui was permitted by the NCHA in 2019 to excavate the tomb and salvage its archaeological remains. An official start to the excavation work was made a year later, and it was recognized as a national project to use archaeological research to determine the origins of Chinese civilization.
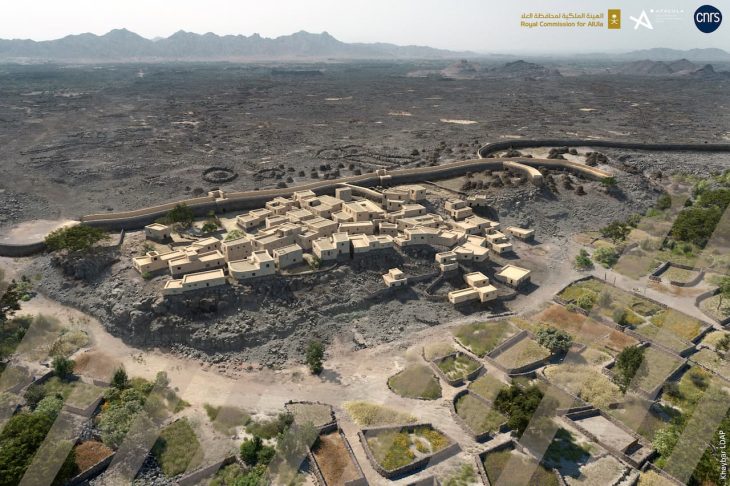
The Wuwangdun tomb complex, which covers an area of over 140 square kilometers, includes sacrificial pits, chariot and horse pits, accompanying graves, and the main burial chamber (Tomb No. 1). Tomb No. 1 is a large, nearly square, vertical pit tomb with sides that are about 50 meters long. There is a 42-meter-long, sloping tomb passage on the east side.
Around the pit, eight side chambers were found, and a central coffin chamber with several layers of planks covering it was also found. 443 coffin lid planks and the 78 bamboo mats that covered them have been removed thus far. On the planks of the coffin lid, there were about 1,000 ink-drawn characters that represented the locations and purposes of each side chamber.

“The findings can provide an overall picture of the political, economic, cultural, technological and social conditions of the Chu state in the Warring States period,” Gong Xicheng, an archaeologist part of the excavation told Chinese state news agency Xinhua.
“The findings can help us learn about the historical evolution as well as the formation of a unified nation and its culture,” he added.
These discoveries provide systematic archaeological data for studying the high-level tomb system in the Chu state during the late Warring States period (475BC-221BC).
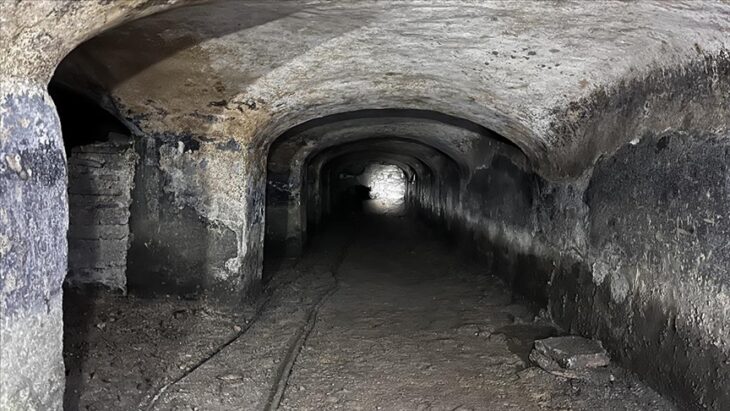
To discover while also preserving the unearthed remains archaeologists worked within a special low-oxygen laboratory built at the site.
Cover Photo: Part of artifacts unearthed from the tomb complex. CCTV