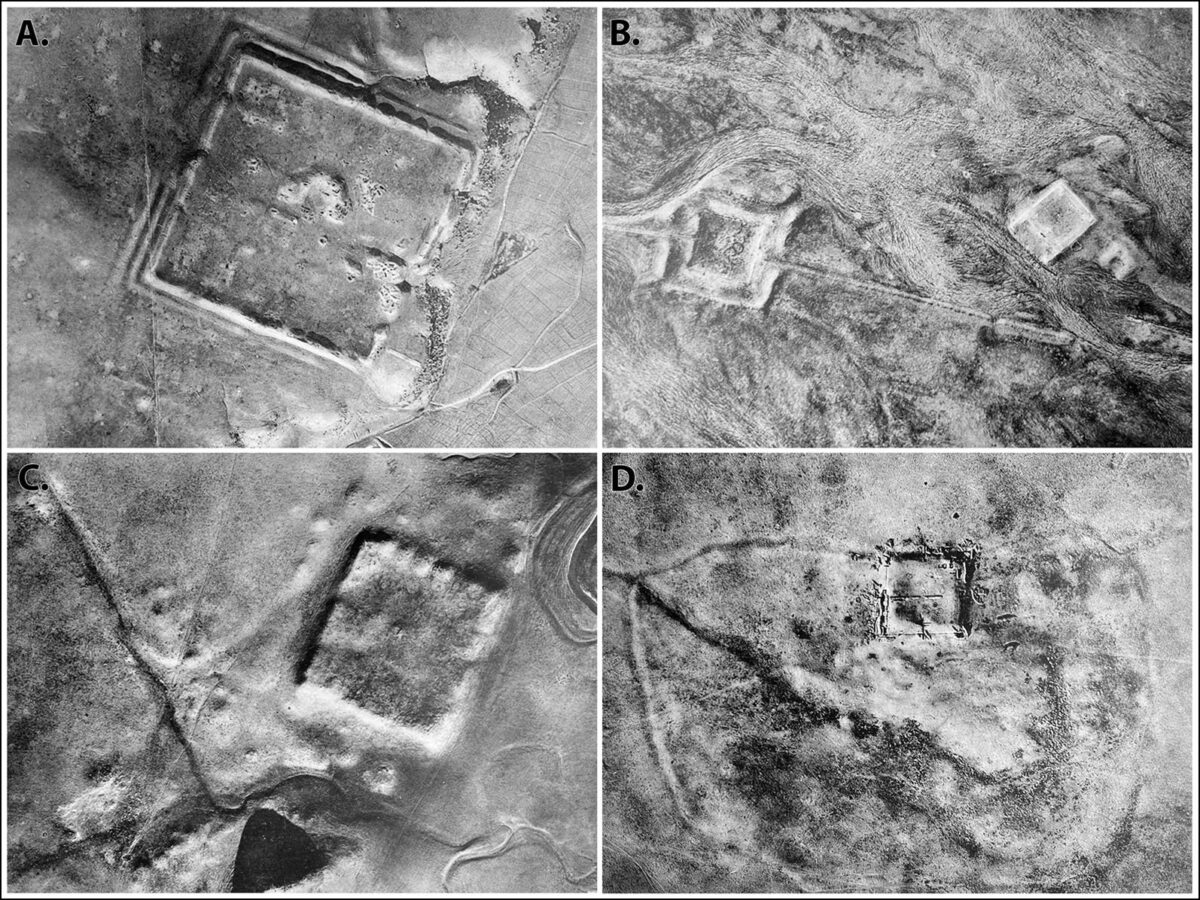
Archaeologists have discovered “massive” ancient Roman forts that redraw the borders of the ancient empire using images from a declassified satellite spying program of the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA).
High-resolution images were analyzed in a new study that was taken by multiple satellites during two U.S. military programs: the Corona Project (1960 to 1972) and Hexagon (1971 to 1986).
The photos, which were taken by the U.S.’s CORONA and HEXAGON spy satellites, shed new light on the farthest reaches of the Roman Empire, revealing a constantly shifting frontier as the Romans grappled with Arab nomads and Persian armies for dominance over a strategically important region known as the Fertile Crescent.
Before the publication of the study in the Antiquity Journal, it was believed that Roman forts in what is now Syria and Iraq were a line of defense. But this new data questions that hypothesis and suggests that the forts were actually for the safe passage of goods and people.
A 1934 study, conducted by French archaeologist Antoine Poidebard, suggested that the forts were established as a defensive line against the Parthians and the Sasanians.However, researchers studying the newly discovered satellite imagery found that the forts did not follow a discernible north-south defensive pattern against eastern threats but were scattered throughout the region.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
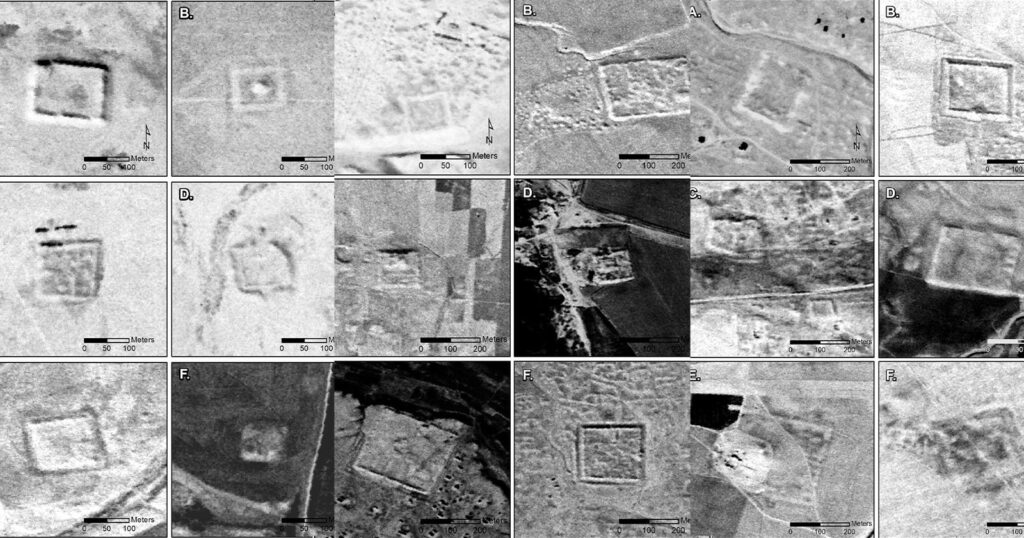

Researchers Jesse Casana, David Goodman, and Carolin Ferwerda from Dartmouth College have analyzed declassified footage from the U.S.’s CORONA (1960-1972) and HEXAGON (1970-1986) spy satellite programs that they say redraws and expands the edges of the Roman Empire in the same region Poidebard surveyed.
This discovery supports the theory that these forts might have served as protectors of trade caravans, facilitating communication, and intercultural exchange.
“We show that the forts form a roughly east-west line following the margins of the inland desert, connecting Mosul on the Tigris River in the east with Aleppo in western Syria,” the archeologists write in the paper.
Incredibly, many of the forts show evidence of occupation over hundreds of years, with many dating to between the 2nd and 6th century, a period that encompasses the tumultuous fall of the ancient Roman empire and the rise of Constantinople.
“Comparative evidence also suggests widespread abandonment of forts by the sixth century AD, although many of the larger fortifications have long histories of later occupation into the medieval period,” the researchers write.

The researchers report that the scale of the new forts they discovered were in some cases stunningly large with sides as long as 200 meters. “Many of these larger sites include extensive remains of outlying architectural features surrounding or within the fortifications, multiple fortified buildings, or large citadels,” they wrote.
Unfortunately, the modern-day wars and conflicts that beset this region mean it is hard to do ground-based investigations of the sites. But the authors say that more declassified material can help piece together this raucous period of history.
“As more declassified and historical imagery becomes available, including… resources such as HEXAGON imagery, U2 spy plane imagery, and other forms of early twentieth century aerial photography, careful analysis of these powerful data holds enormous potential for future discoveries in the Near East and beyond.”
Cold War-era spy satellite imagery has become a valuable resource for archaeologists in recent years. Another team of researchers said in a 2022 Antiquity paper that CORONA satellite images had become “an integral part of archeological research” over the last 25 years, particularly in “sparsely vegetated regions” like the Middle East. Imagery from CORONA’s successor program, HEXAGON, was declassified more recently, in 2020, and has quickly become just as important as CORONA’s imagery was to researchers.