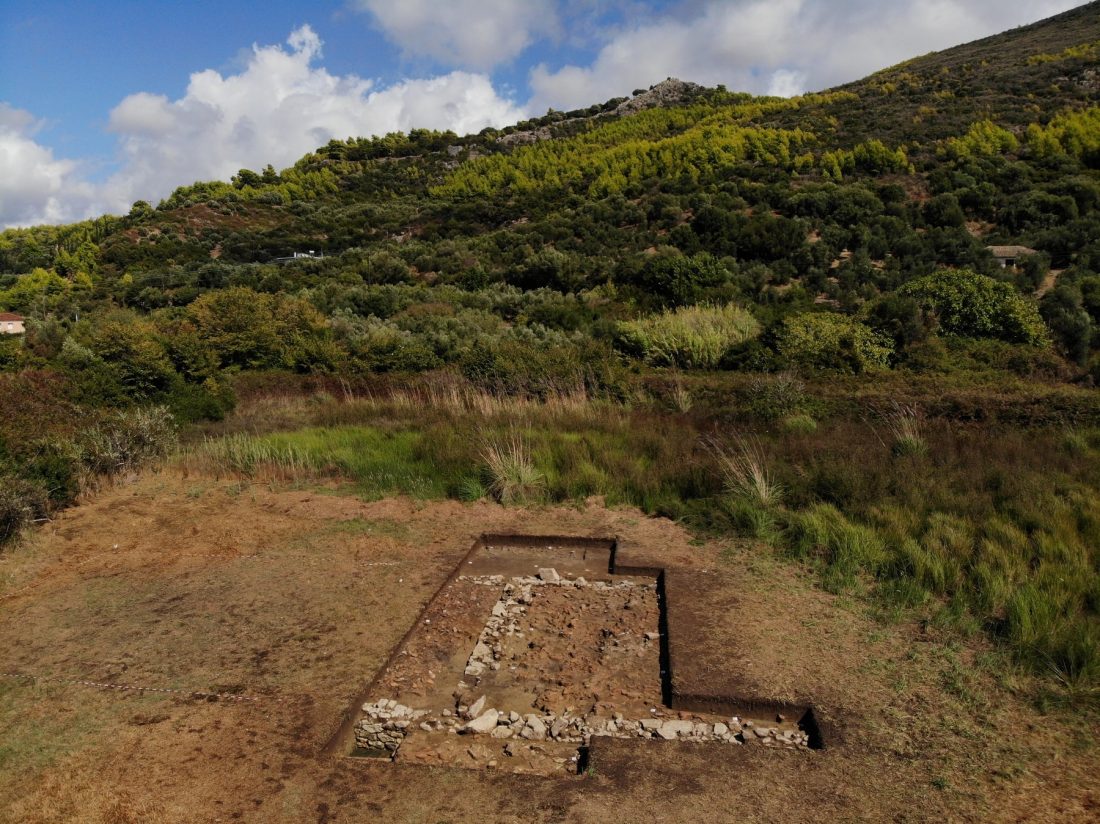
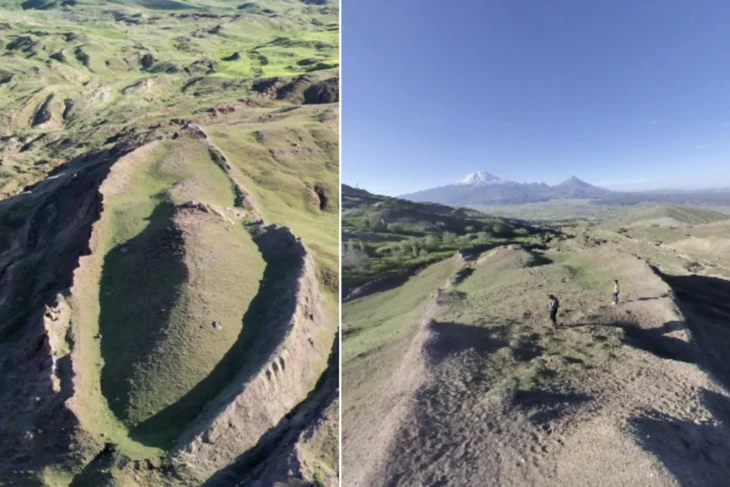
During excavations in the foothills at the ancient acropolis of Samicum in Greece, archaeologists may have found the sanctuary of Samian Poseidon.
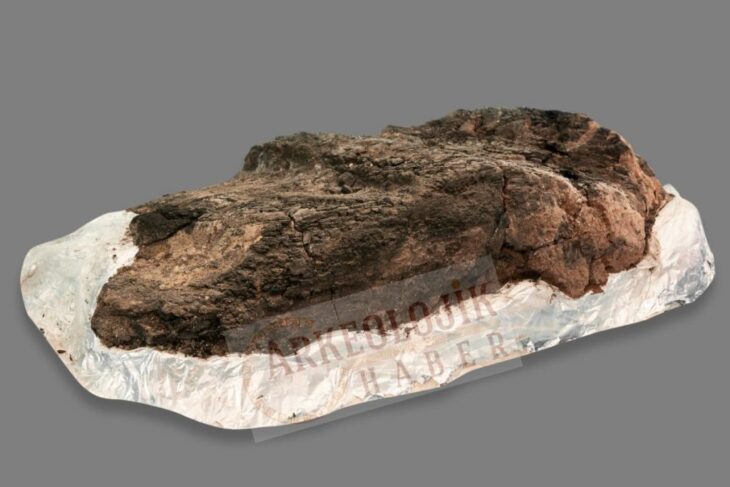
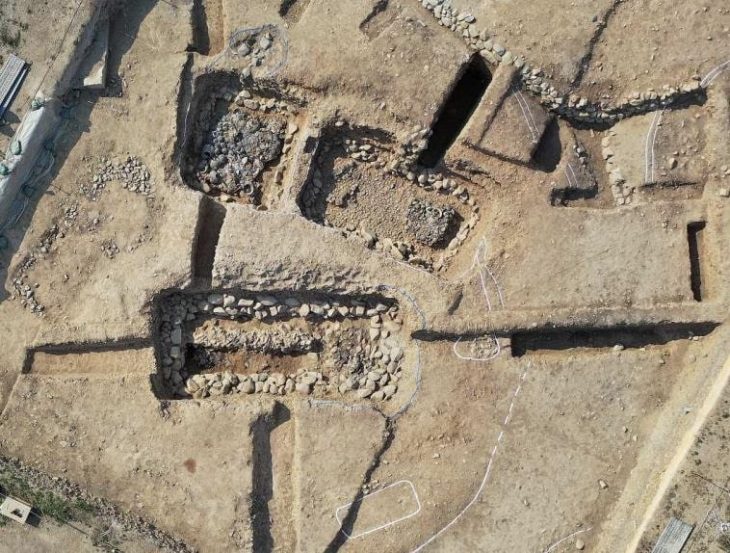
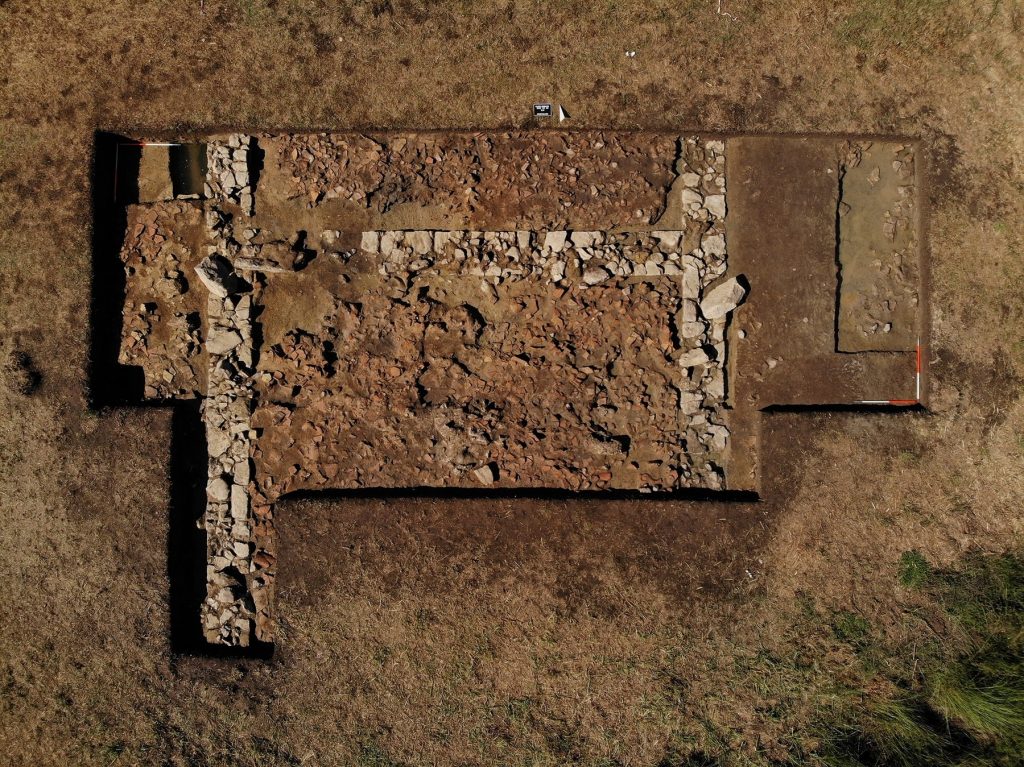
According to the Greek Reporter, archaeologists unearthed large sections of the foundation of a building 9.4 meters (30.8 feet) wide with heavy stone walls .8 meters (2.6 feet) thick. The remains have been dated to the 6th century B.C.
The sanctuary of Poseidon in Samikos was the regionally important religious center of the six cities of Triphylia, according to ancient sources Strabo and Pausanias. They formed an amphictyony, a confederation dedicated to the defense, upkeep, and veneration of a cult site. Strabo’s Geographica, Book VIII: “Then comes the mountain of Triphylia that sees Macistia from Pisatis; then another river called Chalcis, and a spring called Cruni, and a settlement called Chalcis, and, after these, Samicum, where is the most highly revered temple of the Samian Poseidon. About the temple is a sacred precinct full of wild olive-trees. The people of Macistum used to have charge over it; and it was they, too, who used to proclaim the armistice-day called “Samian.” But all the Triphylians contribute to the maintenance of the temple.”
The location where the potential temple was found fits with texts by Ancient Greek geographer Strabo who wrote about the temple in his work Geographica.

Samicum, also called Samikon, was an ancient city during the middle and late Helladic periods, located in the Peloponnese at Kleidi Hill near Kato Samiko, halfway between the mouths of the Alpheius and the Neda.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Scholars have proposed based on ancient descriptions that the temple of Poseidon was on a plain below the ancient acropolis of Samikon whose remains are on the hilltop overlooking the Ionian Sea.
A possible site of the temple was suggested following ongoing investigations conducting geophysical surveys in 2017, 2018, and 2021. This year archaeologists from the Ephorate of Antiquities of Ilia, the Austrian Archaeological Institute, the University of Mainz, and the University of Kiel (Dr. Dennis Wilken) embarked on the first comprehensive excavation of the site as part of a five-year program to explore the area to identify the sanctuary and the ancient port of Samikos.

The Athens Branch of the Austrian Archaeological Institute explains in a Facebook post: “Thick layers of roof tiles fill the space between the walls. Based on the anomalies of the geophysics, a building of at least 28 meters (92 feet) in length can be calculated, which had two interior rooms as well as a pronaos and an opisthodome or adyton. The elongated large building can be nothing other than an archaic temple located on the site of the sanctuary of Poseidon, perhaps even dedicated to the god himself.”
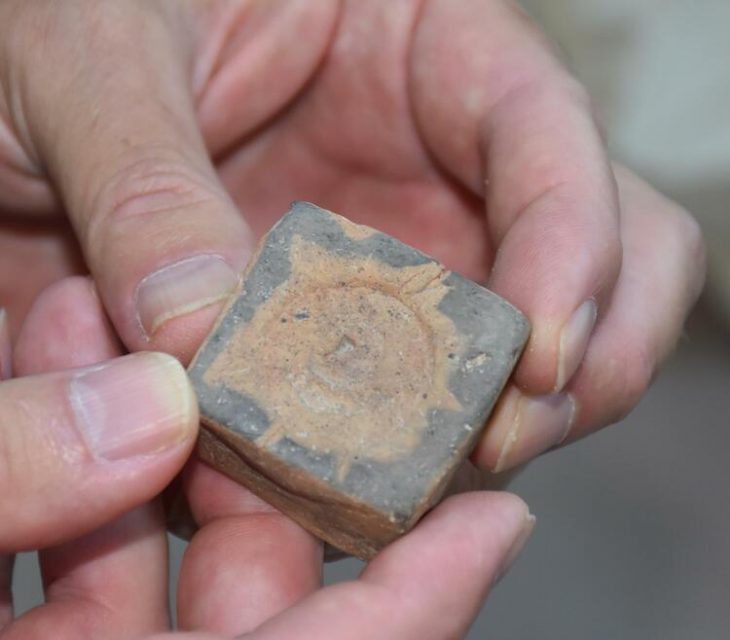
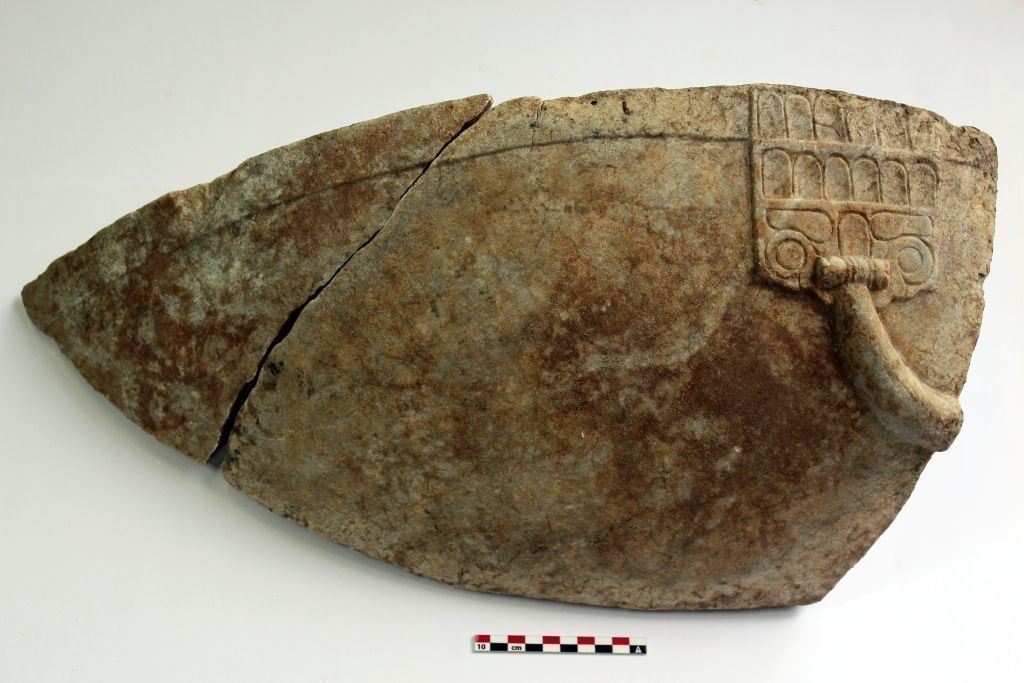
In connection with the fragments of a laconic roof, the discovery of a marble perirrhanterion provides evidence for dating the large building to the Archaic period. The large marble vessel itself, imitating a bronze bowl, is characteristic of the inventory of a sanctuary.
This discovery sheds new light on the political and economic significance of the Triphylian cities’ amphictyony in the sixth century BC when the sanctuary of Poseidon at Samikon served as the center of their religious and ethnic identity.
Cover Photo: Greek Ministry of Culture and Sports