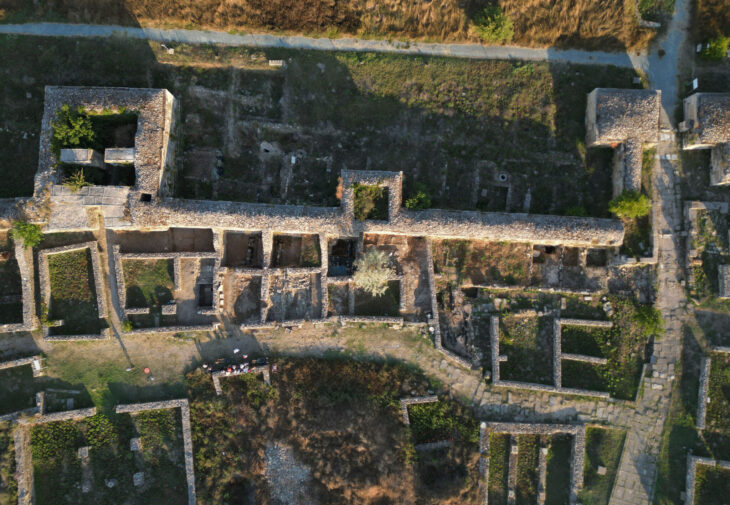
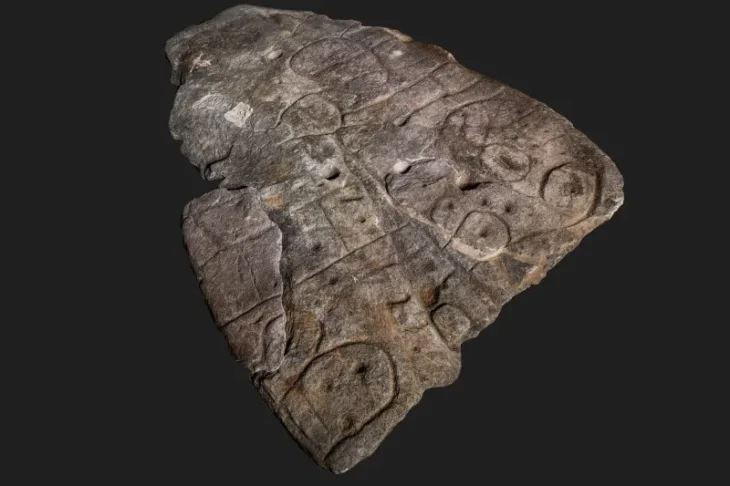
A recent archaeological survey led by the Alutiiq Museum has revealed significant discoveries on Shuyak Island, part of the Kodiak Archipelago, including what is believed to be the island’s oldest known Alaska Native settlement—estimated to be nearly 7,000 years old.
The multi-year survey, completed this spring by the museum’s archaeology team, uncovered dozens of previously undocumented village sites, particularly on the lesser-studied eastern side of the island. These findings expand the historical understanding of Alutiiq (Sugpiaq) settlement patterns across Kodiak’s rugged and remote landscape.
Discovering Alaska’s Deep Indigenous Past
Shuyak Island, known in Alutiiq as Suu’aq, meaning “rising out of the water,” has long been a quiet part of the state’s geography—rich in natural beauty but sparse in modern habitation. Today, it is largely encompassed by Shuyak Island State Park, a haven for kayakers and wildlife enthusiasts. But beneath its coastal grasslands and spruce forests lie remnants of ancient life.
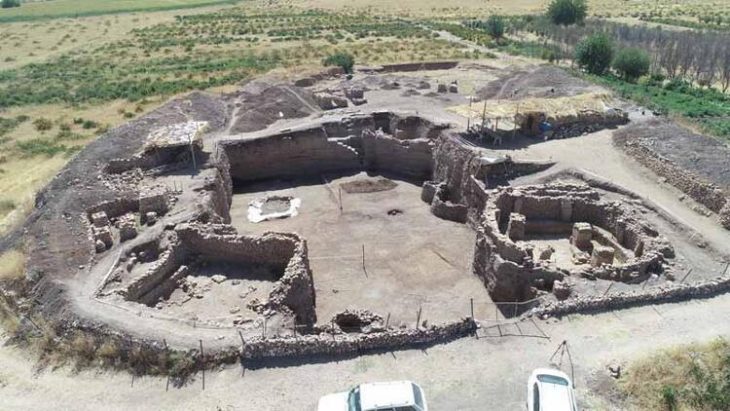
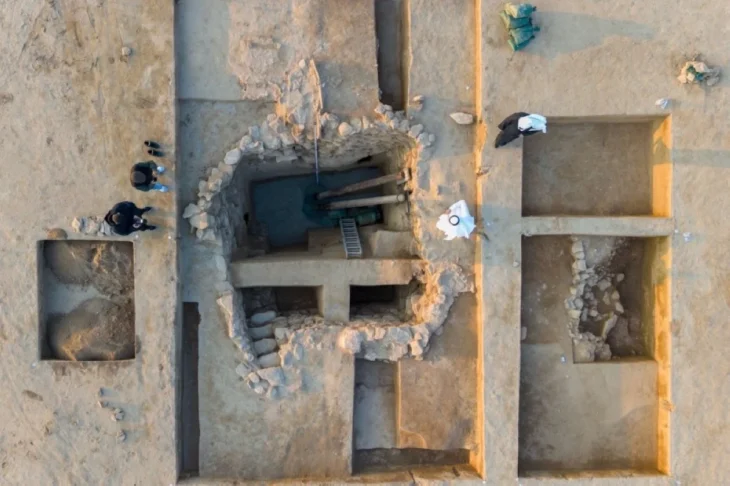
Patrick Saltonstall, curator of archaeology at the Alutiiq Museum, led the recent survey and described the discovery of a large village featuring 11 house pits. “We think that village housed 200 to 300 people about 300 years ago,” he explained. “But what’s more surprising is the nearby site that dates back roughly 7,000 years—making it the oldest we’ve ever found on the island.”
This new evidence challenges previous assumptions that Shuyak was lightly inhabited. “You go in thinking one thing, but the archaeology tells a more complex story,” Saltonstall added.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
A History of Community, Conflict, and Change
Archaeological and historical records confirm that Alutiiq people have inhabited the Kodiak Archipelago for at least 7,500 years. Shuyak Island itself was once home to several villages. One of these, according to historical accounts, had a trading relationship with Russian fur trader Gregorii Shelikov in the late 1700s. However, tensions escalated when local villagers killed two Russian workers and an interpreter—prompting Shelikov to destroy the village. The remaining communities abandoned the island shortly thereafter.
By the 20th century, Alutiiq families returned to Shuyak not to settle, but to fish. The island hosted fish salteries and later a processing facility, which operated as the Washington Fish and Oyster Company until 1976.
Protecting a Fragile Heritage
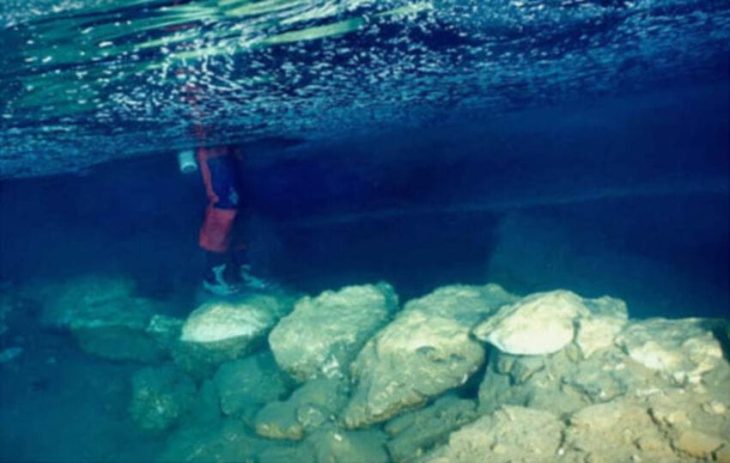
The 1989 Exxon Valdez oil spill prompted renewed archaeological interest in Shuyak, as many coastal sites were thought to be eroding into the sea. But recent geological shifts may be protecting these cultural treasures. “The land has been rising since the 1964 earthquake—outpacing sea level rise,” said Saltonstall. “Now we’re seeing grass stabilizing the beaches, which is good news for site preservation.”
Molly Odell, director of archaeology at the Alutiiq Museum, emphasized that the stabilization of the island’s terrain reduces threats from both erosion and looting. “It means these sites are not only safer but also less likely to be disturbed by visitors collecting artifacts,” she said. “We urge people to leave cultural materials where they find them and report any findings to the museum.”
The museum’s work on Shuyak is conducted in partnership with Alaska State Parks, and a new archaeology exhibit is planned for the Big Bay Ranger Station later this summer.
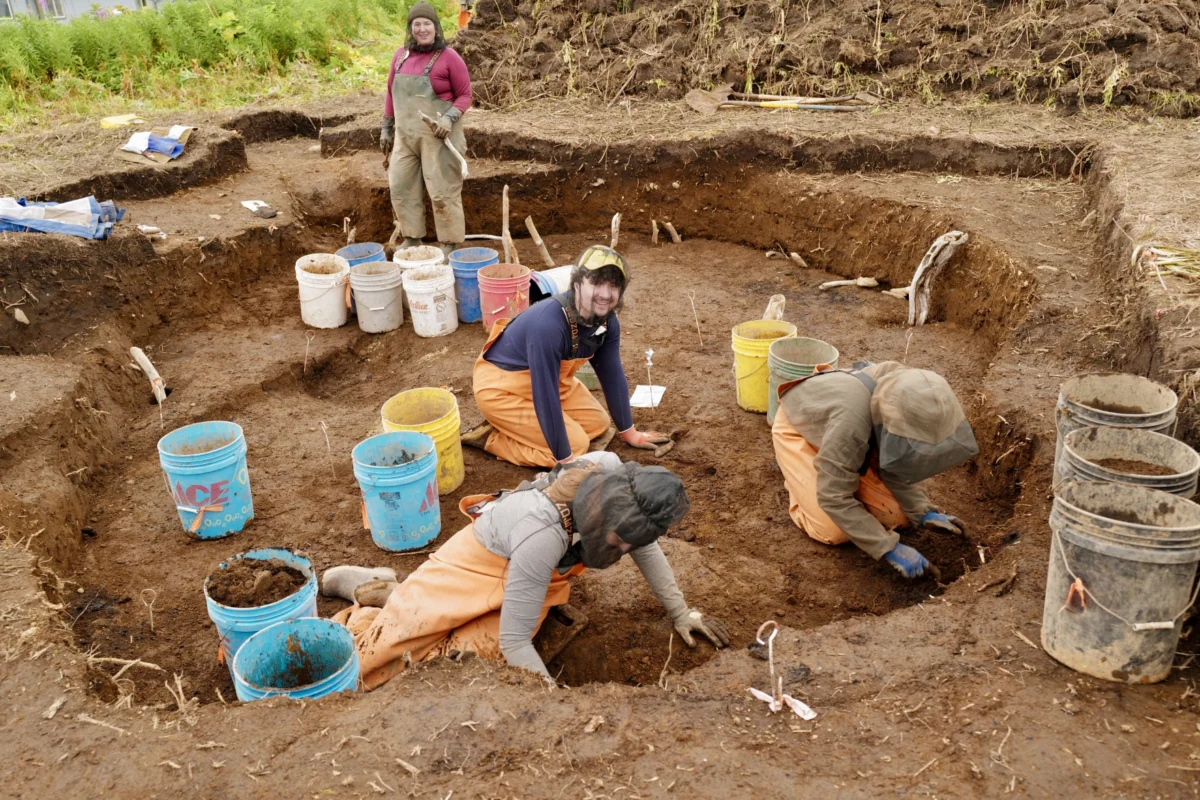
Cover Image Credit: Archaeologists with the Alutiiq Museum dig into layers on layers site at Karluk Lake called site 309, which revealed a ‘super structure’. This is separate from what was surveyed on Shuyak Island. Credit: Alutiiq Museum Archaeology Department & Repository
















