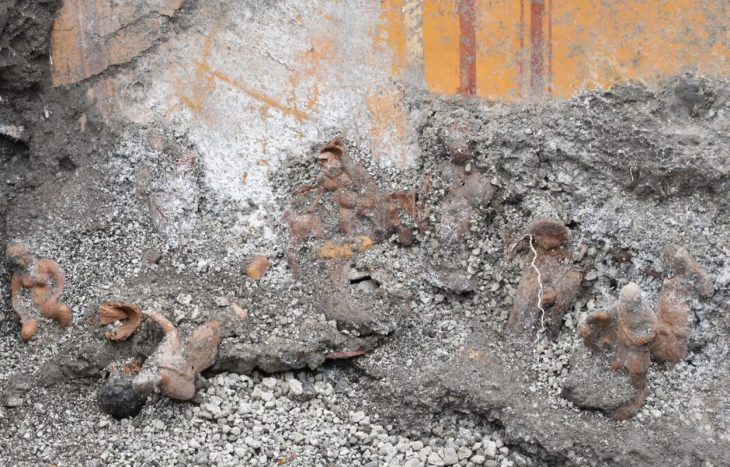
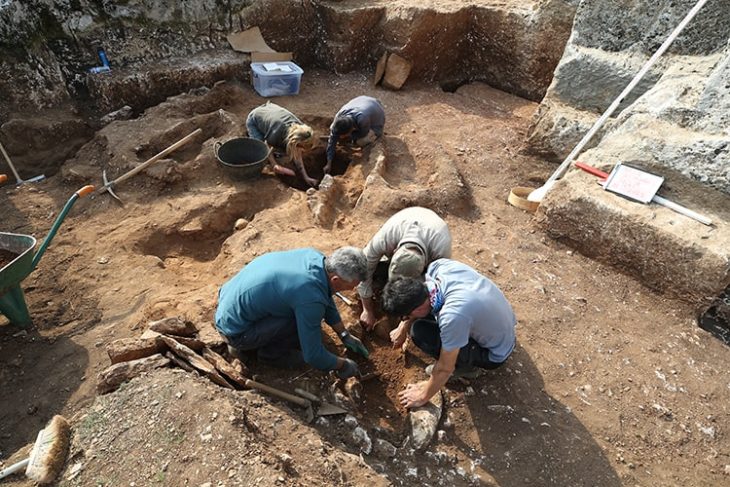
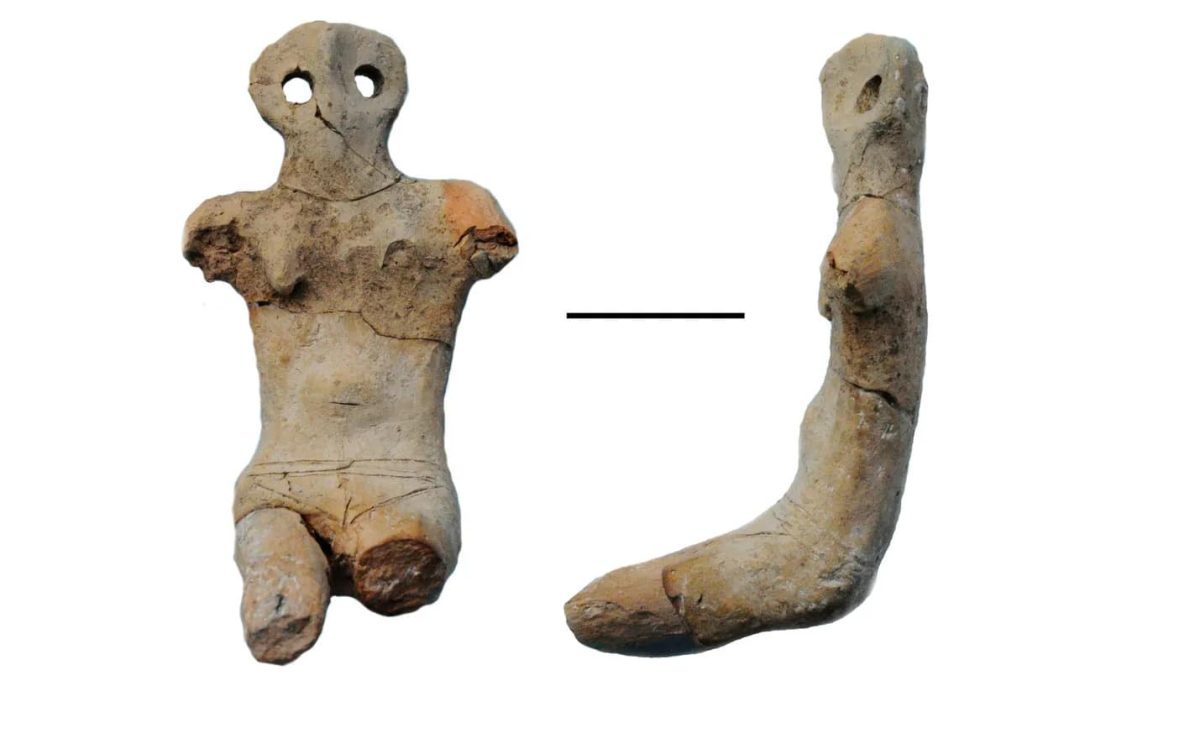
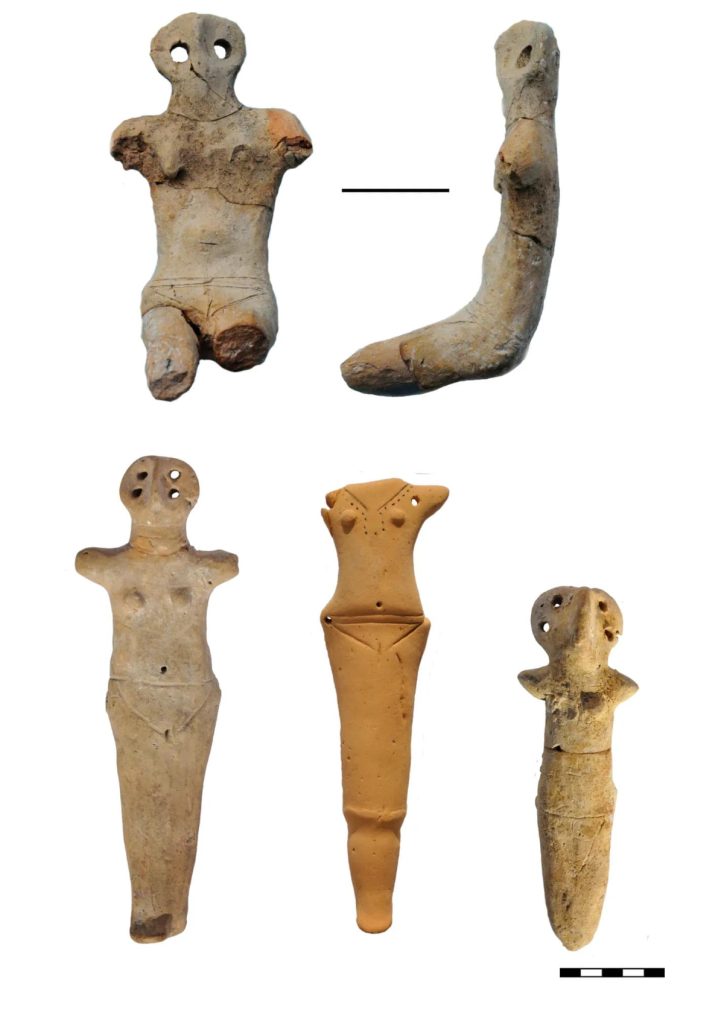
Archaeologists discovered five clay female figurines hidden inside a hole in a wall in Verteba Cave, in the Borshchiv Region of western Ukraine.
Ritual hoard found in Verteba Cave from around 5,000 years ago illuminates the ritual life of the mysterious Cucuteni-Trypillian culture.
These stylized figurines, which date from the first millennium BC, have been linked to the Cucuteni-Trypillian culture, which dominated a large swath of Eastern Europe during the Late Neolithic period and the Copper Age (6,000 to 2,750 BC).
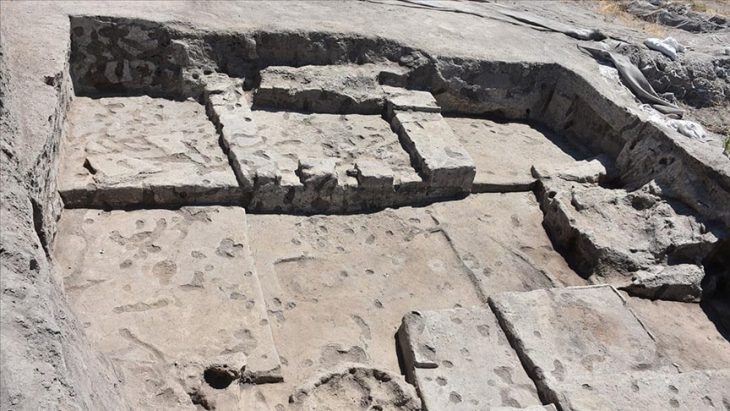
The Vertaba cave contains up to 8 kms of passageways used as a Sanctuary by the Cucuteni-Trypillia Culture.
The discoveries were made in March by archaeologists from the Borschivskyy Local History Museum in Ukraine, led by Sokhatskyi Mykhailo, a leading scholar of the Trypillian culture and director of the museum.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The Cucuteni-Trypillian culture is known to have been highly developed for its time, the late Neolithic and Chalcolithic. Some of their settlements were extraordinarily large; they farmed and husbanded domestic animals and had pottery and metallurgical skills.
Each individual dwelling site had a lifespan of roughly 60 to 80 years, and the regular destruction or burning of settlements was a mysterious aspect of the culture. Experts still debate the reason behind the burning of these settlements.
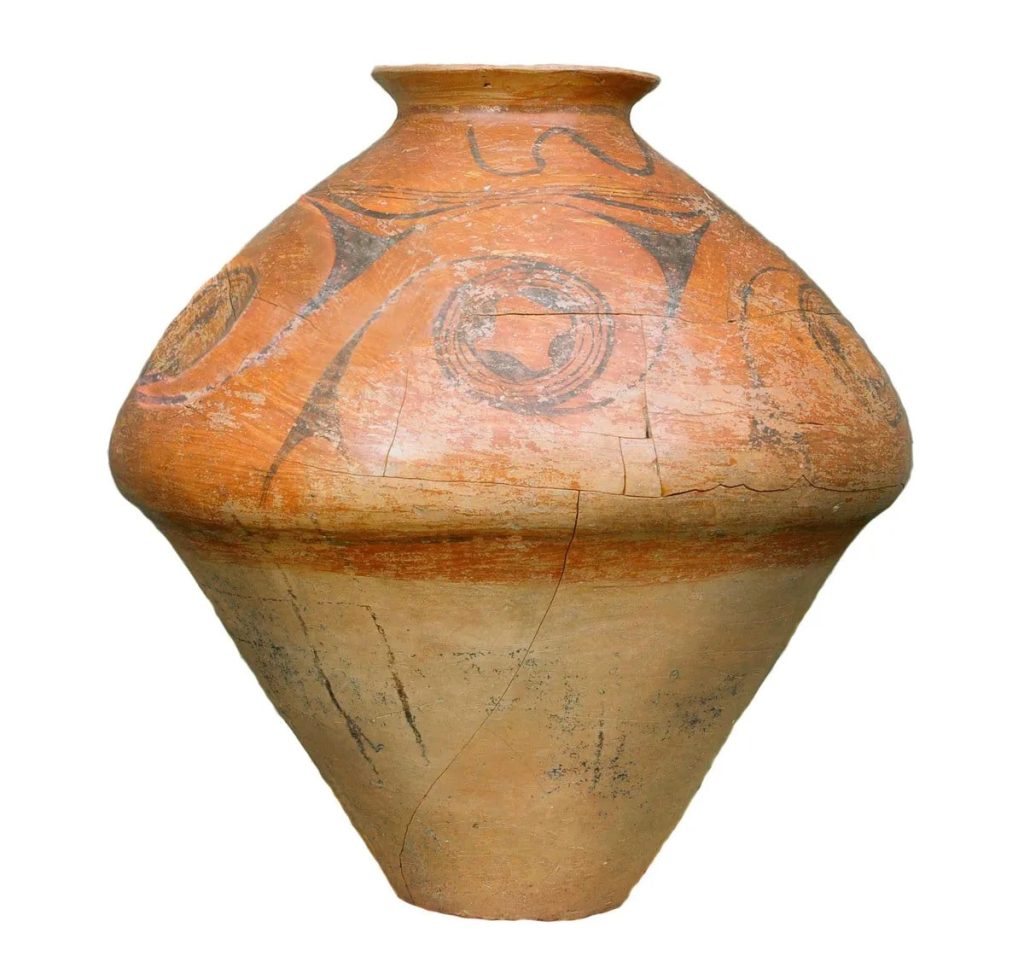
The religious practices of the Cucuteni-Trypillia Culture are poorly understood, and examples of ceramics discovered are extremely rare. Archaeologists excavating in Verteba Cave, on the other hand, have discovered a massive clay storage jar containing a white organic material (yet to be analyzed).
The figurines were most likely used in Trypillian rituals. These statuettes have been identified by archaeologists as totems, which are sacred objects that can protect people from harm. In this case, the figurines were placed inside the cave wall and covered with an unusual seal for equally enigmatic reasons.

“Female figurines are not rare in Trypillian contexts , and hoards of figurines are known,” confirmed Sokhatskyi Mykhailo, a scholar of the Trypillian culture and the director of the Borschivskyy Local History Museum, in an interview published in Haaretz. “But these were sheltered by the tusks of a wild boar.” He emphasized that this arrangement was unique, having never been seen before at any Eastern European archaeological site.
Boar remains are generally scarce in Trypillian complexes. Although some Early and Middle Trypillian graves contained their tusks, the rituals of this culture appeared to have been more centered on domesticated animals like cattle, sheep, goats, and dogs. Typically, bears or deer are used to represent wild animals.
The archaeologist explains that Verteba is a “late Trypillian” and that this find is unique in that context. In Verteba, the team discovered jewelry and tools (for pottery production) made of boar teeth, as well as a small clay boar figurine in 2016.
The boar may have played an important role for the people in the cave for some reason. Sokhatskyi noted that the Trypillians had a habit of resurrecting old cultural traditions. They were known to reuse pottery ornamentation styles periodically, and the scholar speculates that some remnant of an ancient boar-worshipping culture may have been preserved by the people who occupied Verteba Cave.
Cover Photo: Mykhailo Sokhatskyi