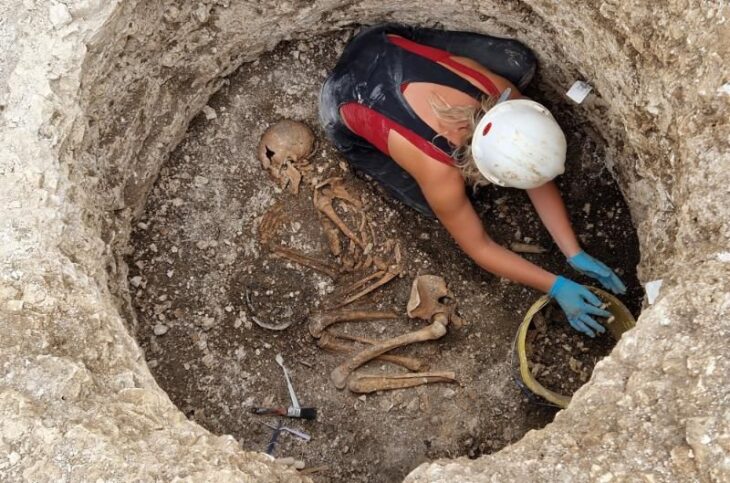
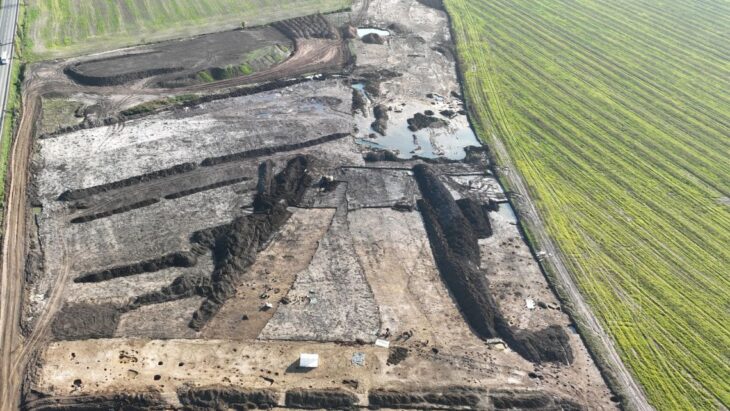
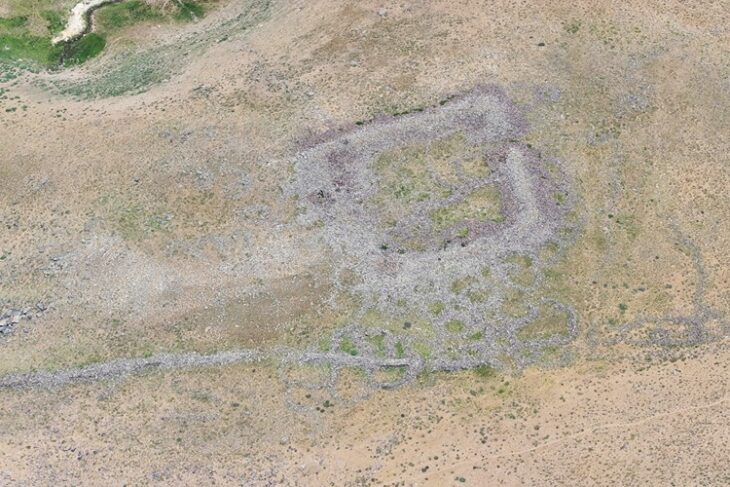
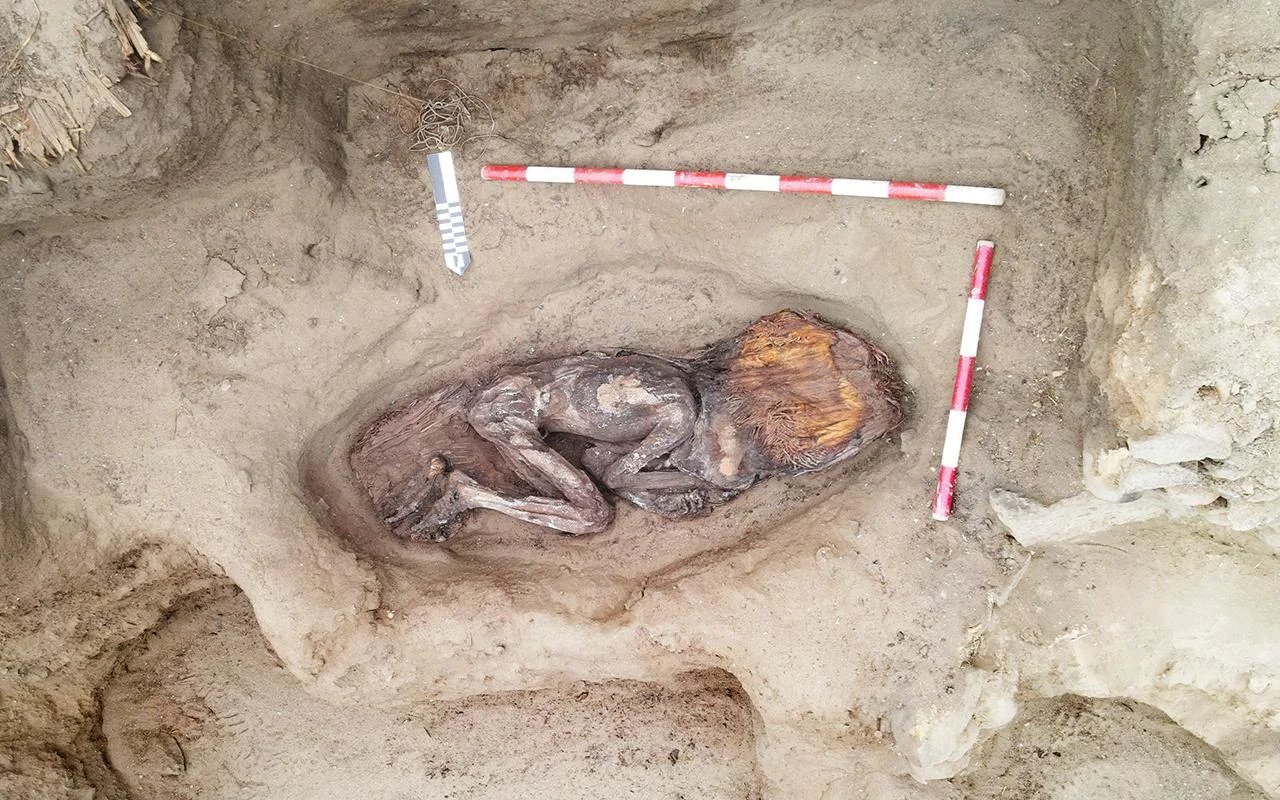
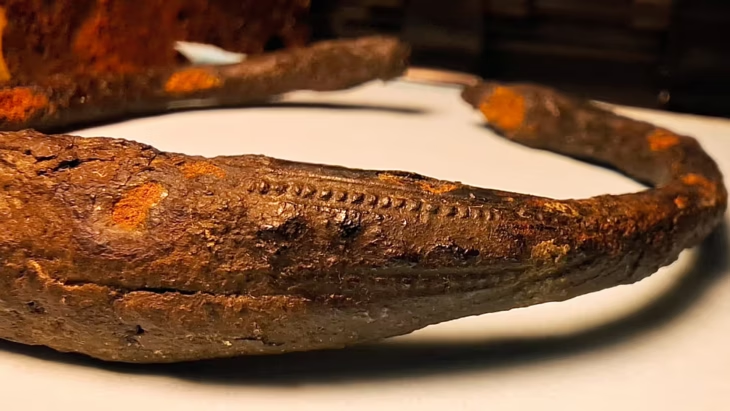Archaeologists in Peru have announced the remarkable discovery of a 5,000-year-old burial of a woman of high social standing at the Áspero archaeological site. Áspero, an ancient fishing settlement, was a significant satellite city within the Caral civilization, the oldest known civilization in the Americas. The well-preserved remains, unearthed by Dr. Ruth Shady Solís and her team from the Caral Archaeological Zone (ZAC), offer unprecedented insights into the influential roles women held in early Andean society.
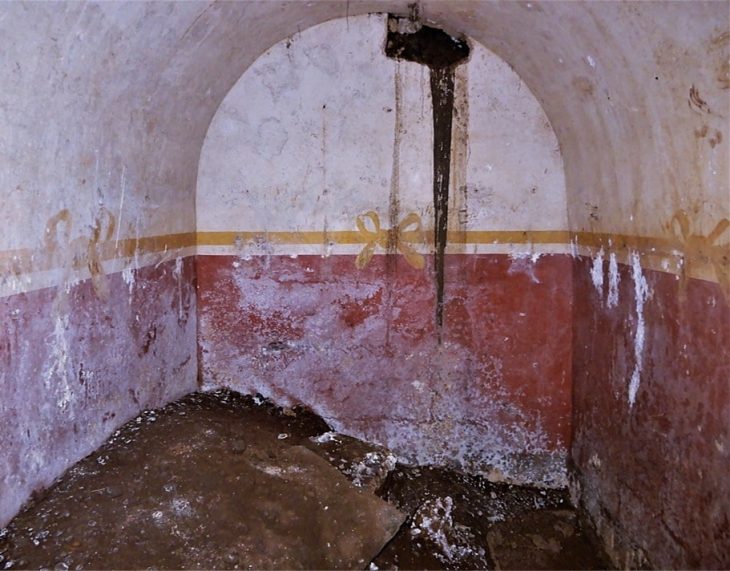
The burial site, located at Huaca de los Ídolos within the ancient fishing settlement of Áspero, is approximately 180 kilometers north of Lima. Áspero was a key satellite city of Caral, which thrived from 3000 to 1800 BC, contemporaneous with ancient Egypt, Sumer, and China, yet developed in isolation. The remains belong to a woman estimated to be between 20 and 35 years old and approximately 1.5 meters (5 feet) tall. Notably, the state of preservation is exceptional, with parts of her skin, nails, and hair recovered—an uncommon occurrence for human remains in the region.
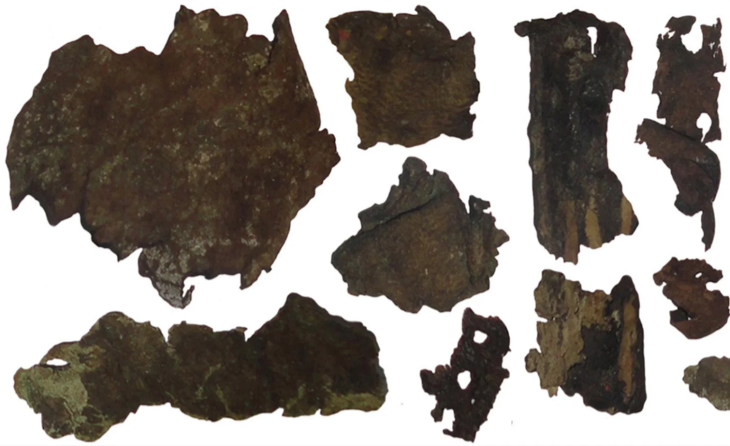
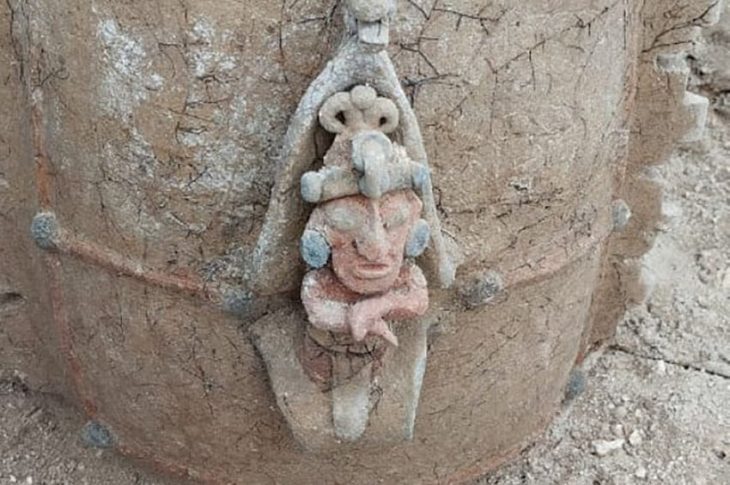
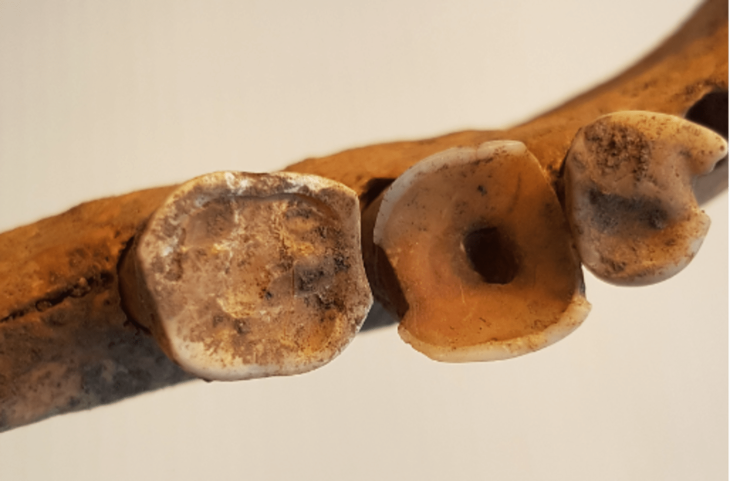
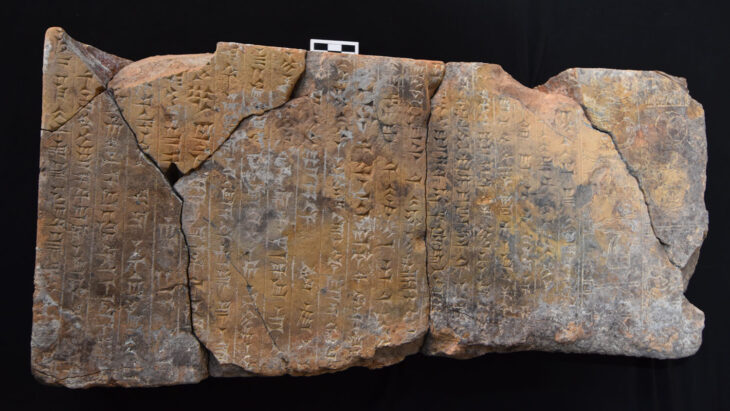
The woman was found wrapped in multiple layers of cotton fabric and rush mats, adorned with an embroidered feather mantle made from vibrant macaw feathers, showcasing one of the oldest examples of Andean featherwork. Accompanying her were a rich array of funerary offerings, including intricately crafted vessels, weaving tools, a bone needle, a shell likely from the Amazon basin, and over thirty sweet potatoes. These items not only highlight her elevated social status but also reflect the advanced trade networks of the Caral society, which extended as far as the Amazon.
According to an official statement from the Peruvian State, the discovery of the feathered panel and other finely crafted objects indicates a high level of specialized techniques during the Caral civilization. The feather artwork, in particular, underscores the aesthetic and symbolic sophistication achieved by this ancient society.
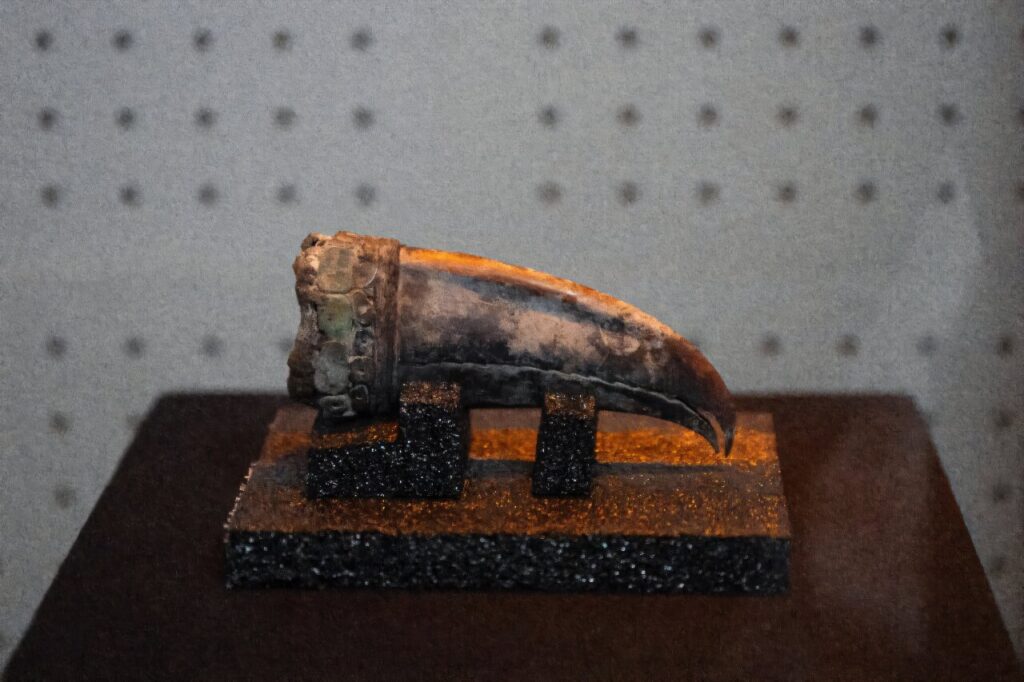

Archaeologists have noted that this burial aligns with other elite burials found at Áspero in recent years, such as the “Lady of the Four Tupus” and the “Elite Man,” suggesting a pattern of ceremonial burials among the elite class. This evidence supports the hypothesis that women held special status and power in Caral society.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
A multidisciplinary team is currently analyzing the remains and associated artifacts to gain further insights into the woman’s health, diet, cause of death, and the sociocultural significance of the objects buried with her. Archaeologist David Palomino emphasized that this discovery challenges the traditional view that rulers were predominantly male, highlighting the important roles women played in the Caral civilization.
The city of Caral, situated in the fertile Supe Valley and declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2009, continues to provide invaluable insights into the lives of its ancient inhabitants, revealing a complex society where women were integral to its development and cultural richness.
Cover Image Credit: Remains of a 5000-year-old woman from the Caral civilization. Credit: Ministry of Culture of Peru (Ministerio de Cultura del Perú)