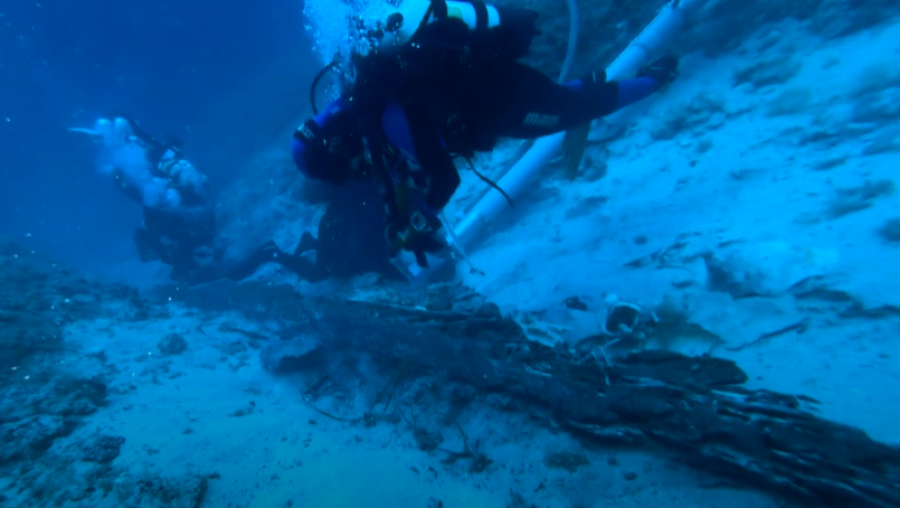
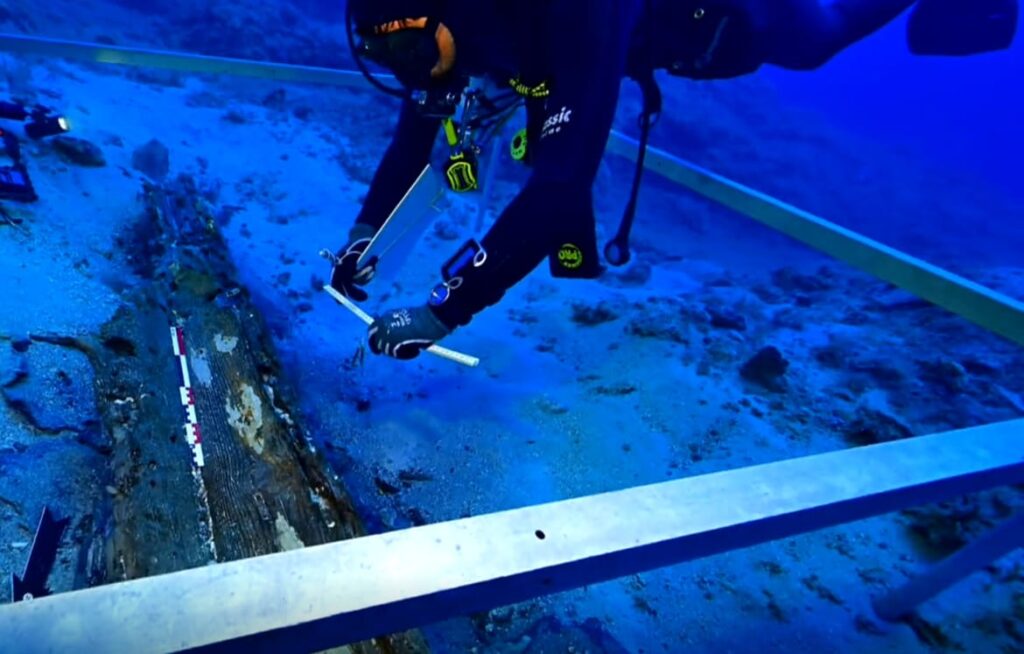
A significant archaeological find has been confirmed off the coast of Komiža, near the Croatian island of Vis, where researchers have uncovered the remains of a Greek merchant ship dating back to the 4th century BC — a crucial period when the ancient Greeks established colonies on the Adriatic islands of Issa (modern-day Vis) and Pharos (now Hvar).
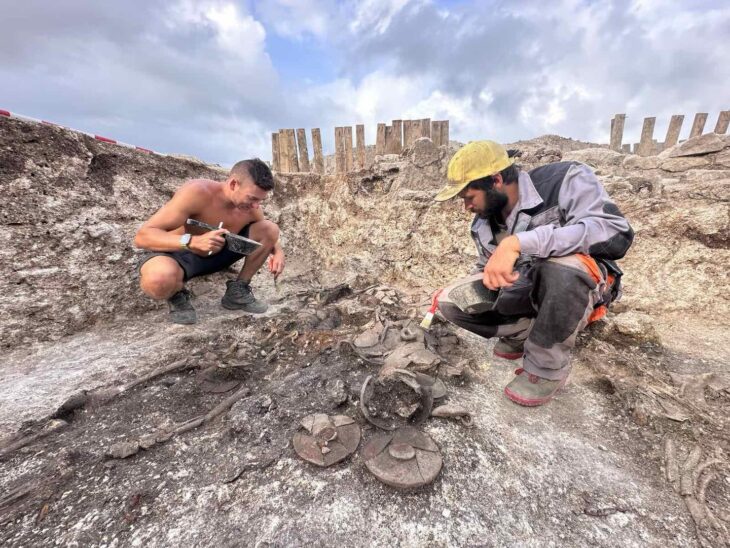
The wreck, located at a depth of 30 to 50 meters, was initially spotted in 2023. Now, experts from the Underwater Archaeology Department of the Croatian Conservation Institute have officially confirmed the site’s exceptional historical value.
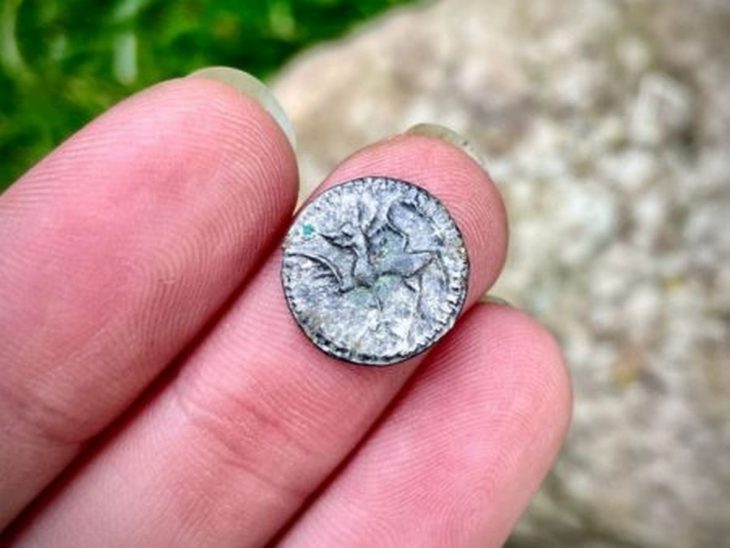
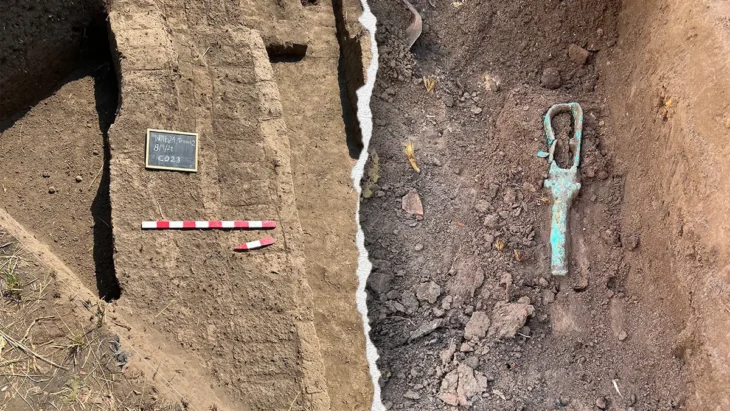
“From our first dive, we sensed the site was something extraordinary,” said diver Marko Lete in an interview with HRT. “We recovered a coin, still undergoing analysis, but the surrounding pottery clearly indicated a 4th century BC origin. This makes it one of the oldest shipwrecks ever discovered in the Adriatic Sea.”
As excavations progressed, the team uncovered well-preserved artefacts, including fine Hellenistic pottery, personal items, human remains, and a remarkably intact section of the ship’s wooden hull.
Jurica Bezak, lead archaeologist and senior conservator at the Croatian Conservation Institute, highlighted the ship’s exceptional state of preservation.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“This site has no equal in the region,” Bezak stated. “The luxury ceramics and the lead-plated wooden structure are extraordinarily well-preserved, offering unique insights into ancient shipbuilding techniques.”
The ship is believed to have been transporting supplies to the newly established colony of Issa. Among the cargo were amphorae, fine ceramics, containers filled with olive oil, spices, and preserved food — artifacts that shed light on the daily life and trade practices of early Greek settlers in the Adriatic.

“Some items emerging from the silt appear as if they were made yesterday,” Lete added, praising the craftsmanship and engineering of the ancient vessel.
Bezak noted the broader cultural importance of the discovery:
“Beyond its archaeological significance, this find will enhance the cultural and educational landscape of Vis. Once restored, many of the recovered artefacts will be displayed in the island’s museum, benefitting both the local community and tourism.”
The Croatian Conservation Institute continues to lead the ongoing excavation in collaboration with local diving clubs and the Vis Heritage Museum. Research at the site is expected to continue for several years due to the complexity and delicacy of the preservation process.
The Founding of Issa and Pharos in the 4th Century BC
The 4th century BC was a transformative era for the Adriatic region, marked by the expansion of Greek colonial influence. During this period, Greek settlers from Syracuse in Sicily founded the colony of Issa (on the island of Vis) around 397 BC. Shortly thereafter, they helped establish Pharos (on Hvar Island) in 384 BC.
These colonies played a crucial role in the spread of Hellenic culture, trade, and maritime dominance in the eastern Adriatic. Issa, in particular, became a thriving center of commerce and culture, complete with fortifications, public buildings, and its own coinage. It served as a key strategic outpost for Greek influence in the region and later played a pivotal role during Roman expansion.
The discovery of this 4th-century BC shipwreck offers direct physical evidence of that era’s advanced shipbuilding and trade networks, providing a rare connection to the daily life and seafaring practices of early Greek colonists in the Adriatic Sea.
Cover Image Credit: HRT