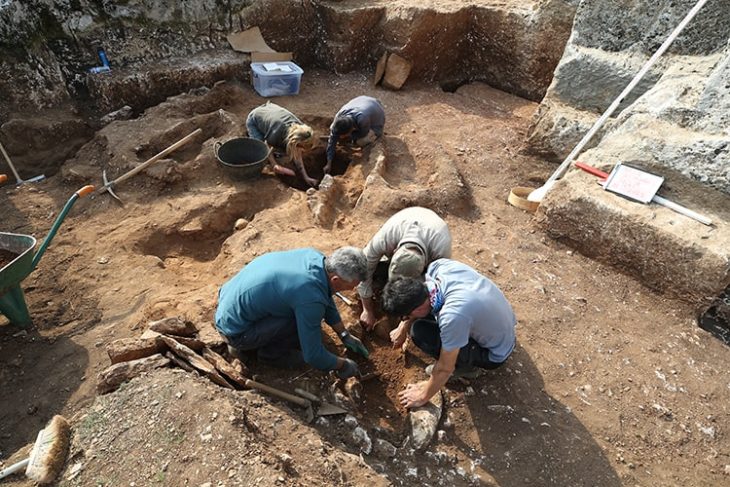
A joint German/Egyptian archaeological mission at the Temple of Esna on the west bank of the Nile, 35 miles south of Luxor in Egypt, has revealed some original colors and patterns in the part of the temple complex during restoration work.
Sand dust, filth, salt efflorescence, and bird and bat guano and bones had collected on the walls, ceilings, and columns over the ages, obscuring the inscriptions to the point that they were almost invisible to the human eye.
The construction of the Esna Temple dates from Ptolemaic times, however, most of the parts that survive today are from the Roman period.
The Esna Temple is dedicated to the Ancient Egyptian god, Khnum, and his consorts Menhit and Nebtu, their son, Heka, and the goddess Neith.
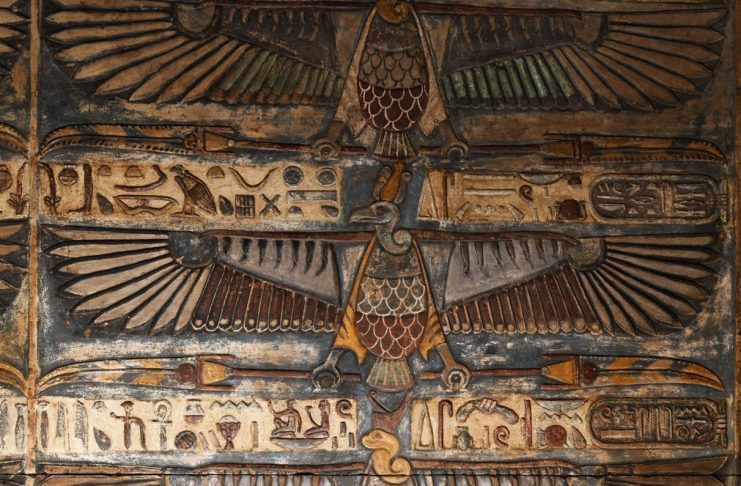

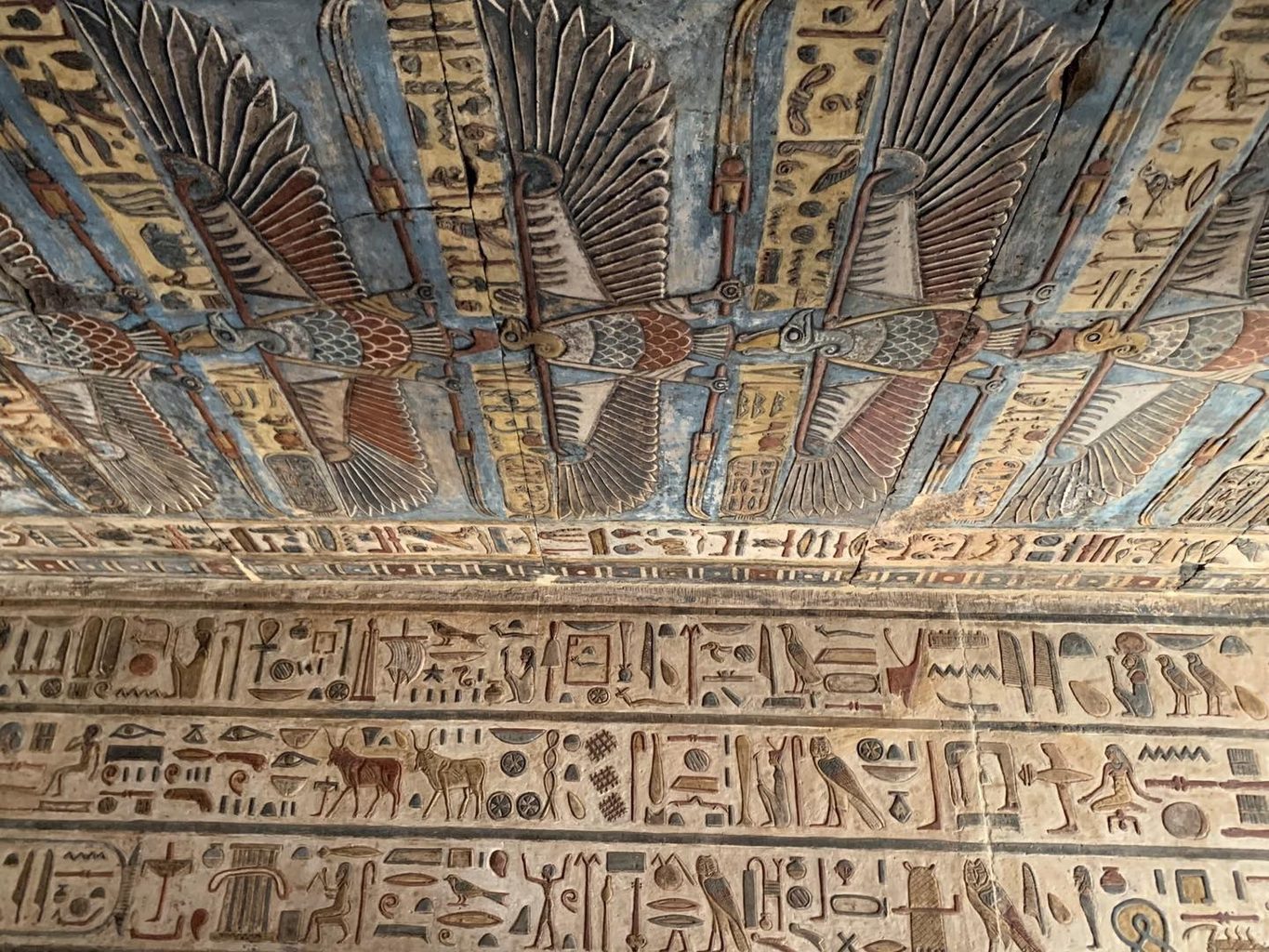
The restoration project found the original colours and patterns under the middle ceiling above the entrance to the temple. A careful process of cleaning revealed a painting that depicts 46 eagles in a row, 20 of which have an eagle head (representing Upper Egypt), whilst the remainder the head of a cobra (representing Lower Egypt).
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The murals on the middle ceiling over the entry hall are particularly noteworthy. The ceiling is more than 45 feet high and decorated with 46 eagles in two rows. The goddess Nekhbet and Upper Egypt are represented by twenty-four of them, which have eagle heads. Wajit, the goddess of Lower Egypt, is represented with twenty-two cobra heads. Between 1963 and 1975, French Egyptologist Serge Soniron studied and photographed the temple inscriptions, but the ceiling with the 46 eagles was never recorded or published.

Dr. Hisham El-Lithy, head of the Central Administration for Egyptian Archaeology Registration and Head of the Egyptian Archaeological Mission said: “The colourful inscriptions have suffered over the past centuries from the accumulation of thick layers and impurities.”
Researchers also discovered Greek inscriptions written in red ink while cleaning the western wall of the temple. It was discovered in the temple axis’ western wall frieze, totally buried in layers of black soot. The inscription specifies the date and month, Epiphi 5, which corresponds to late June or early July during Emperor Domitian’s reign (81-96 A.D.) Archaeologists think that this is the date when the Esna Temple was finished.