Findings that will change our perception of Neanderthals’ sophistication
A team from the University of Tübingen have proved that Middle Paleolithic people in the Swabian Jura employed experience, planning, and skill when manufacturing stone tools.
It’s still impossible to say how smart the Neanderthals were, but it’s clear that they were far more intelligent than previously imagined.
Stone tools were made by Neanderthals living in the Swabian Jura more than 45,000 years ago using complex methods and a variety of manufacturing tactics. (Modern humans first arrived in Europe 43,000 years ago during the last ice age.)
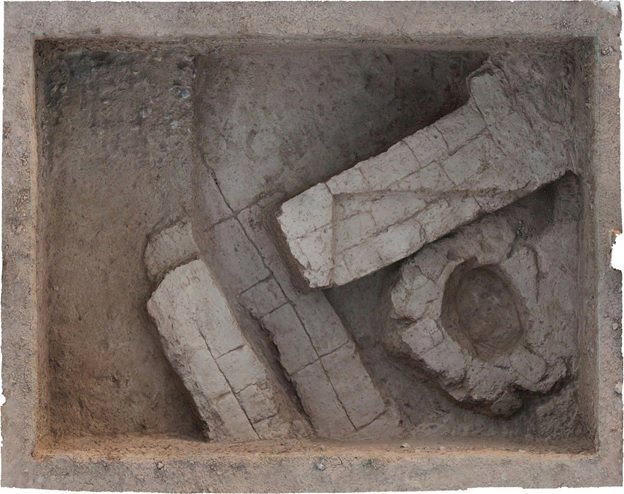
Many stone artifacts and byproducts of the toolmaking process have been discovered at the Heidenschmiede site. The researchers replaced the parts created from stone cores and were able to demonstrate the procedures employed in the process, which required preparation and thinking.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Dr. Berrin Çep, Benjamin Schürch, and Dr. Jens Axel Frick of the Institute of Prehistory and Medieval Archaeology, as well as Dr. Susanne Münzel of the Institute of Scientific Archaeology, all of the University of Tübingen, published the results of their research in the journal PLOS ONE.
The findings demonstrate that Neanderthals had highly developed skills once again.

The Heidenschmiede, a rock shelter in Heidenheim in southern Germany, was found and excavated in 1928 by amateur archaeologist Hermann Mohn, who identified it as an important site for early human stone and bone activity.
“Our study is the first detailed investigation since then that deals with the many finds and classifies them in more detail,” explains Benjamin Schürch.
The bone and stone tools originate from the Middle Paleolithic and are at least 50,000 to 42,000 years old, according to him. “In this period, modern humans of our current species Homo sapiens were yet to come to the region. It was late Neanderthals living at the Heidenschmiede.”
Stone was used by Neanderthals to make blades, scrapers, and single-edged hand axes, known as Keilmesser, for jobs such as leatherworking, as well as spearheads used for hunting. “It was known that they used various strategies to make such tools,” says Berrin Çep, the study’s primary author.

She has been attempting to reassemble individual parts in order to have a better understanding of how the inhabitants of the Heidenschmiede operated. “In some cases, we have been able to trace in detail how other basic shapes, such as flakes and blades, were first made from stone cores and then processed into tools,” Çep says. “Reconstructions like this are rarely possible at Neanderthal cave sites in the Swabian Jura because not all of the material from the manufacturing process remains at the site.” In addition, not all findings were typically documented in early digs.”
Early research in the region
“Based on the reconstructions, we were able to prove that the Neanderthals at the Heidenschmiede used a branched manufacturing system in which various techniques known to the makers were applied to one core piece of stone,” Schürch explains, adding that such sophisticated manufacturing processes have only rarely been attested from the Middle Paleolithic.
“This is the first such evidence from the Swabian Jura,” says Jens Axel Frick.
Whoever worked the raw material was able to consider from the outset that parts of the stone could be further worked using a different technique. “This requires strong three-dimensional visualization, creativity, and mentally flexible planning,” says Berrin Çep.
The research team has shown that the early humans who worked the stones from the Heidenschmiede had an excellent working memory overall. The new study results supported other investigations, according to which the Neanderthals possessed great mental flexibility and adaptability, coupled with manual dexterity. At the same time, the varied and elaborate manufacturing processes made visible also provide an explanation as to why a great variability of the assemblages are found in stone artifacts from the Middle Paleolithic.