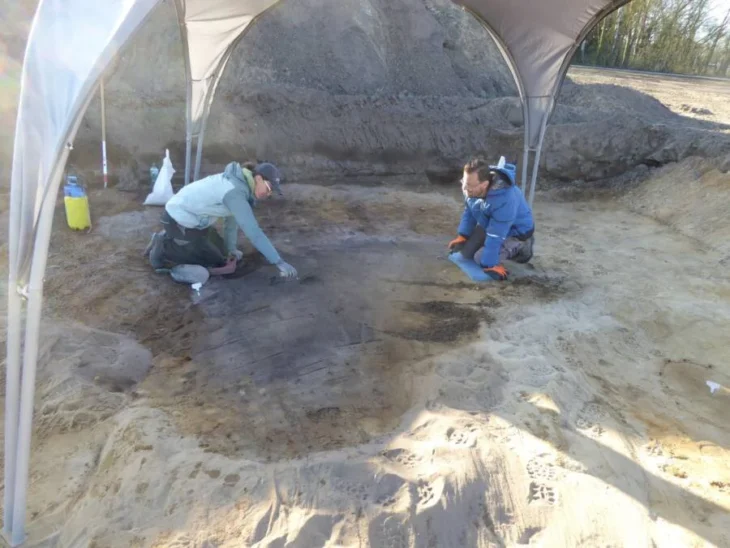
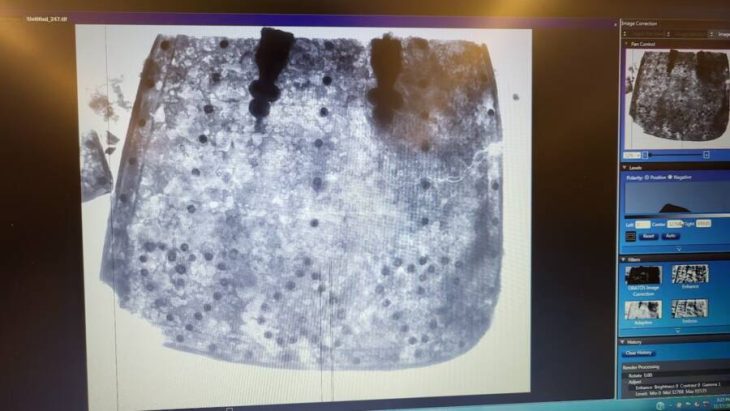
Archaeologists discovered, well-preserved brain and skin remnants of two individuals dating to the Bronze Age during excavations at Tavşanlı Höyük (Tavşanlı Mound) in western Türkiye’s Kütahya province.
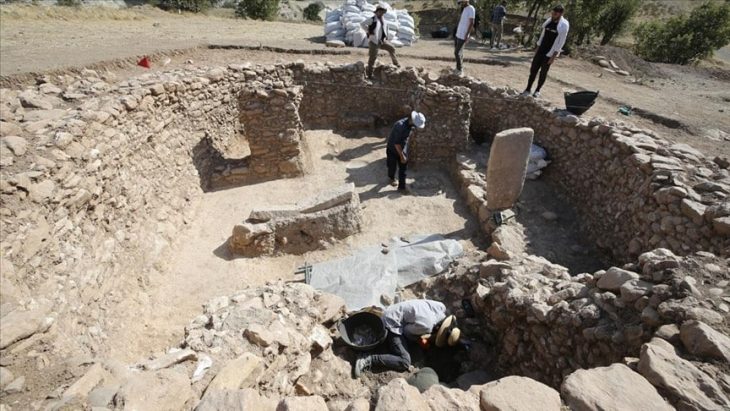
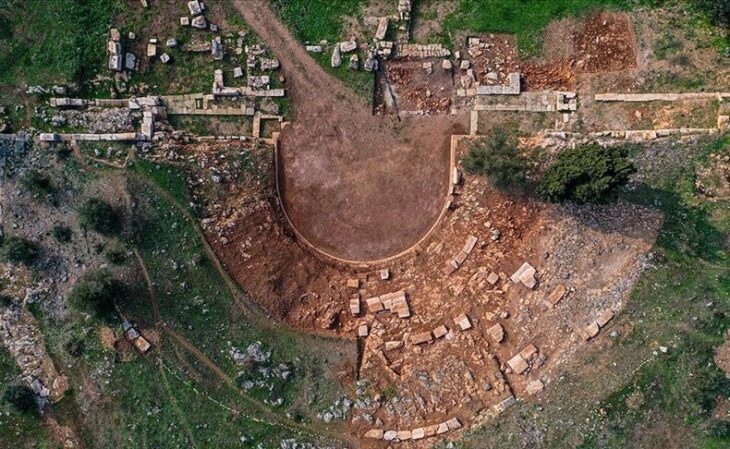
The excavations started in Tavşanlı Höyük, which is called the “Heart of Western Anatolia” because it looks like a heart in aerial shots, and continue in cooperation with the Ministry of Culture and Tourism and Bilecik Şeyh Edebali University.
Since Tavşanlı Höyük is located on the transition route between Western Anatolia and Central Anatolia regions, the studies carried out here are crucial in terms of understanding interregional communication.
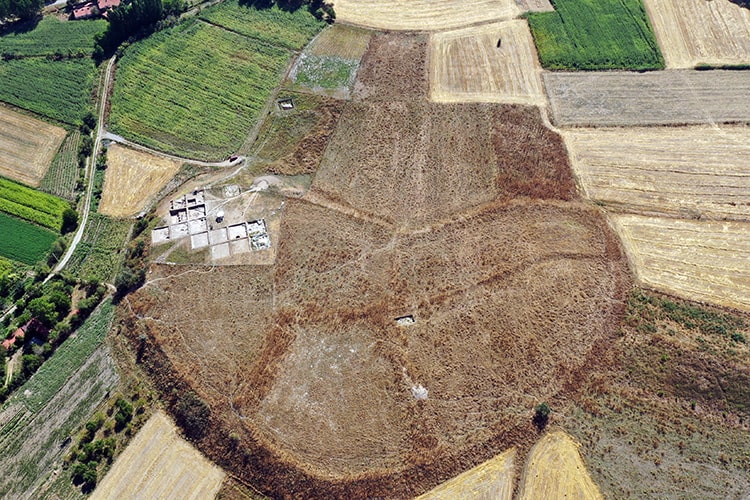
The excavations of the mound, which spans an area of 45 hectares, are carried out by the Archeology Department of Bilecik Şeyh Edebali University. A team of 25 local and foreign experts accompanies the research carried out under the chairmanship of Professor Erkan Fidan.

According to experts, the discovery was noteworthy because it was the first time that skin remains had been found during archaeological excavations in Türkiye, whereas brain remains had only been found four or five times.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
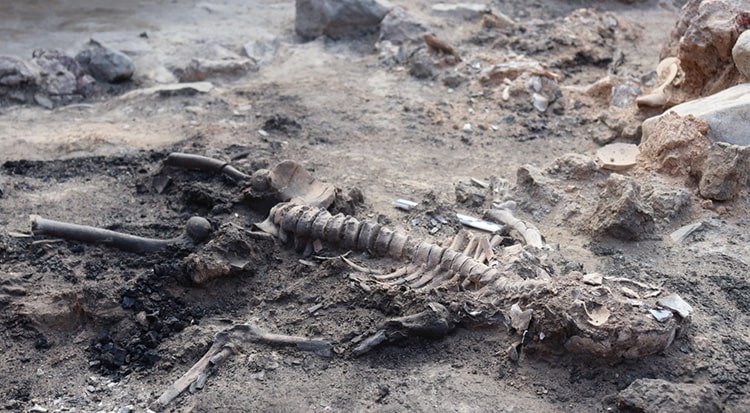
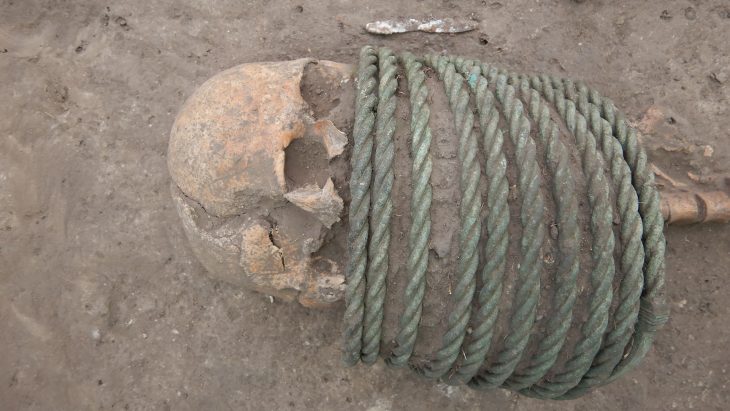
The brain and skin remnants of a young (15-18) and middle-aged man (40-45) were preserved through carbonization, according to Anadolu Agency (AA), adding that experts believe it belonged to two people who were unable to flee their homes after it was set on fire during an attack 3,700 years ago.
The findings were revealed at a conference organized by the European Association of Archaeologists in Belfast, Northern Ireland on Aug. 30-Sept. 2.

Professor Erkan Fidan told the conference that the mound is the oldest settlement in the area and that experts believe it was the capital of the region back in the Bronze Age. He added that they believe there was a large-scale attack on the city in around 1,700 BCE and the whole city was burnt to the ground.
Meanwhile, Professor Yılmaz Selim Erdal from Hacettepe University’s Anthropology Department noted that both skeletons were exposed to high degrees of heat, which allowed the brain to be preserved inside the skull. They also noted that they found skin remnants in one of the skeletons, between the chest and abdomen, also carbonized by heat.
It was emphasized that while there have been very few instances of brain remnants found in excavations conducted in Anatolia, the presence of carbonized human skin is considered “the first and only example found in archaeological periods in Turkey,” making it highly significant.
Experts stated that they will now investigate why the attack was carried out and who carried it out.