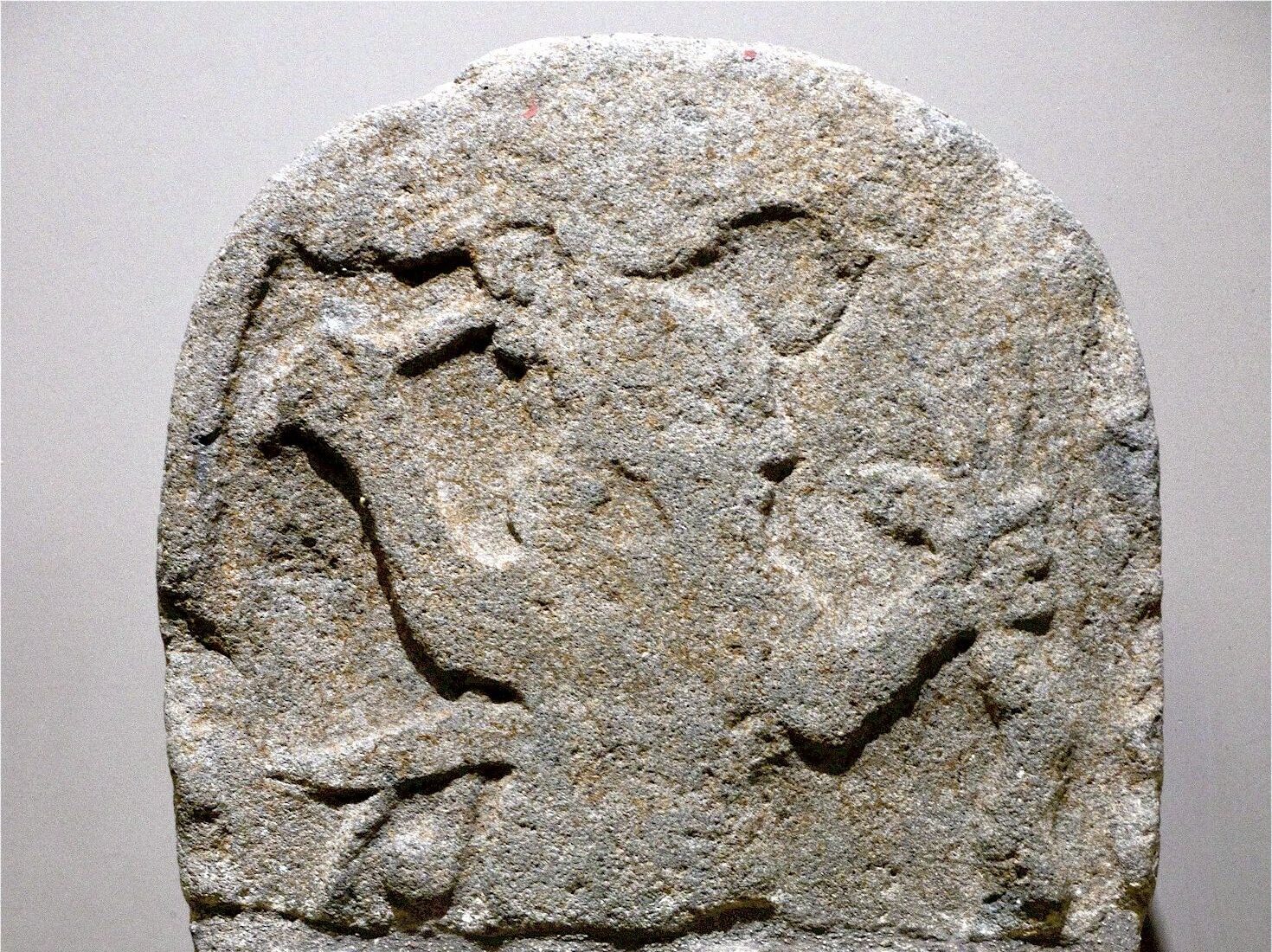
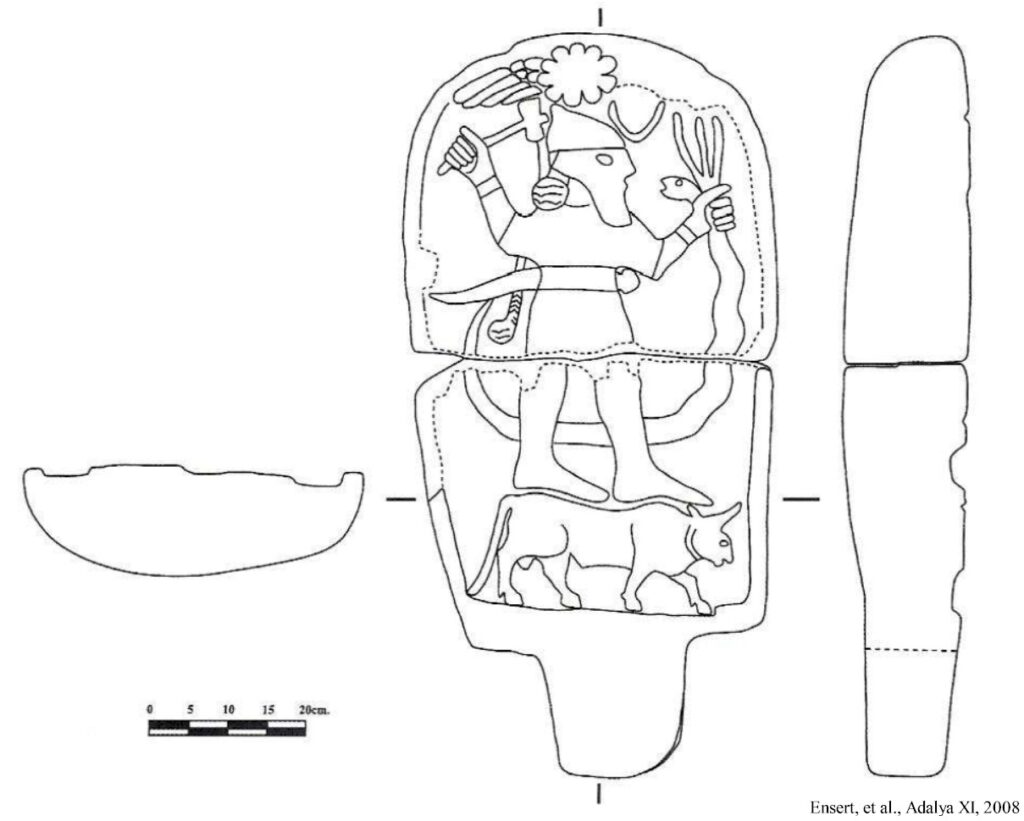
In a significant archaeological discovery, a basalt stele was unearthed in 1987 by O. Günay while plowing his field at the Yurtlak locality, located just a few kilometers west of Erzin in Hatay Province. This remarkable artifact, registered with inventory number 17183 at the Hatay Archaeology Museum, is broken in half but retains its historical and artistic significance, offering valuable insights into ancient mythologies.
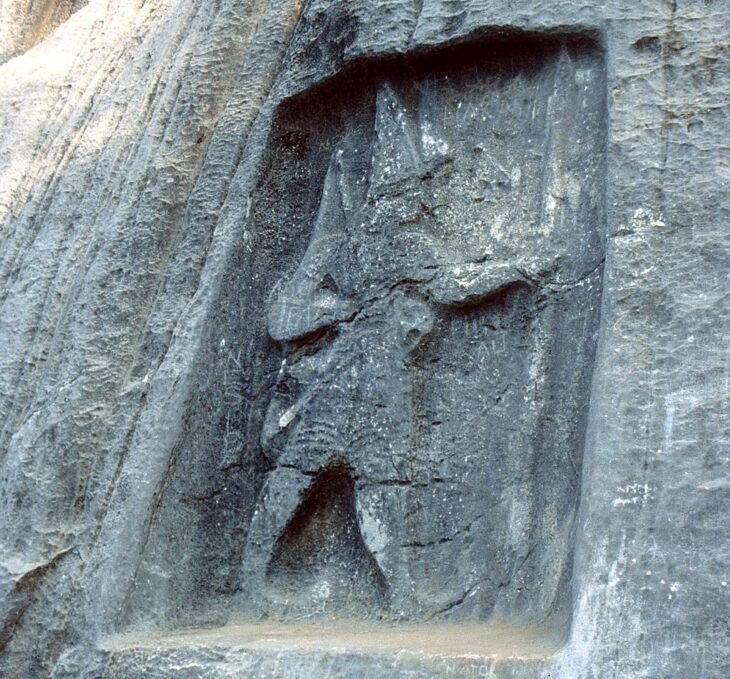
The Erzin stele features a tenon extension at the bottom, indicating that it was originally erected on a base, which adds to its architectural context. When measured with the tenon, it stands at an impressive height of 0.96 meters, with a width of 0.46 meters and a thickness of 0.16 meters. The front face of the stele showcases a highly abraded relief that depicts the Storm God in a typical pose, standing majestically on a bull. In his right hand, he wields a double-headed axe, a symbol of power and authority, while his left hand holds a lightning symbol, representing his divine connection to storms and weather. Uniquely, he also grips a snake by the neck, a departure from traditional representations of the Storm God. The snake’s body curls around the god, its tail rising upwards on the left side, suggesting a dynamic struggle between the two figures.
This scene likely illustrates the Storm God’s battle with a serpent, a motif that resonates with both Anatolian and Syrian mythologies. The struggle between the Storm God and the serpent is a recurring theme in ancient Near Eastern myths, symbolizing the conflict between order and chaos. In the Hurrian myth of Hedammu, for instance, a giant serpent named Hedammu lives in the ocean and is ultimately defeated by the Storm God, who is often associated with fertility and rain. Similarly, the Illuyanka myth from Hatti culture tells of a serpent that the Storm God must overcome, further emphasizing the significance of this motif in the region’s mythology.
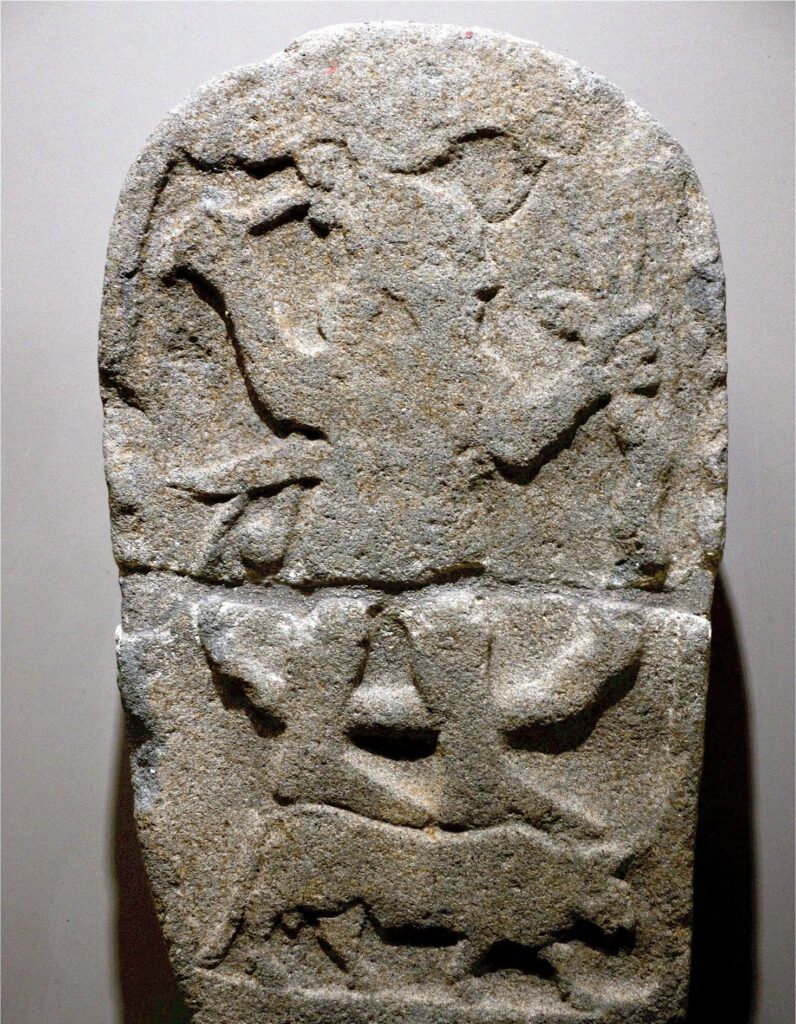

Above the Storm God, a partly damaged winged sun disc symbol can be seen, which further emphasizes his divine status and connection to celestial powers. This iconography is significant as it links the Storm God to solar deities, a common practice in ancient cultures where gods often embodied multiple aspects of nature. The presence of the winged sun disc also suggests a possible connection to later Greek mythology, where similar motifs appear, particularly in the representation of gods like Helios and Apollo.
Experts have dated the stele to sometime between the 9th and 8th centuries BCE, placing it within a significant period of ancient history characterized by the flourishing of Hittite culture and its interactions with neighboring civilizations. The Hittites were known for their rich mythology and complex pantheon of gods, and this stele serves as a valuable artifact that sheds light on their beliefs and artistic expressions. The transition of mythological themes from Hittite to Greek culture is particularly noteworthy, as it illustrates the cultural exchanges that occurred in the region over centuries.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The discovery of the Erzin stele highlights the importance of archaeological research in uncovering the rich tapestry of human history. Each artifact tells a story, and the stele is no exception. It invites us to ponder the beliefs, struggles, and artistic achievements of those who came before us, reminding us of the enduring legacy of ancient cultures. As scholars and enthusiasts alike delve deeper into the significance of such finds, we are continually reminded of the interconnectedness of human experience across time and space.
The Erzin stele stands as a bridge between the past and the present, encouraging us to reflect on our own narratives and the myths that shape our understanding of the world today. The ongoing study of artifacts like the Erzin stele not only enhances our knowledge of ancient societies but also inspires a sense of wonder about the complexities of human belief and creativity throughout history. As we explore the connections between Hittite and Greek mythologies, we gain a deeper appreciation for the ways in which ancient peoples understood their world and the divine forces that influenced their lives.
In conclusion, the Erzin stele is not merely an artifact; it is a testament to the rich mythological traditions of the ancient Near East and their lasting impact on subsequent cultures, including the Greeks. The themes of struggle, power, and divine intervention depicted in this stele resonate through time, reminding us of the universal human experience of grappling with the forces of nature and the unknown. As we continue to uncover and study such artifacts, we enrich our understanding of the past and its relevance to our present and future.
Source: ENSERT, H., Görmüş, A., & Kara, D. (2008). The Stele of Erzin. Adalya, (11).
Cover Image Credit: Kübra Ensert, et al., 2008.