A 2,300-year-old Punic tomb was discovered during work in a car park near Mater Dei Hospital in Msida, Malta.
The archaeological discovery was made during trenching works near Mater Dei Hospital while preparing the site for the installation of a new potable water line.
The Superintendence of Cultural Heritage (SCH) has been overseeing the site since the start of the project, ensuring the protection and study of any potential discoveries during development works.
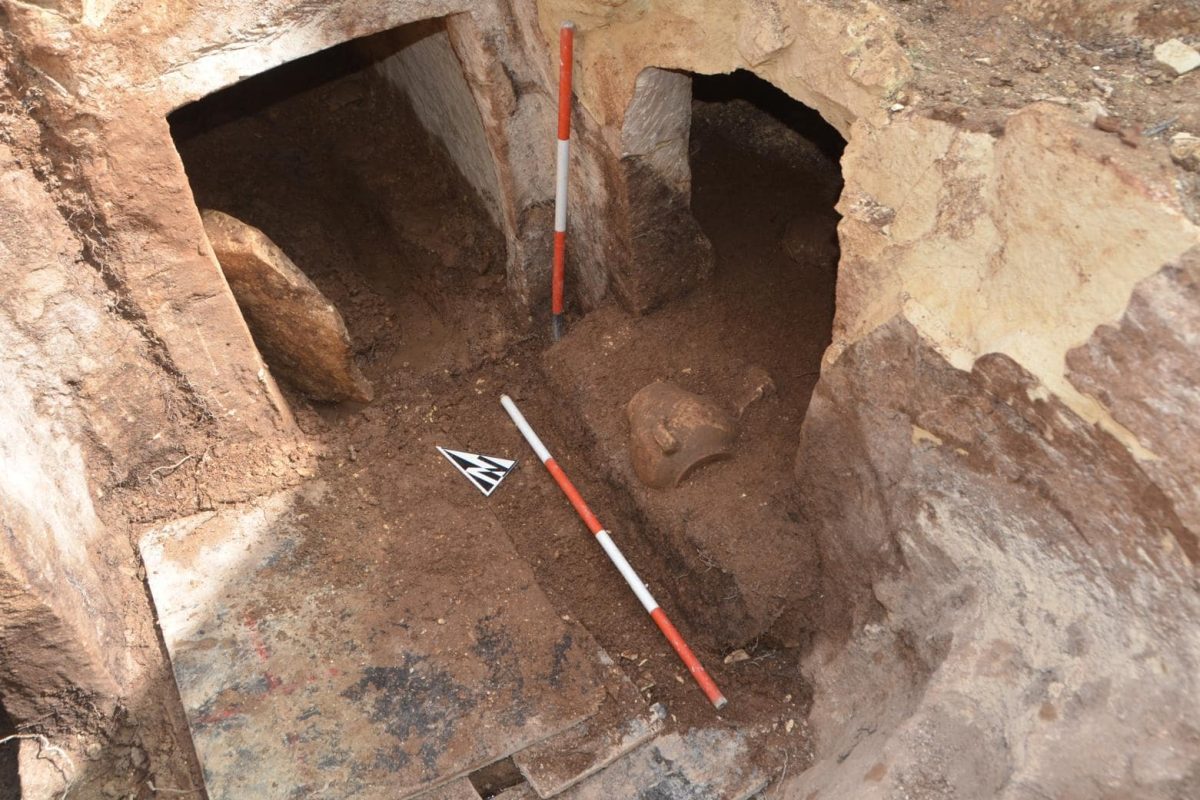
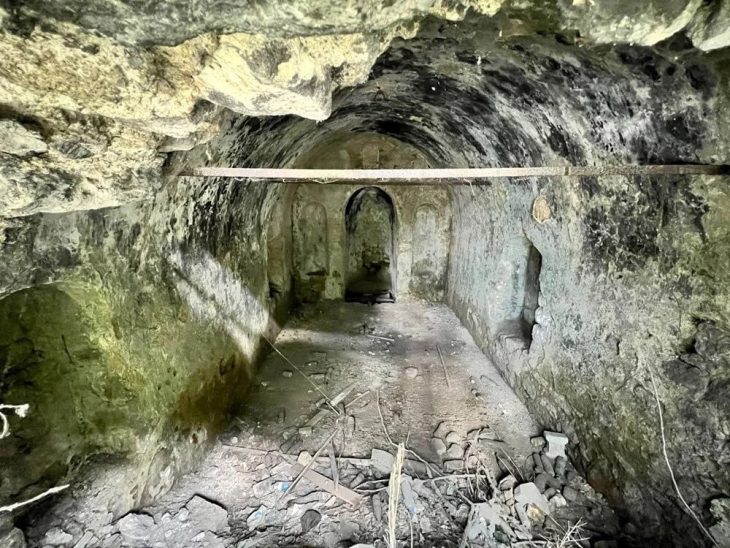
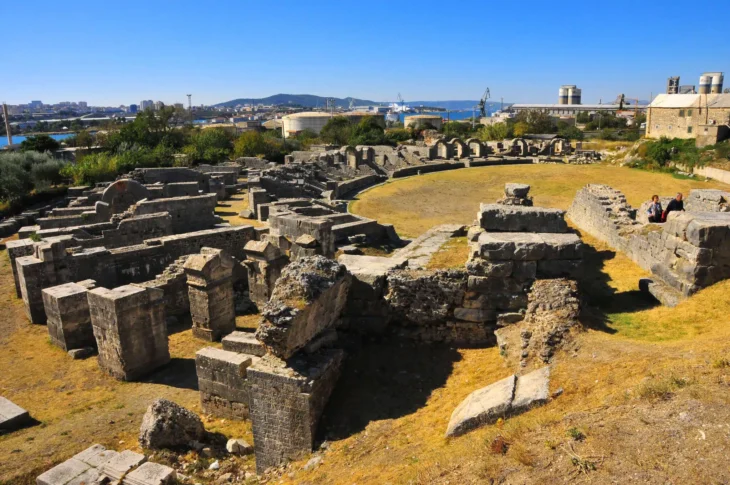
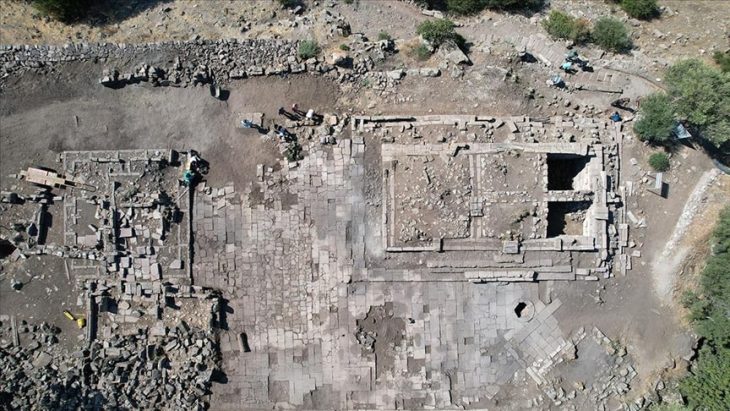
An excavation revealed a chamber hewn out of solid natural rock. After additional examination by the SCH’s on-site archaeology monitors, it was found that the chamber was a component of a larger burial complex.
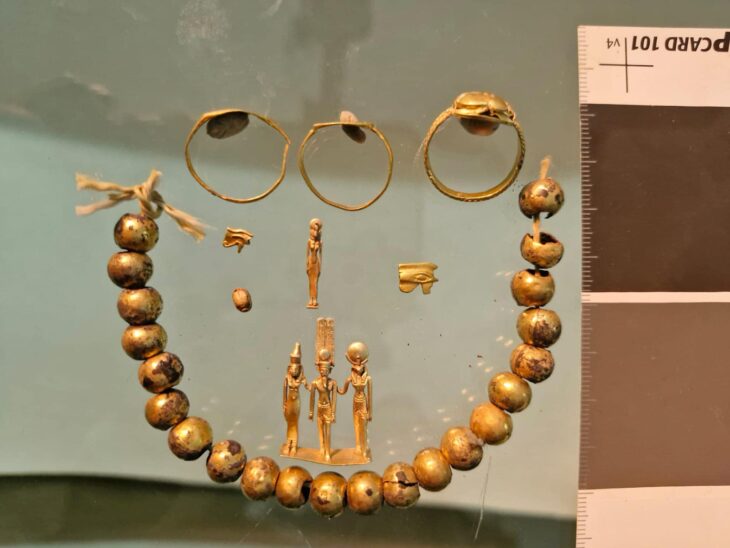
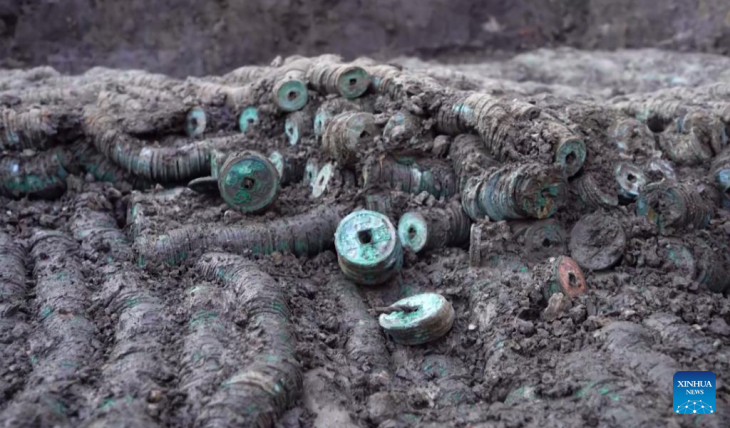
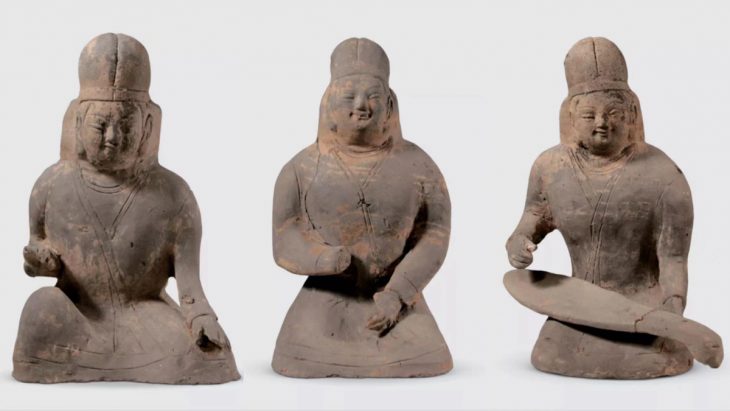
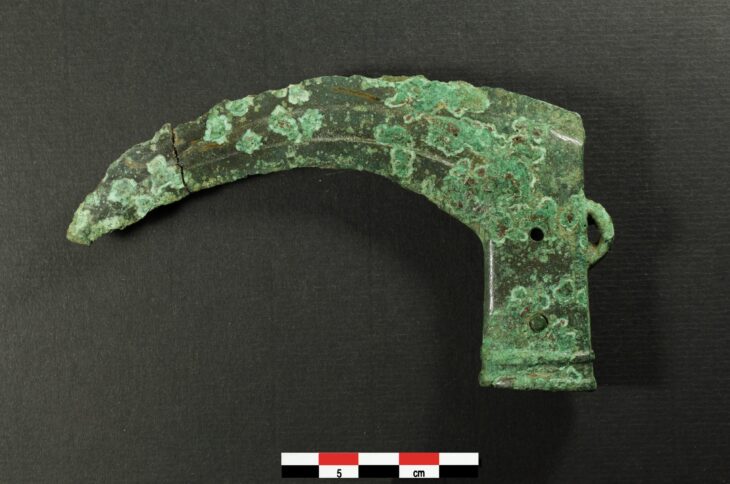
The discovery consists of three burial chambers, each accessed through a central shaft, characteristic of Punic and Roman tombs. It is thought to have been used for multiple inhumations during the Punic and Roman periods. Remarkably, the entrance to each chamber was sealed with original slabs, and the contents inside included human remains and grave goods.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
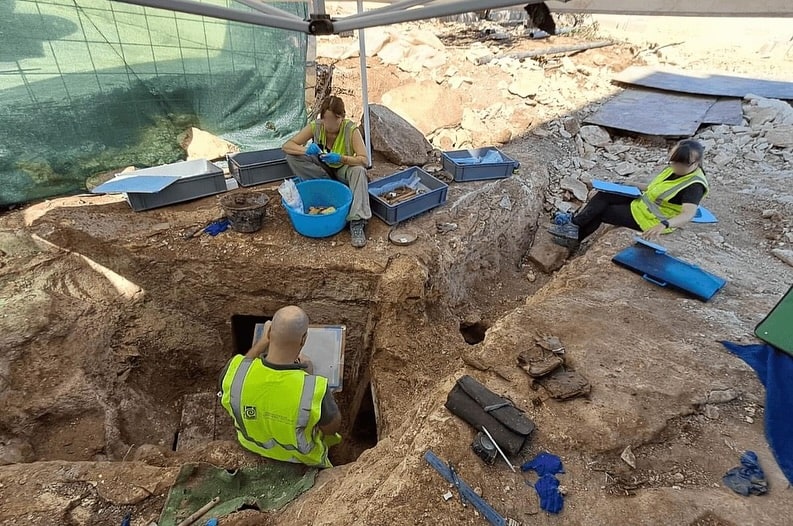

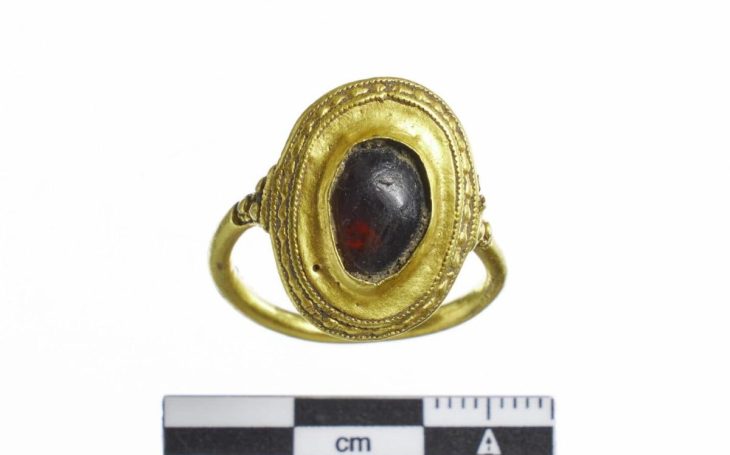
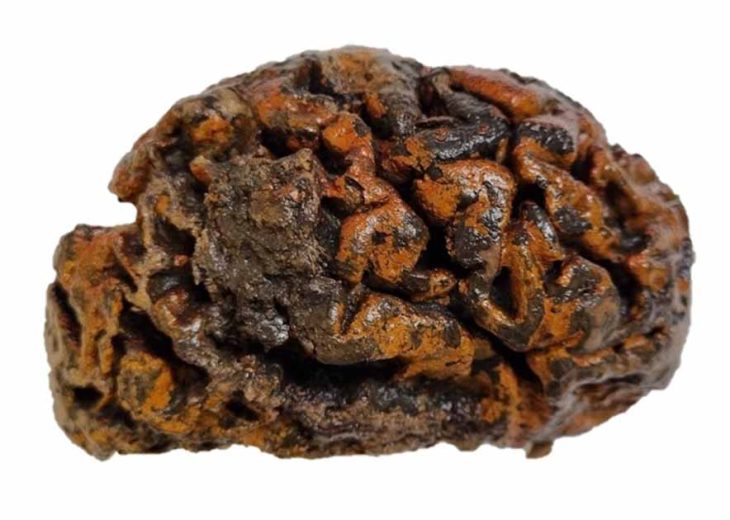
The burial chambers were meticulously excavated over two weeks by a committed team of SCH archaeologists and osteologists. The human remains were primarily inhumations, with some cremated remains stored in urns. The fact that many of the bones were arranged in a methodical manner raises the possibility that earlier remains were moved to make room for later burials. There were several inhumations in each chamber, with at least six in Chambers 2 and 3 and at least two in Chamber 1. A small collection of grave goods and cremation urns were also discovered, offering important new information about the burial customs of the time.
A team of experts, has been working on site to excavate, document, and interpret the remains, some of which have been transferred to the laboratory of the superintendence for further analysis.
Researchers will examine the remains for evidence of the age, sex, and health of the individuals, and conduct DNA analysis.
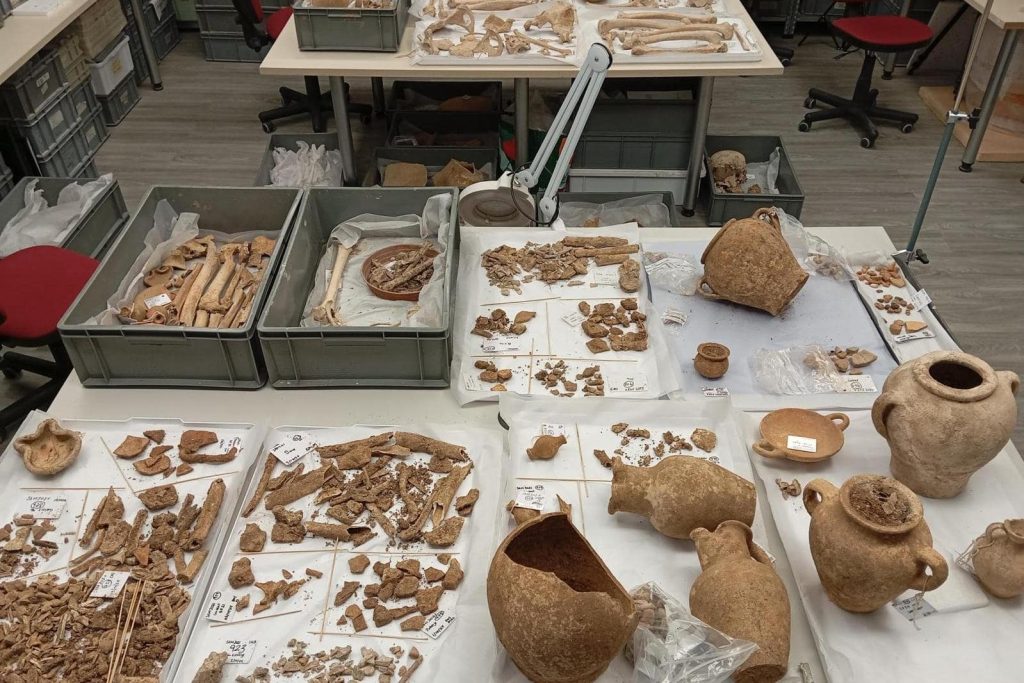

“The findings, which include skeletal remains, cremation urns, and other funerary artifacts, provide valuable insight into the ancient community that once inhabited the region. Preliminary analysis indicates a Punic timeline, although some artifacts suggest an extended period of use into the early Roman era,” the Foundation for Medical Services and SCH said.
Efforts are underway to ensure the tomb is retained in its entirety, with plans for permanent controlled access to allow for continued study and preservation of this significant archaeological site.
Foundation for Medical Services and SCH
Cover Photo: Foundation for Medical Services