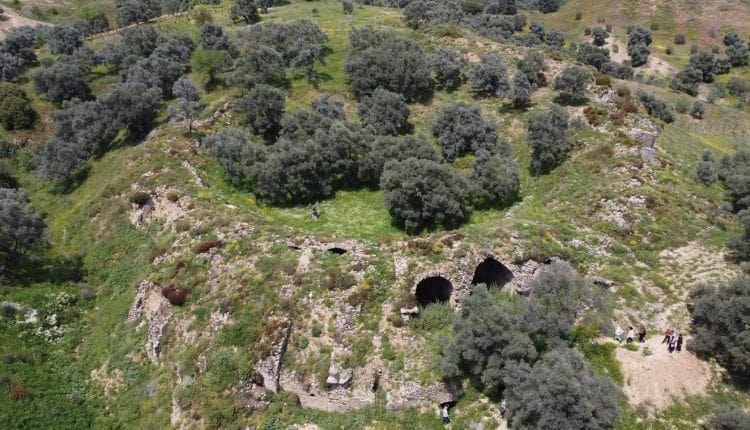
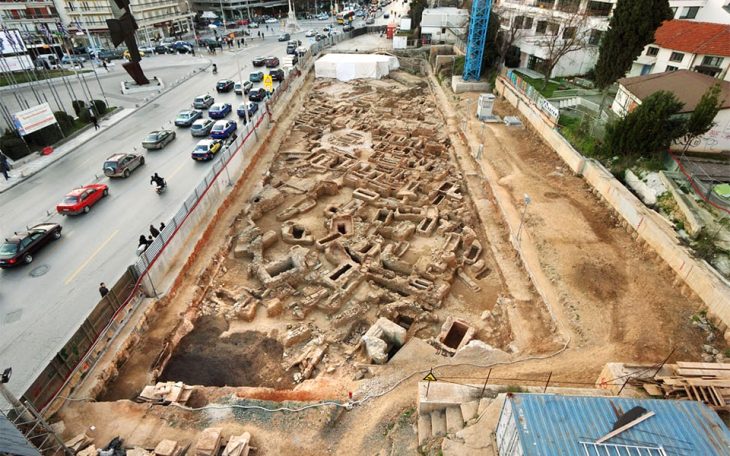
Archaeologists found an 1800-year-old sewer system during excavations in the ancient city of Mastaura, in the Nazilli district of Aydın province in western Turkey.
Researchers have been working on the site, located inside a narrow valley and some 3 kilometers north of Nazilli, for the past two years. The ancient city spans an area of some 160,000 square meters.
“The size of the structure is amazing. A person can easily walk through the system, which spreads all over the ancient city. It appears to represent an early example of municipality work,” said Umut Tuncer, provincial director of culture.
The head of the excavations, Sedat Akkurnaz, a member of the archaeology department at Aydın Adnan Menderes University said in ancient times, a river ran through Mastaura and people settled on both sides of the waterway.
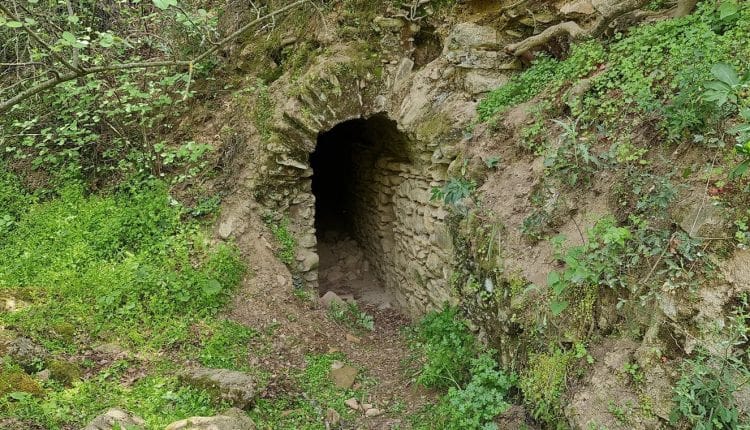

“What we see here is the sewer system built underground. The engineering technique and materials used in the structure suggest that the construction work started sometime around 200 B.C., and the sewer system was in use throughout the ancient period during the Roman Empire era,” Akkurnaz explained.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
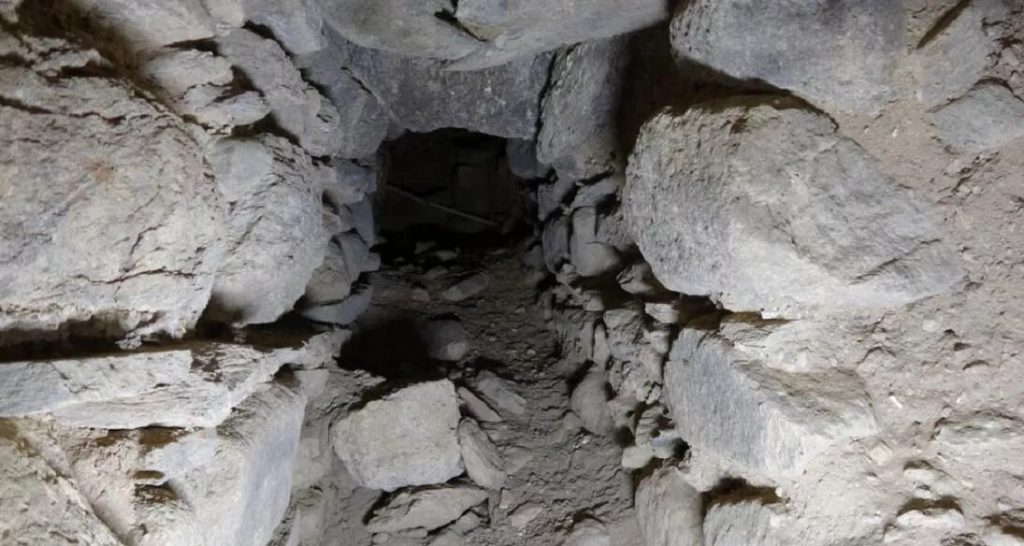
“We can only go some 20 meters into the sewer because there are cave-ins inside the structure blocking the path.”
About 2 years ago, a structure similar to the Colosseum in Rome, which is considered the best example of Roman architecture in the world, was unearthed in the 2,700-year-old ancient city of Mastaura.

Inspired by the notes of European travelers who traveled in the region about 200 years ago, archaeologists discovered the only example of the Colosseum in Rome. There are seven to eight similar examples in Anatolia but they have not survived until today.
The Mastaura ancient city was on the route of commercial places and had the privilege of minting money. Strabon mentioned about Mastaura as well as Orthosia. It was the episcopal centre during Christianity Period and it participated to Ephesos and Khalkedon councils. Some monuments and coins were found in the region that is called “Mastavra Castle” among public.