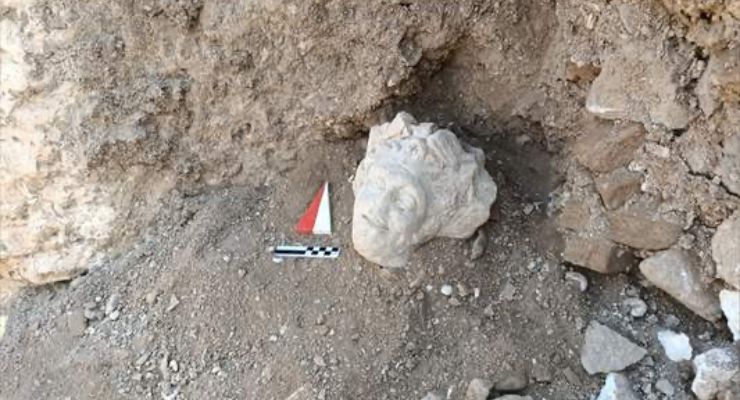
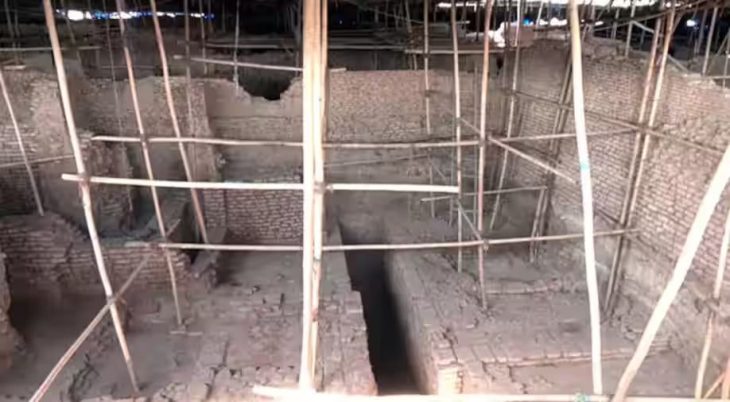
A statue head dated to the 2nd century AD was unearthed during the excavations at the Ancient Smyrna Theater, located on the slope between Izmir, Kadifekale, and the Smyrna Agora.
The Turkish Culture and Tourism Ministry’s Department of Excavations announced on Twitter that a head of a statue dating to the 2nd century AD had been discovered.
It also shared a 33-second video showing the process of unearthing the ancient statue.
During the excavations of İzmir Katip Çelebi University, a statue head with human head measurements was found in the area called ‘Eastern Vomitorium’. It was determined that the head of the statue symbolizes the mythological being Satyros (Satyr) and was made in the 2nd century AD.
During the Hellenistic Period, Smyrna was relocated to its present position after outgrowing its first colony in Bayraklı. Rapidly developing into a trading hub, the town reached its highlight during the Roman Empire. By the second century CE, Smyrna had grown into a large Roman metropolis that stretched from Kadifekale to Konak, from Eşrefpaşa to Halkapınar, whose ruins can still be seen today in the Konak district’s Çankaya area.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Smyrna according to the geographer Strabo “It is the most beautiful of all cities.” Smyrna owed its charm to its architectural structures and city plan.

It gets its share of these praises in the ancient theater. The first information about the Smyrna Theater can be found in Vitruvius’ De Architectura. Vitruvius (V.IX.1) notes that there was a portico called Stratonikeion adjacent to or in the immediate vicinity of the skene (scene) building of the Smyrna Theatre. He praises the fact that such a portico was planned around the theater and shows it as an example for other cities.
The theater, which was built on the northern slope of Pagos (Kadifekale) hill, has a position to watch İzmir Bay and Smyrna from an angle that can be called visually perfect. It is not known when the theater was built for the first time. It is possible that it was built in the 1st century BC, probably because it was the subject of the writings of Vitruvius. The theater was repaired during the reign of Emperor Claudius, possibly after an earthquake during the Roman imperial period, but it is thought that it took its final form with the repairs and additions made after the earthquake in 178 AD.