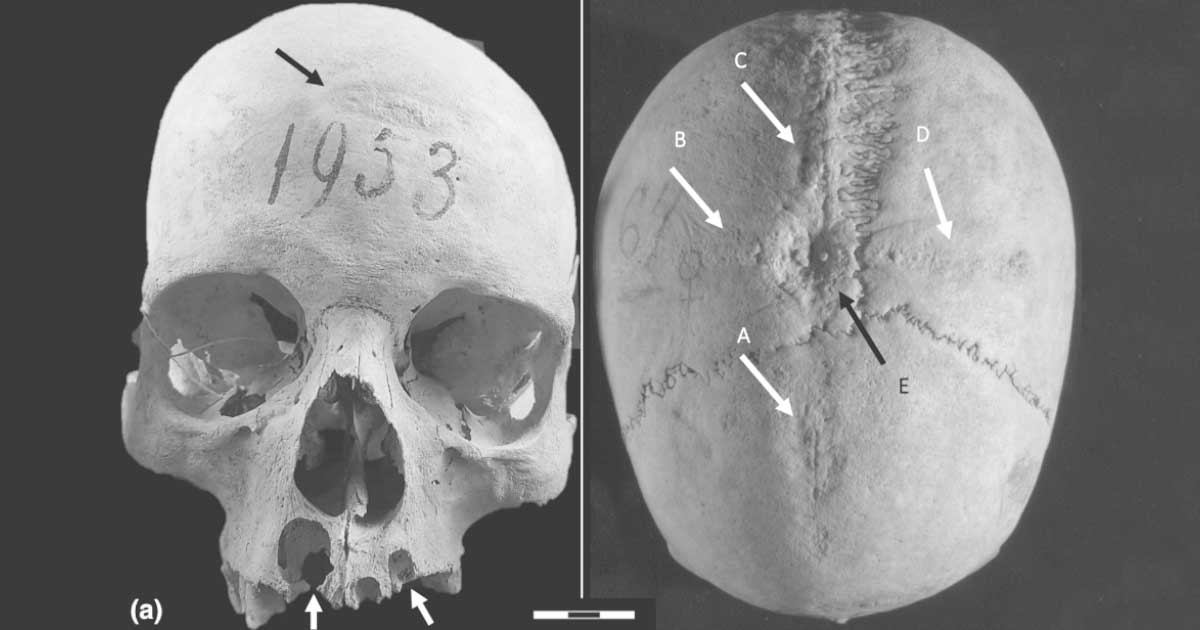
A detailed examination of the skull of a woman who lived at the medieval settlement of Castel Trosino in central Italy more than 1,300 years ago revealed that this middle-aged woman had undergone not once, but at least twice, invasive surgical procedures.
Macroscopic, microscopic, and computed tomography analyses of a skull found near Ascoli Piceno revealed signs of at least two surgical operations.
The study, published in the International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, was carried out by an international and multidisciplinary team coordinated by Sapienza University in Rome.
A new international study, coordinated by Sapienza in collaboration with Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore in Milan, the McDonald Institute for Archaeological Research in Cambridge, the Universities of Aix-Marseille and Caen in France and University of Washington, reveals the existence of drillings in the skull of a Longobard woman, found in the cemetery of Castel Trosino, near Ascoli Piceno, central Italy.
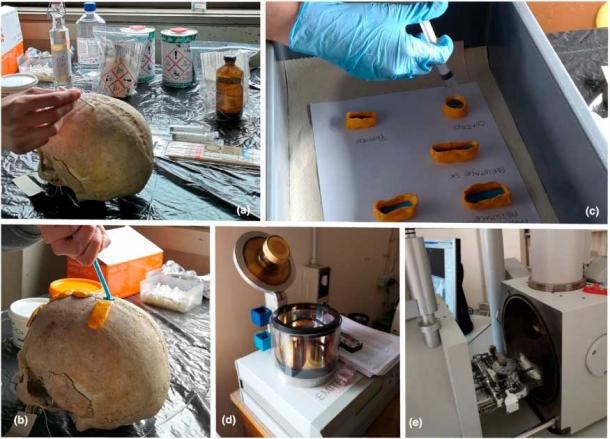
Macroscopic, microscopic and computed tomography (CT) analyses revealed signs of at least two operations performed on the skull, including a cross-shaped surgery, shortly before the woman’s death. Furthermore, thanks to a new high-resolution biochemical investigation method applied to one of the preserved teeth, specific changes in the woman’s diet and mobility from early life to adulthood were reconstructed. This allowed the researchers to identify changes in her diet and environment throughout her life and to highlight the care and interest provided to her by the community.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“We found,” says Ileana Micarelli of the University of Cambridge, a former postdoctoral fellow at Sapienza and first author of the study, “that the woman had survived several surgeries, having undergone long-term surgical therapy, which consisted of a series of successive drillings.”

“The last surgery”, concludes Giorgio Manzi of the Department of Environmental Biology, “appears to have taken place shortly before the individual’s death. There are no lesions suggesting the presence of trauma, tumours, congenital diseases or other pathologies. Moreover, although it is intriguing to consider the possibility of a ritual or judicial motive, no osteological or historical evidence supports such hypotheses.”
The specific surgical techniques used involved the scraping of bone from the cranium as part of trepanation, a medical treatment. This type of treatment was discussed in European medieval literature, and some records date back even further. However, this is the first time that scientists have been able to prove that an Early Medieval skull was subjected to these dangerous procedures.
The discovery of the rare evidence of a drilling operation paves the way for future studies on the reasons and methods of treatment, as well as the caring role of the community towards the sick during the Middle Ages.
The medieval cemetery at Castel Trosino, known as the Longobard Necropolis, was first excavated in the nineteenth century. Only 19 skulls were discovered in good enough condition to be examined. Archaeologists, anthropologists, and other researchers have continued to examine these Early Medieval Period remain in order to learn as much as they can about the health, physical characteristics, and lifestyles of the people who lived in central Italy between 568 and 774 AD when the necropolis was in use.