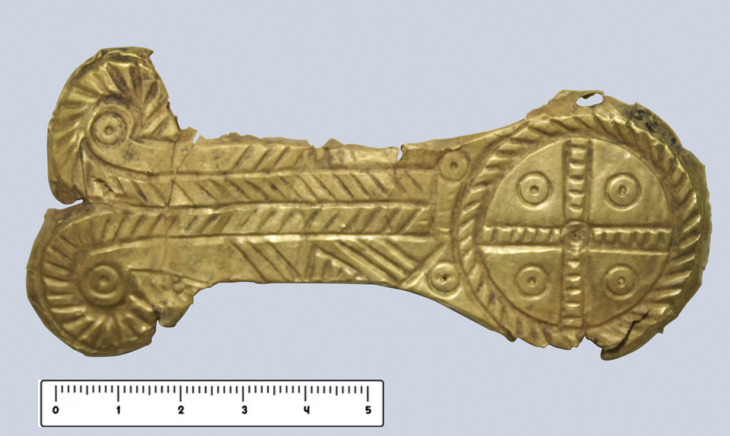
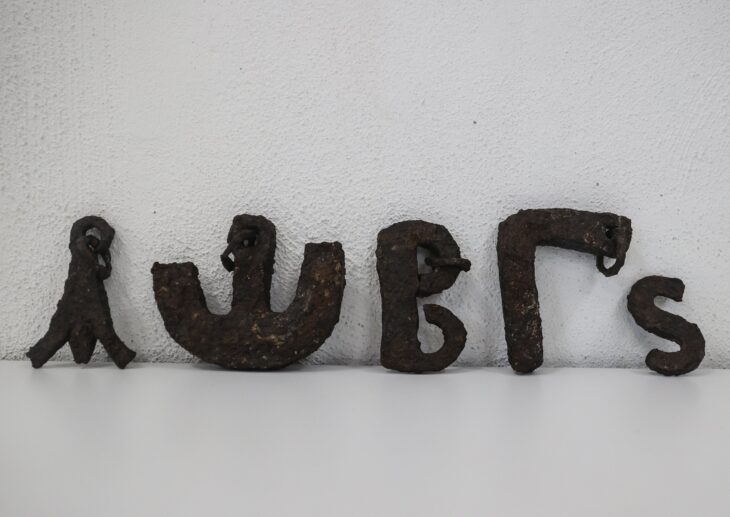Archaeologists uncover a luxurious Roman domus and a one-of-a-kind bronze box in the civilian quarter of Legio V Macedonica at Potaissa, modern-day Turda, Romania.
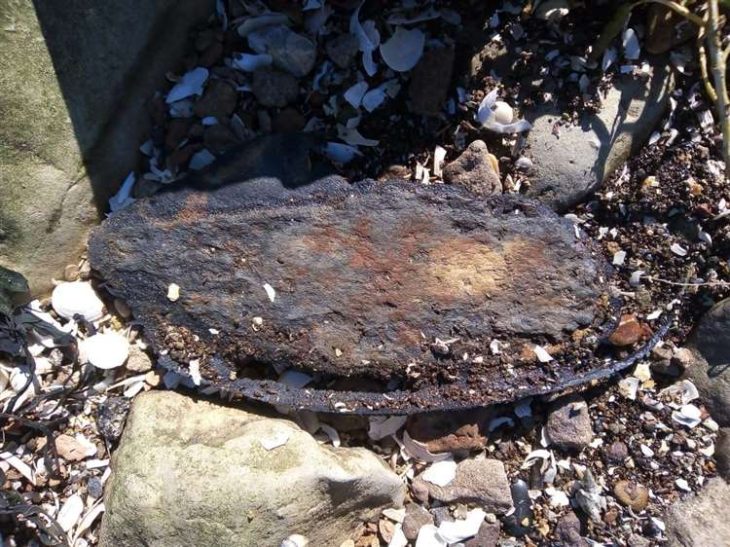
A recent archaeological campaign in Turda, in Romania’s Transylvania region, has brought to light one of the most remarkable Roman finds ever recorded in the former province of Dacia: an exceptionally preserved bronze box adorned with the façade of a temple. The discovery, described as unique in Roman Dacia, emerged from the canabae — the civilian district that once thrived beside the fortress of the Legio V Macedonica.
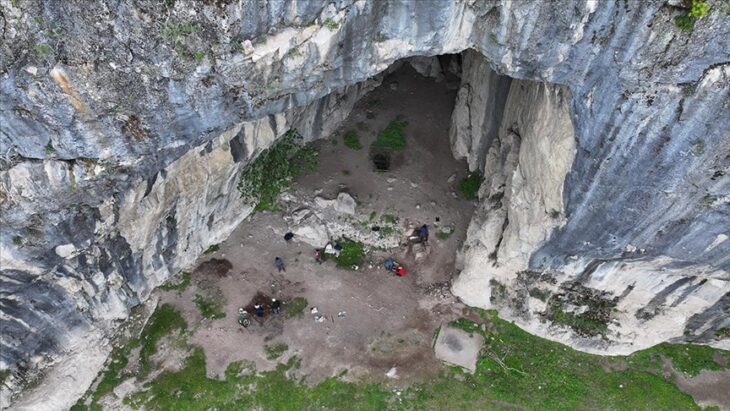
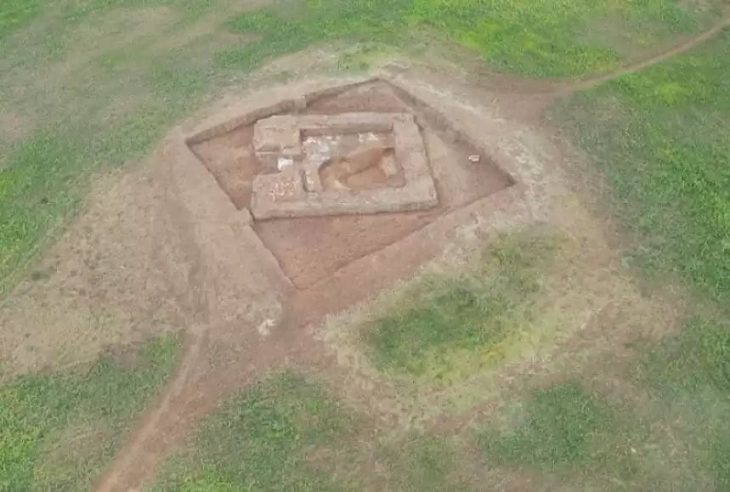
The five-week excavation, conducted jointly by the Turda History Museum, Babeș-Bolyai University, the University of Medicine, Pharmacy, Science and Technology (UMFST), and the National Museum of the History of Transylvania (MNIT), focused on the ruins of a large Roman domus. The team’s trenching revealed the foundations, portico, and associated domestic structures of what was once a refined residence belonging to a wealthy inhabitant of the settlement.
An exceptional archaeological discovery
The bronze box or casket, meticulously decorated and fully intact, stands out as the highlight of this year’s excavation. Its relief shows the front of a Roman temple, complete with columns and a triangular pediment — a motif deeply rooted in imperial religious iconography. According to the archaeologists, no similar artifact has ever been recovered from the territory of ancient Dacia.
Its craftsmanship and state of preservation make it an extraordinary artifact, offering a glimpse into the intersection of faith and artistry in provincial Roman society. Researchers believe the box likely served a ritual or religious purpose, possibly as a container for offerings, incense, or sacred tokens. The level of workmanship suggests it belonged to a person of status, perhaps connected to the temple cults or priestly circles that operated near the legionary fortress.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
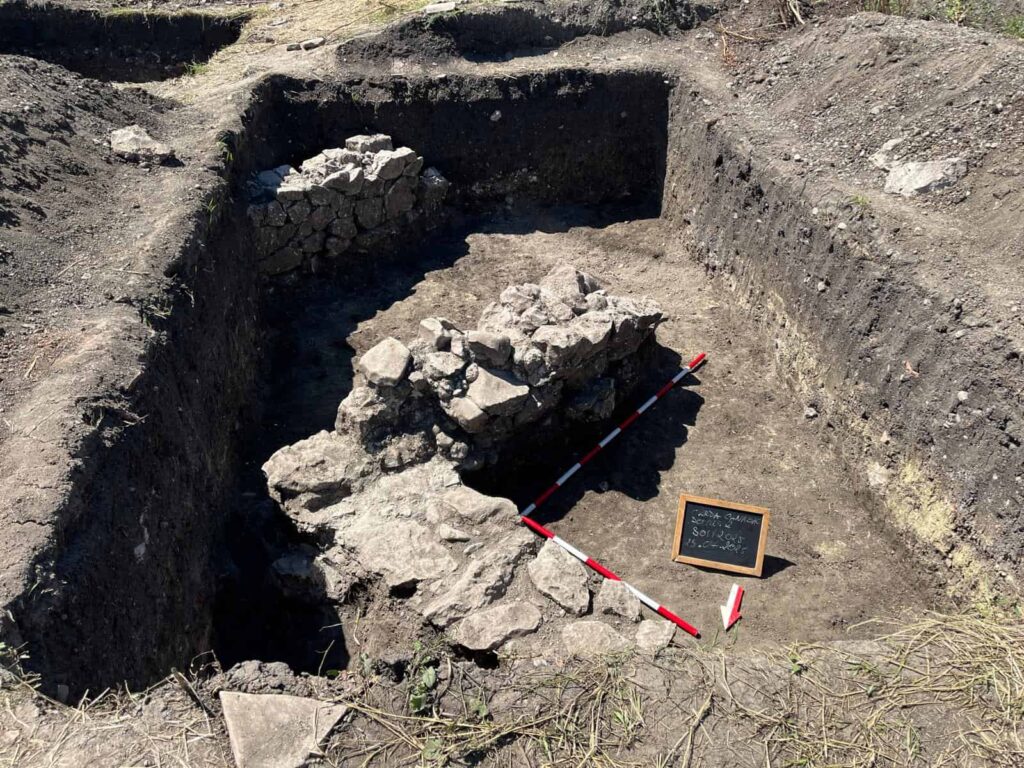

Treasures from daily life
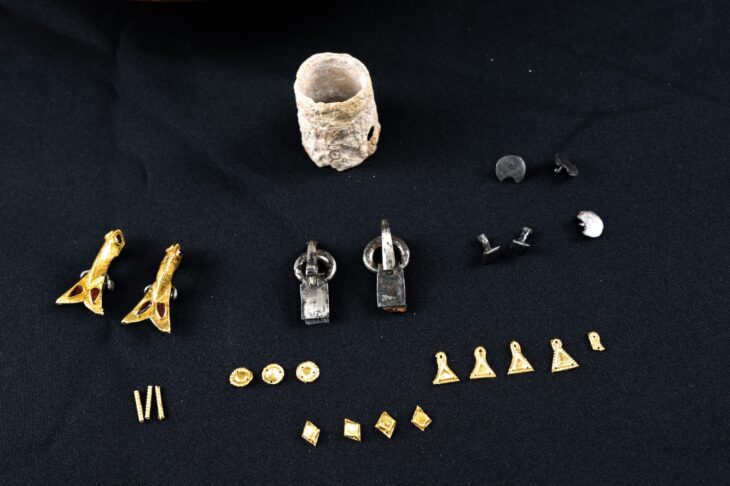
In addition to the bronze casket, the excavation produced an abundant collection of artifacts that shed light on the domestic and spiritual life of the inhabitants of the canabae. Among them were bronze jewelry, glass beads, and a bronze ring, as well as bone hairpins, belt fittings, and furniture elements such as a tripod leg with zoomorphic decoration — an elegant symbol of the household’s artistic refinement.
A small but significant group of Roman coins adds an economic dimension to the discovery, helping to date the occupation of the house to the late 2nd and early 3rd centuries CE, a period of stability following the Marcomannic Wars. The recovered objects collectively portray a vibrant community living in the shadow of a military fortress but thriving in its own cultural and economic rhythms.
The Roman world of Potaissa
The ancient site of Potaissa, today the town of Turda in Cluj County, was a major stronghold of the Legio V Macedonica, one of the Empire’s elite units stationed along the Danubian frontier. The fortress was erected around AD 168, during the reign of Emperor Marcus Aurelius, and covered an area of over 23 hectares. Its geometric plan — a massive rectangle with gates, barracks, and administrative buildings — symbolized Rome’s military order in the region.
Surrounding this stronghold developed the canabae, the civilian settlement where families, artisans, traders, and former soldiers built homes and businesses. Archaeological evidence shows that the canabae of Potaissa contained residences (domus), workshops, storehouses (horrea), and paved streets, forming a bustling town that mirrored Roman urban life far from Italy.
The recently uncovered domus fits neatly into this picture of prosperity. Its architectural features — including a columned portico and multiple rooms with ovens whose functions remain under analysis — suggest a comfortable urban dwelling, possibly owned by a merchant or retired officer. The presence of luxury objects within it underlines the wealth that circulated through the frontier provinces of the Roman Empire.
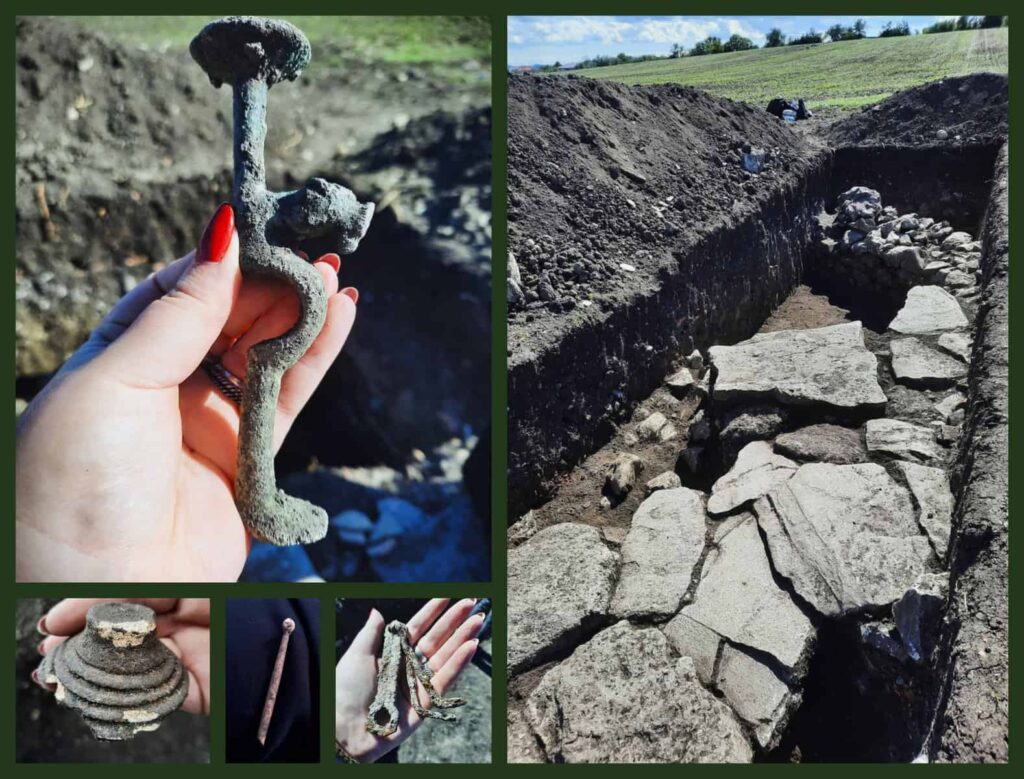

Symbolism and significance
Experts note that the temple façade on the bronze box might not have been a mere decorative motif. It could have symbolized the protection of the gods over the household, or perhaps referenced an actual sanctuary located nearby. The Legio V Macedonica, originally stationed in Moesia before moving to Dacia, was known to have supported imperial cult worship and local syncretic deities — a fusion of Roman and Dacian beliefs that this artifact may reflect.
Such a discovery enriches not only the archaeological record of Turda but also our understanding of how religion permeated daily life in Roman provincial towns. The artifact bridges the gap between military discipline and spiritual devotion, between Roman authority and local identity — a perfect example of cultural hybridity on the empire’s northern frontier.
Continuing excavations
The 2025 excavation campaign marks a new phase in the long-term research of the Potaissa complex. With only a fraction of the civilian district explored so far, archaeologists believe that future work could reveal additional houses, workshops, and possibly a small temple or sanctuary related to the newly discovered bronze box.
The ongoing project, supported by the Romanian Ministry of Culture, aims to create a comprehensive archaeological map of Turda’s Roman layer, documenting how the civilian and military populations coexisted and interacted over time.
“Each artifact we recover — from a coin to a piece of jewelry — tells part of the story of life under Roman rule,” said representatives of the Turda History Museum. “But this bronze box is something else entirely: a personal treasure, an object that connects faith, art, and identity in a single form.”
Facultatea de Științe și Litere “Petru Maior” UMFST
Cover Image Credit: Facultatea de Științe și Litere “Petru Maior” UMFST