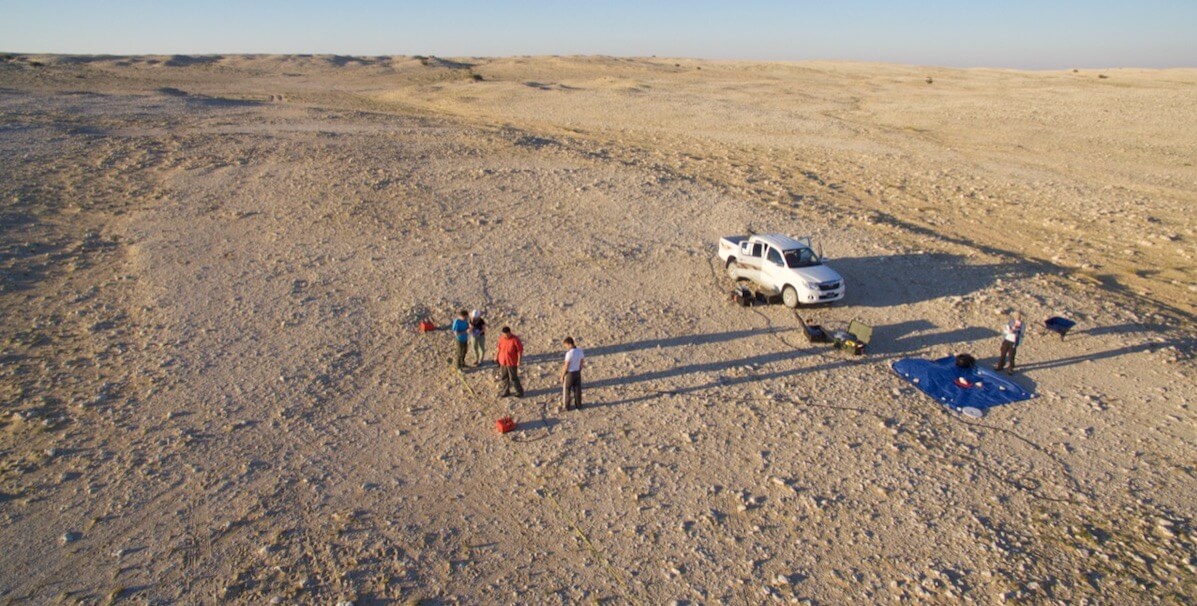
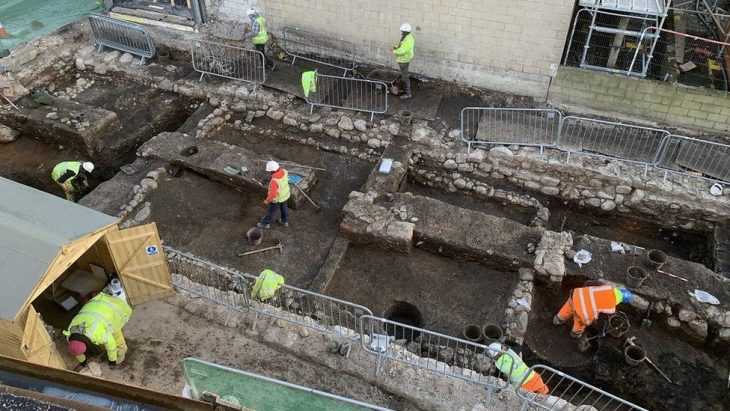
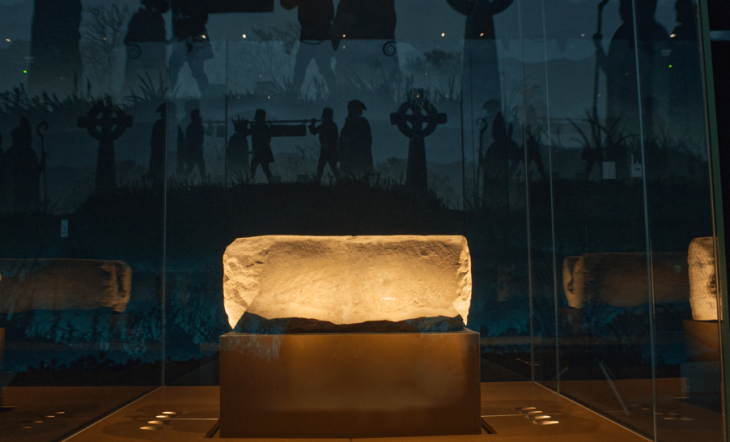
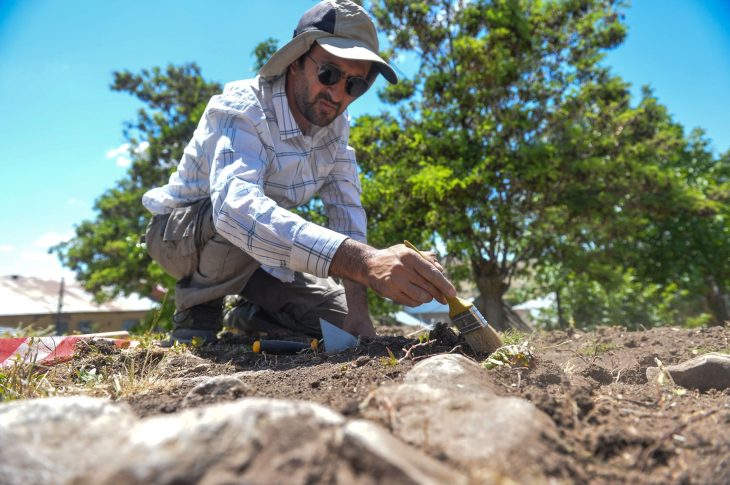
Researchers looking for underground water sources on the Eastern Arabian Peninsula have accidentally uncovered the outlines of a settlement that appears to be over 3600 years old.
According to a statement released by the University of Southern California, researchers led by Essam Heggy discovered traces of an ancient structure while looking for underground water in Qatar with advanced radar satellite images.
The researchers were working on a project funded by the United States Agency for Relief and International Development.
It had been previously thought that people who lived on the eastern Arabian Peninsula were entirely nomadic at this time.
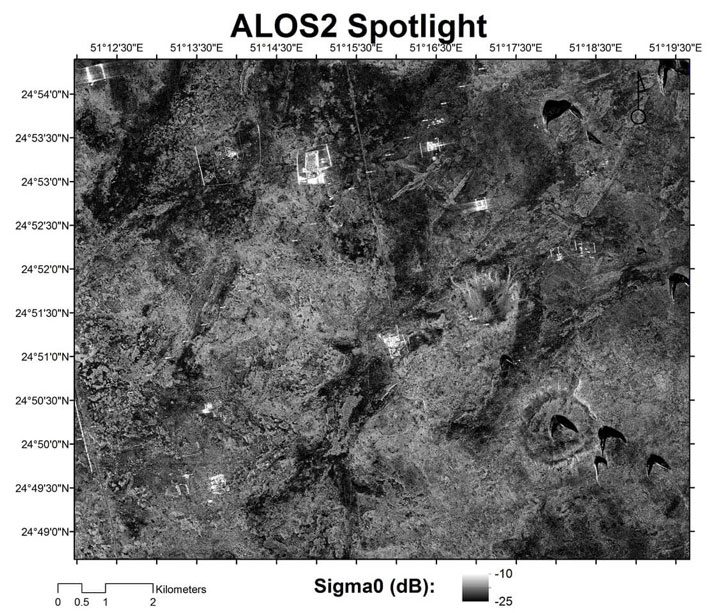
A symmetrical 2 x 3 kilometer, landscaped area—or trace outlines of a settlement (and one of the largest potential settlements uncovered in the area) was identified using advanced radar satellite images in an area of Qatar where there was previously thought to be little evidence of sedentary, ancient civilizations.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Their new study, published in the ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, counters the narrative that this peninsula was entirely nomadic and evidence mapped from space indicates that the population appears to have had a sophisticated understanding of how to use groundwater.
The name “Makhfia,” given to the settlement by researchers at the University of Southern California Viterbi School of Engineering and NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (and referring to an invisible location in the local Arabic language), was discovered using L-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar images from the Japanese satellite ALOS 1 and specially acquired, high-resolution radar images from its successor, ALOS 2.
While the settlement was not visible from space using normal satellite imaging tools nor through surface observation on the earth—the large, underground rectangular plot, it was determined, had to be manmade due to its shape, texture, and soil composition which were in sharp contrast to surrounding geological features.
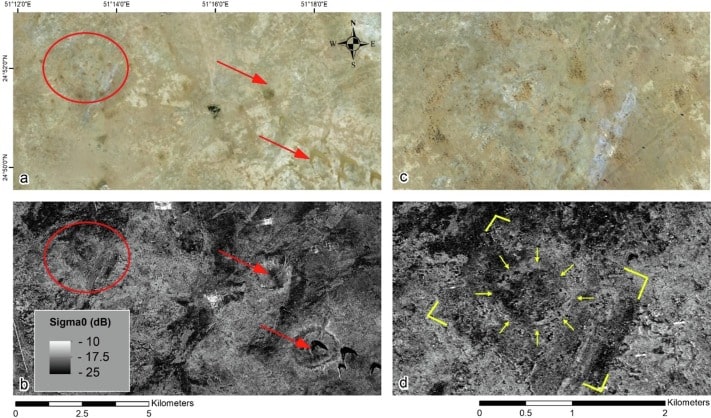
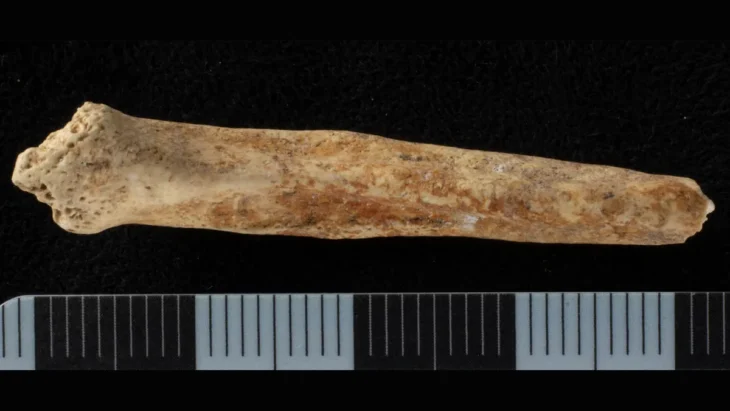
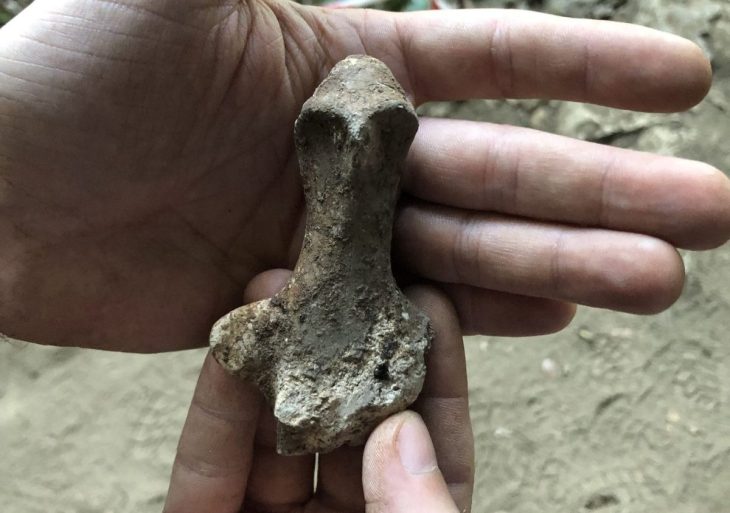
Independent carbon dating of retrieved charcoal samples suggests that the site is at least 3650 years old, dating back potentially to the same era of the Dilmun civilization.
The researchers suggest the site may have been a fortress whose inhabitants landscaped the area and practiced agriculture by accessing deep groundwater through fractures in the ground, Lead author, Essam Heggy, of the USC Arid Climate and Water Research Center explained.
This discovery has significant historic and scientific implications. Historically, this may be the first piece of evidence of a sedentary community in the area—and perhaps evidence of advanced engineering for the time period.
A settlement of this size in this particular area, which is far from the coastline where most ancient civilizations were located, is unusual, says Heggy.
“With this area now averaging about 110 degrees Fahrenheit in summer months, this is like finding evidence of very green ranch in the middle of Death Valley, California dating back thousands of years ago.”
Further, the site yields new insights on the poorly understood climatic fluctuations that occurred in the region, and how these changes may have impacted human settlement and mobility.
Most critically, the scholars believe that this settlement must have been in place for an extended period due to its development of agriculture and reliance on groundwater, a fact which speaks to the civilization’s advanced engineering prowess given Qatar’s complex aquifers and harsh terrain.