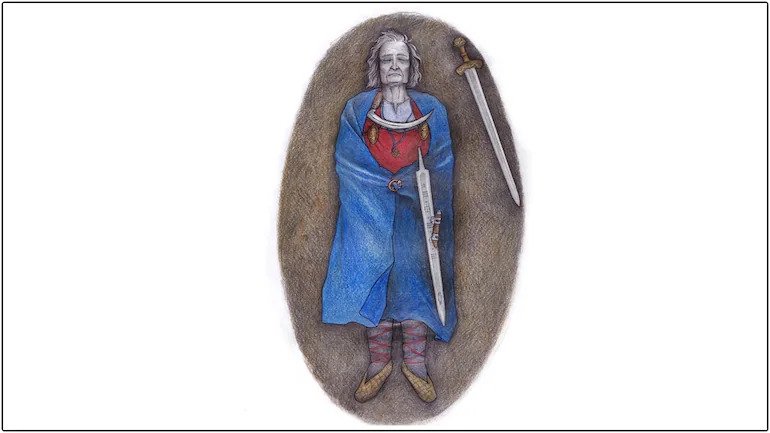
Archaeologists found a weapon grave in Finland’s Suontaka Vesitorninmäki in 1968. The remains discovered in the burial have been at the center of a heated controversy regarding the gender of its inhabitant ever since. Initial interpretations of the bones suggested a lady was buried there, although these views have long been contested.
Now, DNA research of the burial, including an assessment of its contents, soil samples, and microremains, has once again challenged long-held beliefs. According to the study, the 1000-year-old burial might be that of a non-binary individual.
The new findings not only call into question long-held beliefs but also raise the potential that non-binary persons were formerly welcomed and valued among their peers. According to the results of the DNA study, which was published in the European Journal of Archaeology, the inhabitant of the burial was a respected person with non-binary gender identification.
For decades, it was thought that two remains, a man and a woman, were buried in the Suontaka burial. Inside the burial, jewelry resembling modern women’s clothes, such as oval brooches and woolen garments, was discovered. At the same time, it possessed masculine characteristics, such as a hiltless sword.
However, recent DNA research revealed that the burial only contained the bones of one individual, who appeared to have the uncommon Klinefelter disease. One in every 660 males is born with an extra copy of the X chromosome, which causes the syndrome (XXY). Males with the syndrome are still genetically male, but the disease can result in larger breasts, a tiny penis and testicles, poor sex desire, and infertility.
In the researcher’s articles, “For decades, the grave has been a popular example of powerful women in Late Iron Age and early medieval societies. The grave was used as evidence of female leaders in the past. The decorated bronze-hilted sword allegedly found in the Suontaka burial is presented as a female warrior’s weapon, ” they said.
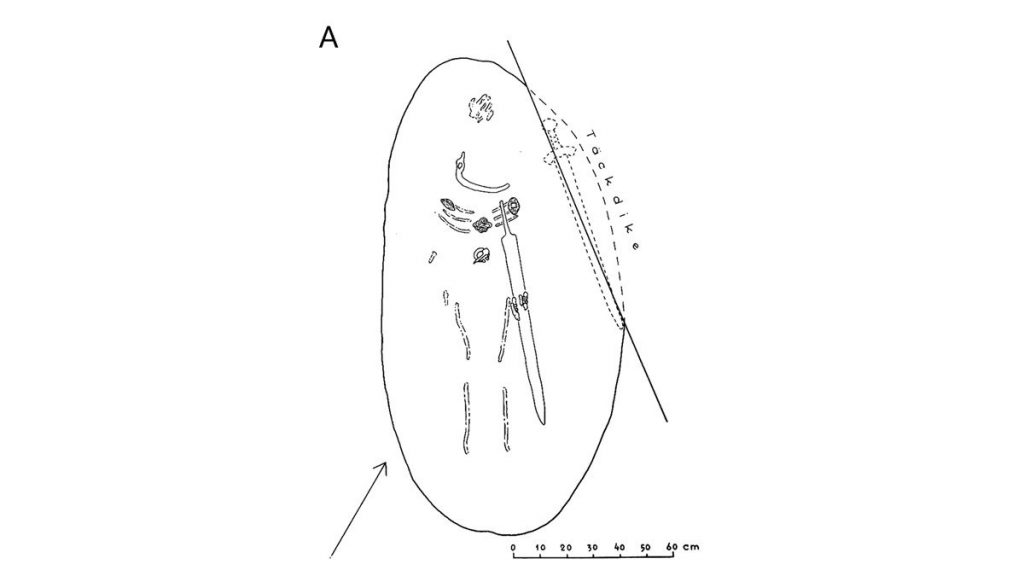
“The buried individual seems to have been a highly respected member of their community,” the study’s leading author Ulla Moilanen an archaeologist from the University of Turku, told The Guardian. “They were laid in the grave on a soft feather blanket with valuable furs and objects.”
According to the researchers, one explanation is that the individual was accepted as a non-binary “because they already had a distinctive or established status in the society for other reasons,” such as being from a wealthy or prominent family or being a shaman.
The researchers studied the microscopic animal hair and fiber remains in the soil retrieved from the grave, and studied ancient DNA (aDNA) in the bone remains to infer the individual’s chromosomal sex. It should be noted that historically, the gender identity of the burials was inferred from the objects or remains of objects found nearby. However, with the advancement of technology and modern genetics, new methods have been developed to determine the sex of the remains.
What is non-binary?
Non-binary individuals are persons who do not identify with a certain gender. People who are neither male nor female, according to the National Centre for Transgender Equality, use a variety of words to identify themselves, with non-binary being one of the most prevalent. Genderqueer, agender, and bigender are examples of alternative words.
None of these phrases signify the same thing, yet they all refer to a gender experience that isn’t just male or female.
Cover Photo: An artist’s reconstruction of the burial, showing the position of the objects on the body. (Photo: Veronika Paschenko/European Journal of Archaeology)