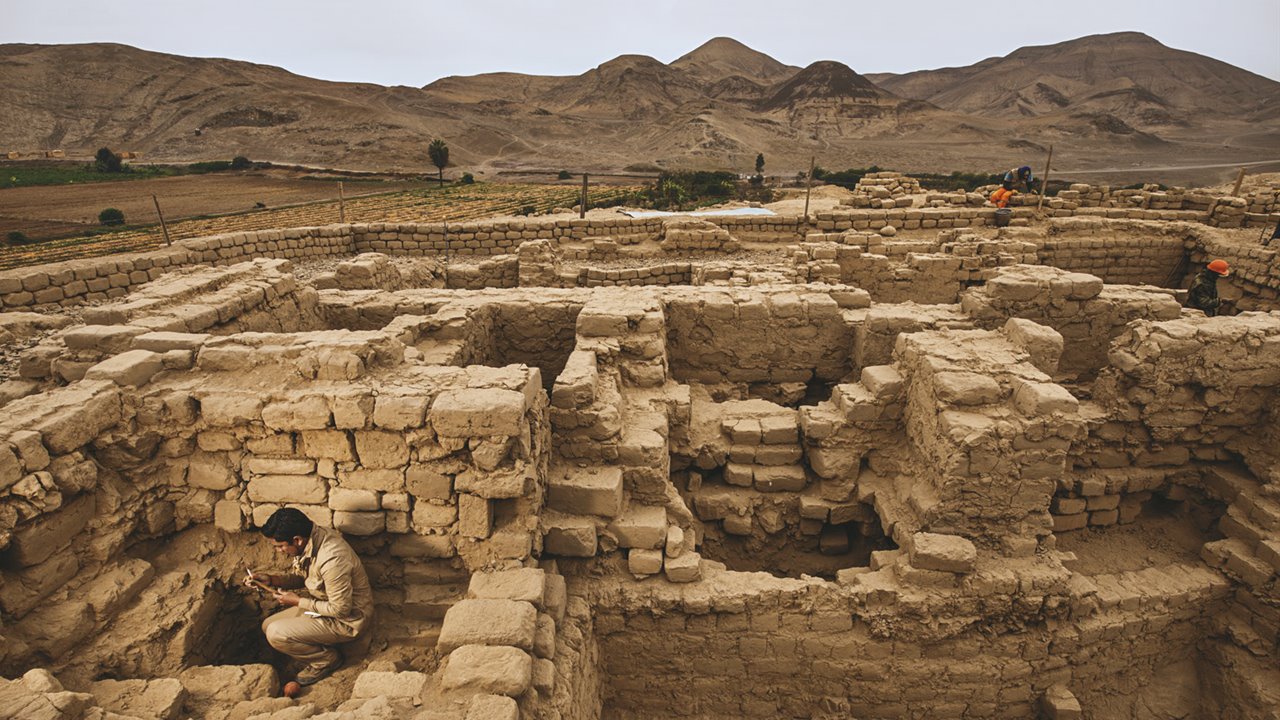
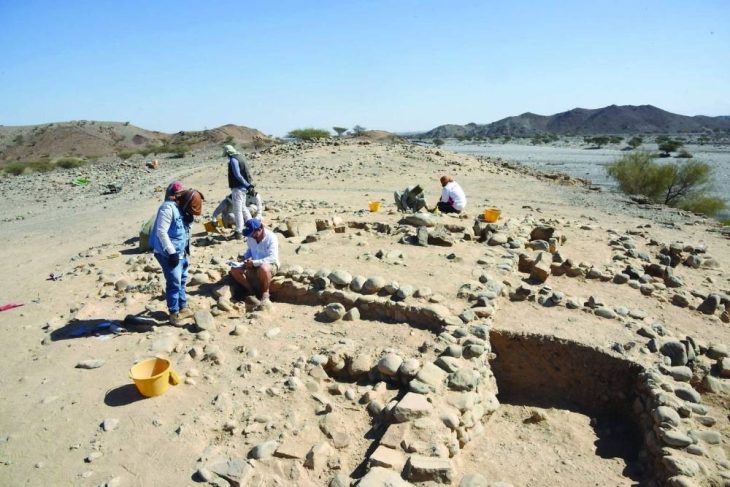
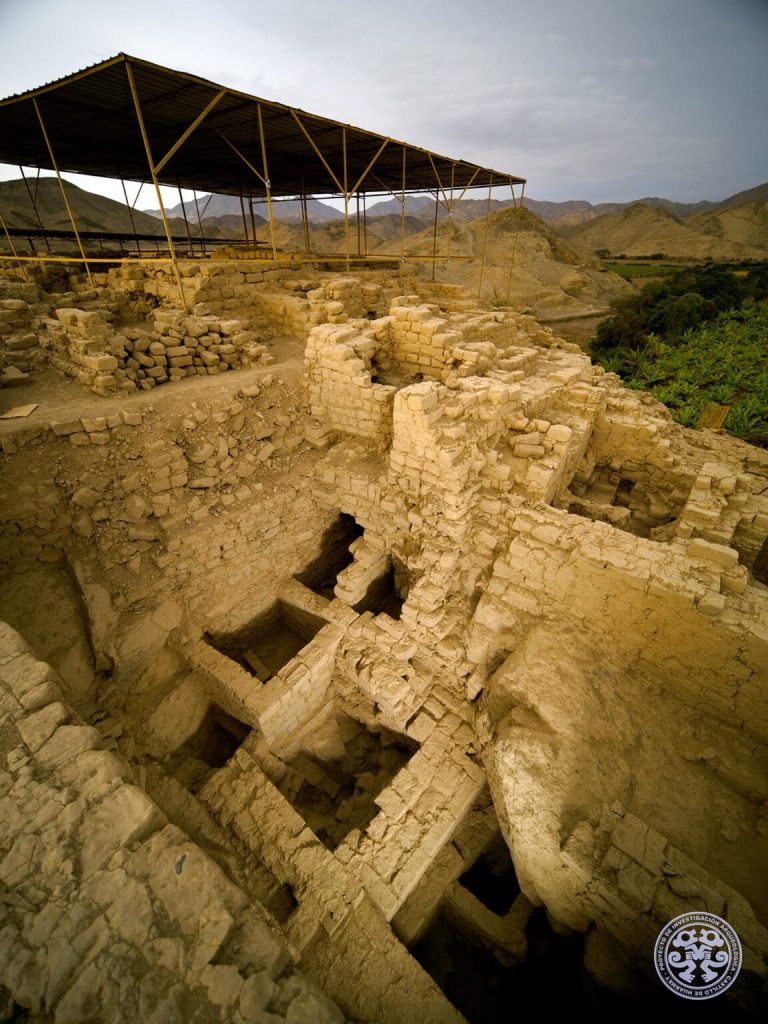
A group of tombs of elite craftsmen of the Wari culture has been discovered at the archaeological site of Castillo de Huarmey, a pyramid-like burial complex in the Ancash Region of Peru.
Castillo de Huarmey, meaning “the Castle on the River Huarmey,” was thought to be a cemetery for Wari royalty, a pre-Inca Middle Horizon civilization that flourished in modern-day Peru’s south-central Andes and coastal area from around AD 500 to AD 1000.
The tombs found are the first ever found tombs of outstanding Wari craftsmen and confirm Huarmey’s importance as an administrative and cultural center.

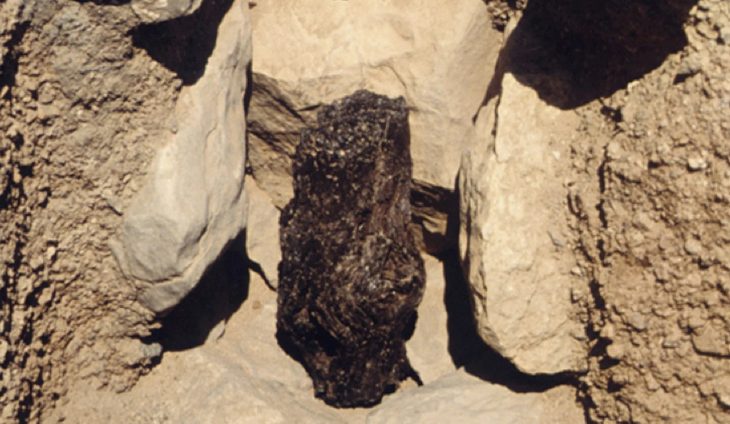
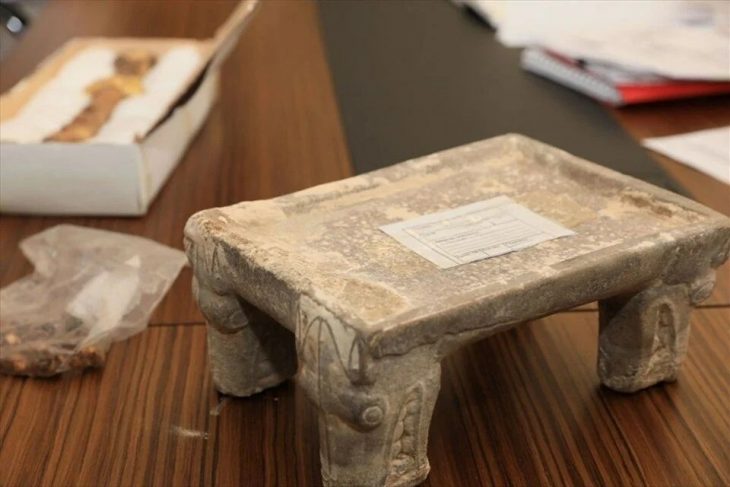
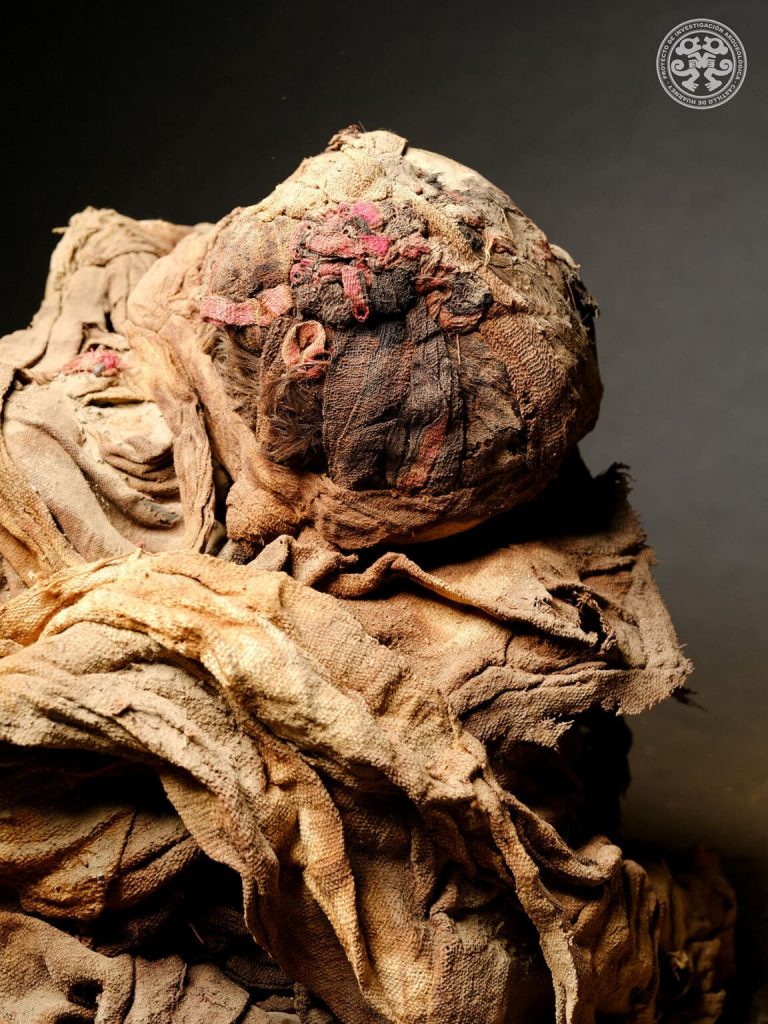
Four adults (two men, two women) and three adolescent burials were discovered inside adobe brick tombs, along with hundreds of the tools and supplies they would have used in their occupations.
The primary burial is most likely that of an adult man who appears to have been a basket weaver based on the grave goods. He passed away at the age of 40 about 1,300 years ago. His body was wrapped in layers of fabric and buried alongside his tools of the trade: axes, knives, saws, and a cane used to make baskets. There was also beautiful jewelry, such as a gold headdress and a gold ear ornament inlaid with a semi-precious stone. The other man and the adolescents were buried with him. The two women were close by. Archaeologists believe they may have all been related.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

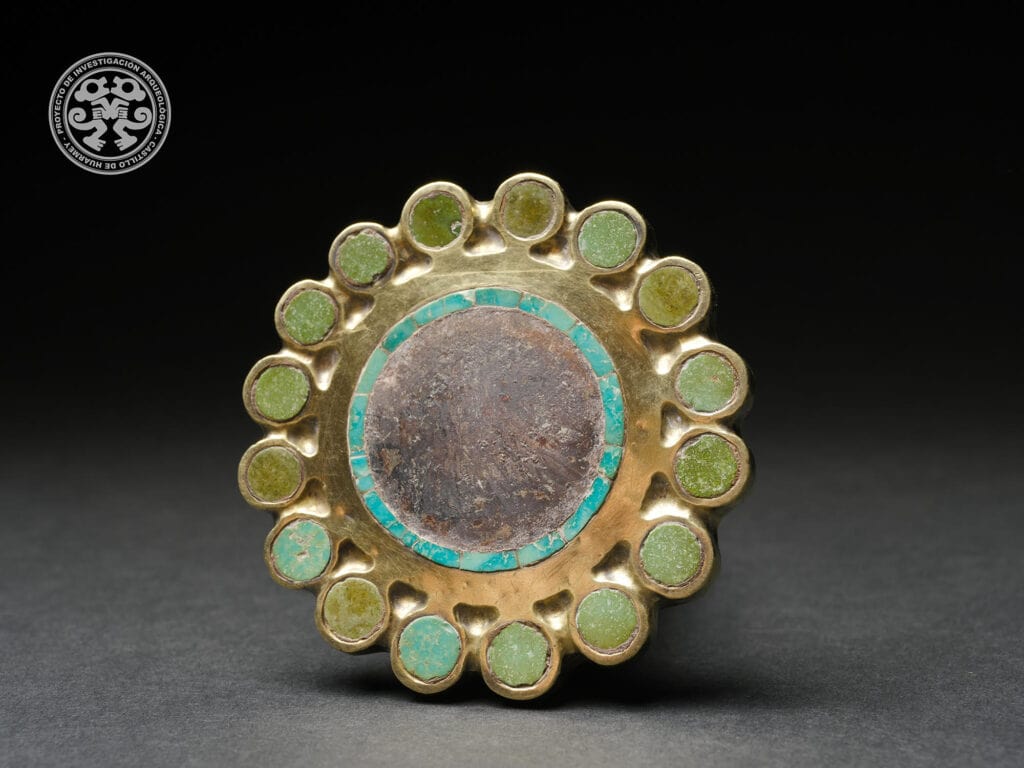
The artisans had to have been attached to the royal court. Archaeologists discovered a royal mausoleum in 2010 that housed the remains of one queen, 57 aristocratic women, six human sacrificial victims, and two guards who had their feet amputated so they could never desert their post. More than 1,300 objects in gold, silver, bronze, gemstones, wood, bone, shell, and painted ceramics were housed in the mausoleum. The tombs of the elite craftsmen were located just below the mausoleum, a step down from the royals in the hierarchy, but so high in status that it’s entirely possible that Wari artisans were either elite-born or able to rise through their work to the upper echelons of society.
Archaeologists have named this part of the cemetery the ‘Gallery of Elite Craftsmen’.

Professor Miłosz Giersz, Head of the Department of Archaeology of the Americas at the University of Warsaw said: ” This discovery confirms what we expected from previous years: both men and women buried in Castillo de Huarmey were devoted to the highest-class craftsmanship and produced elite products of their era.”
All of these new discoveries support the view that Castillo de Huarmey served as the most important power, administrative and craft center, and necropolis of the empire’s highest elites, as well as the most important complex on the Peruvian coast during the Wari period. Furthermore, Giersz remarks that this remarkable discovery occurred in the midst of an uncertain scenario, as Castillo de Huarmey had long been thought to have been looted in its entirety by treasure hunters.