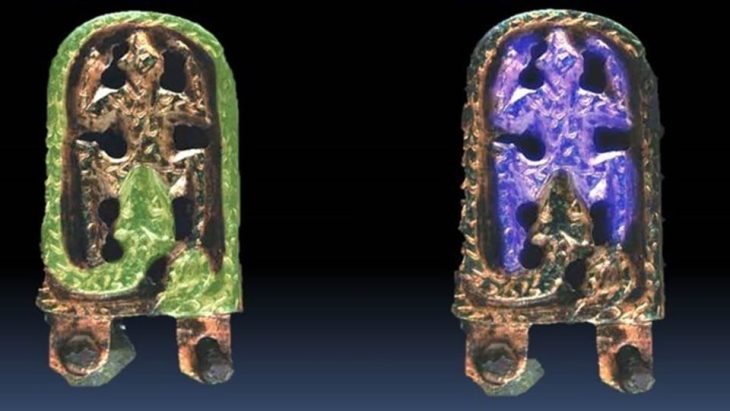
Recent discoveries from a treasure hoard unearthed in Thetford Forest, East Anglia, reveal compelling evidence that the region remained pagan until the 5th century CE, a significant extension beyond the previously established timeline of the late 4th century (380-390s CE).
This finding not only reshapes our understanding of Thetford’s religious landscape but also highlights the enduring cultural practices that persisted well into the post-Roman era.
Recent research has re-evaluated the timeline of the Thetford hoard, suggesting that this significant treasure was buried in the 5th century CE, specifically during the 420s to 440s, which marks a notable shift from the previously accepted date of the late 4th century, specifically the 380s to 390s.
This remarkable finding, presented by Professor Ellen Swift from the University of Kent, is based on a comprehensive analysis of artifacts from the hoard in comparison with context-dated grave and hoard finds across the western Roman Empire.
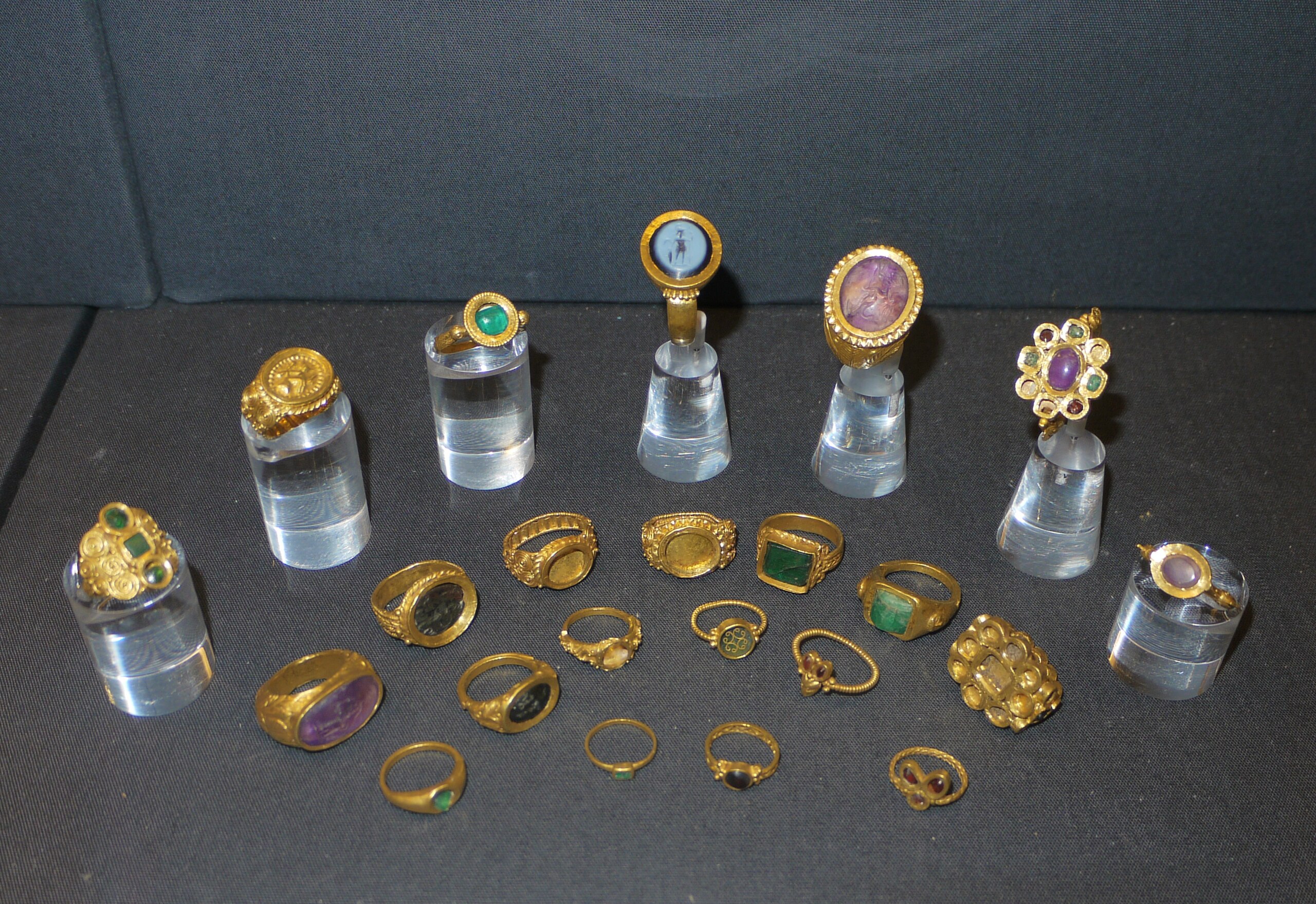
The Thetford treasure, discovered in 1979 by a metal detectorist at a construction site on Fison’s Way in Thetford Forest, East Anglia, consists of 81 objects, including 22 gold finger rings, various gold jewelry pieces, and 36 silver spoons or strainers. Notably, the absence of coins among the recovered items has posed a challenge for researchers attempting to date the hoard. However, the internal associations among the artifacts—considering their technological, compositional, and stylistic features—support the new dating proposed by Professor Swift.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
![Thetford cat. nos. 2, 3 and 4, left, (© The Trustees of the British Museum [used online under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license]) compared with finger-rings from Desana (Turin, Palazzo Madama – Museo Civico d'Arte Antica. By courtesy of Fondazione Torino Musei) and Cortrat, right (photo and copyright © Musée d'Art et d'Archéologie de Châtillon-Coligny).](https://arkeonews.net/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/Thetford-cat.jpg)
One of the most intriguing aspects of this research is the suggestion that the jewelry found in the hoard reflects a rich tapestry of cultural connections, indicating that Thetford served as a pagan cult center well into the 5th century. This finding challenges previous assumptions about the region’s religious transition and highlights the economic significance of the site during a time of political upheaval in Britain, following the collapse of Roman authority. The revised timeline suggests that the hoard was buried during a period marked by migration and displacement, where the economic value of such treasures may have become increasingly paramount.
Professor Swift’s study emphasizes that the hoard’s diverse artifacts point to a broader network of trade and cultural exchange within the Roman Empire. The jewelry’s varied styles suggest origins from multiple regions, including northern Italy and the Balkans, illustrating a shared elite culture that transcended geographical boundaries. This evidence indicates that Britain was more interconnected with the wider Roman world than previously thought, challenging the notion of isolation during this transitional period.
The implications of this new chronology are profound, as it not only alters the understanding of the Thetford hoard itself but also prompts a re-evaluation of other archaeological materials from the period. The findings, published in the Journal of Roman Archaeology, underscore the importance of Thetford as a key reference point for dating artifacts and understanding the dynamics of cultural and economic life in post-Roman Britain.

As the Thetford treasure remains on display at the British Museum, it continues to captivate scholars and the public alike. The collection serves as a testament to the complex history of a region that thrived amidst the challenges of transition and transformation during the waning days of the Roman Empire.
The ongoing research surrounding the hoard not only enriches our understanding of this specific treasure but also sheds light on the broader historical narrative of Britain during a time of significant change.
Swift, E. (2024). Rethinking the date and interpretation of the Thetford treasure: a 5th-c. hoard of gold jewelry and silver spoons. Journal of Roman Archaeology, 37(2), 409–448. doi:10.1017/S1047759424000278
Cover Image Credit: Wikipedia