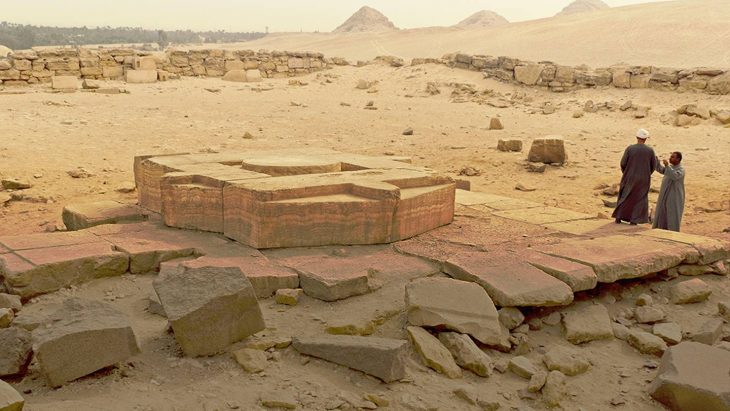
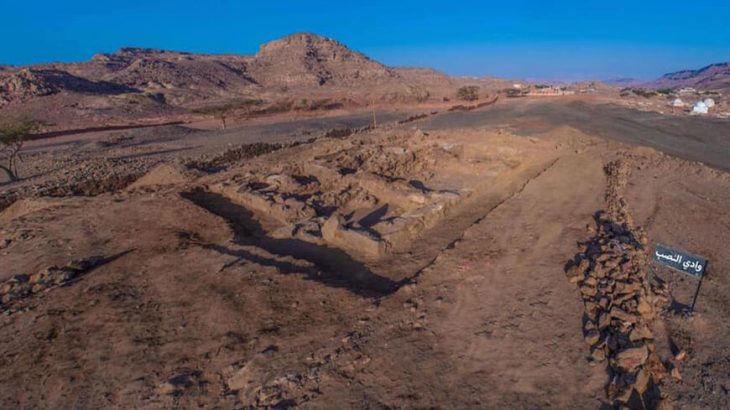
In 275 BC, Egyptian King Ptolemy II (Philadelphos) established a shipping port on the coast of the Red Sea and named it after his mother, Berennike I. The most important reason for establishing this new port was that Ptolemy needed elephants. These were used in the war against the Seleucids in the Near East, which prevented the import of Indian elephants.
The geographical position of Berenike was particularly suitable as it was a natural harbor, protected from the prevailing northern winds by a large peninsula. From Berenice, there were land routes through the eastern desert to the Nile valley, protected by crossing stations (hydreumata). These provided the caravans with water and shelter.
During the Roman period, Berenike developed into a trading mall: spices, myrrh, frankincense, pearls, and textiles were shipped to Alexandria and Rome via Berenike.
As Berenike continued its development, it was interrupted by a period of abandonment of almost half a century before the first phase of the Hellenistic period, around 200 BC, until the city was reoccupied in the second half of the 2nd century BC.
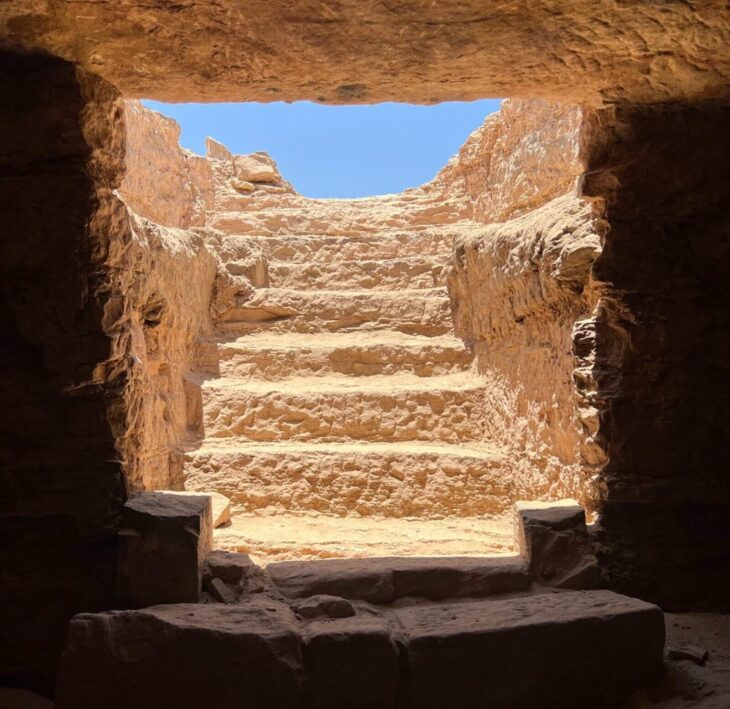
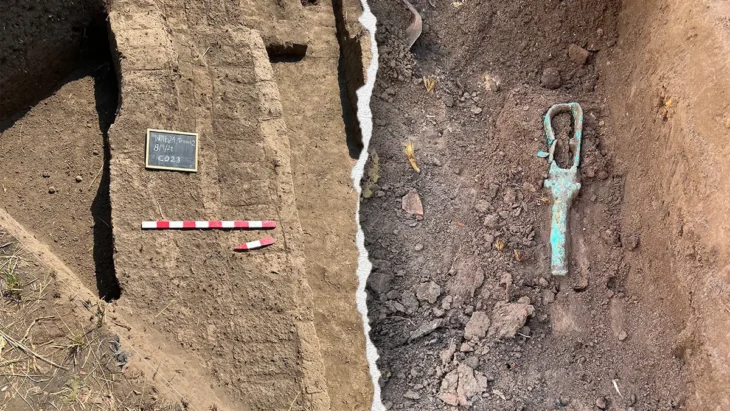
Archaeologists researching an ancient well used by the city garrison in the fortified gate complex suggest that the city was abandoned due to climate change caused by a volcanic eruption.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
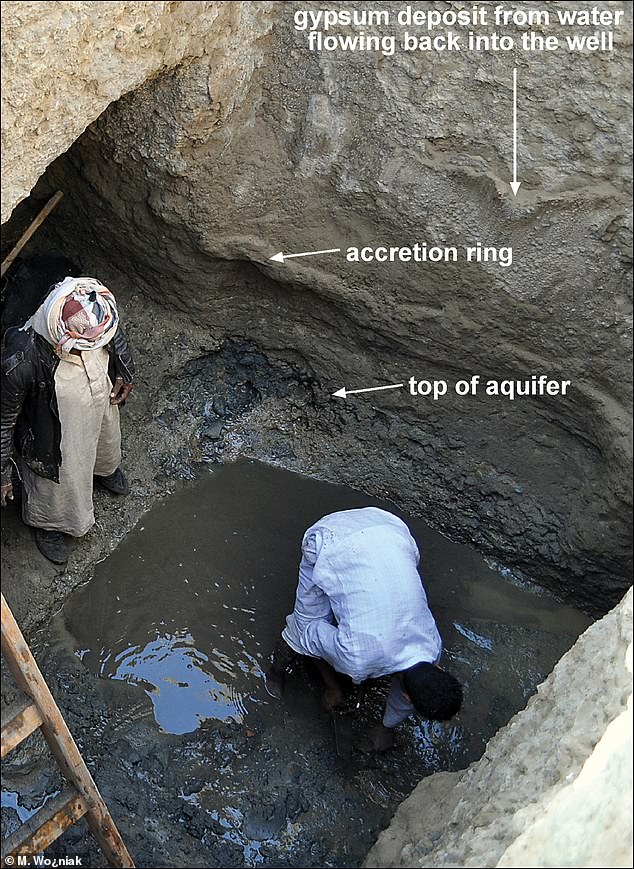

The eruption of an unidentified volcano in approximately 209 BC released large volumes of ash and sulfur into the stratosphere, according to a new report in the journal Antiquity.
This climatic event most likely disrupted the delicate climate of the Red Sea region, causing drought in Berenice, causing the wells to dry out and be buried with wind-blown sand.
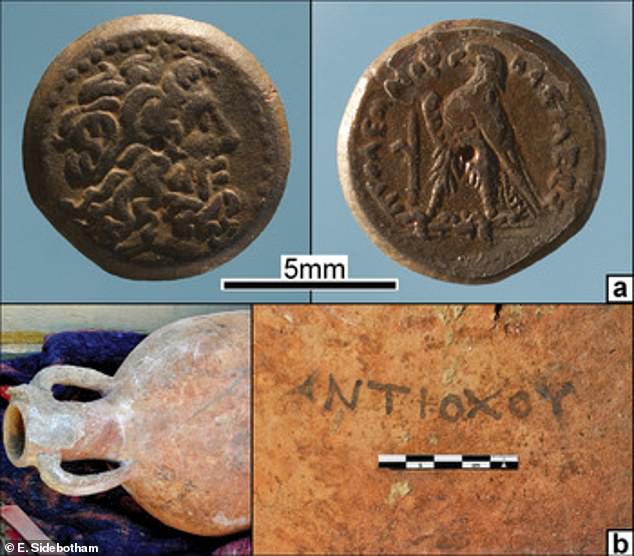
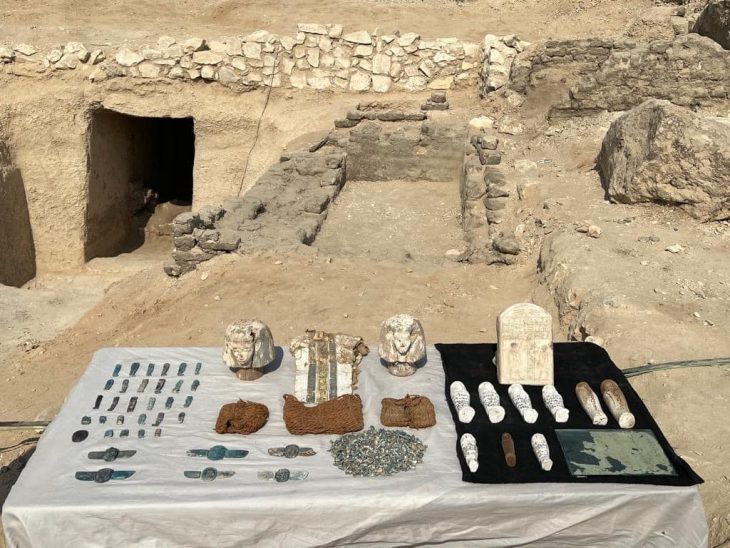
Archaeologists methodically removed the thick layers of sand filling the well, where they found coins, amphorae, and other materials that could be dated, suggesting that the event occurred at the end of the 3rd century BC.
The ceramics found in the sand can be traced back to the same era, probably during the reign of Ptolemy III or IV, who reigned from 246 to 222 BC and from 221 to 204, respectively.
The city was later re-occupied in the second half of the 2nd century BC, becoming an even more prosperous Roman port city, however, by the mid-6th century, the city was abandoned again and was never re-occupied.
İnformation about Berenike source: The Berenike project