According to recent research, burnt seeds discovered in the Utah desert suggest that humans used tobacco initially and that some of the first people to arrive in the Americas utilized the plant.
According to new research, where these individuals gathered — now known as the Wishbone hearth site — is the site of the earliest known use of tobacco. Its existence also suggests the use of tobacco goes back thousands of years earlier than scientists realized. The discovery shows that humans smoked tobacco approximately 10,000 years earlier than previously assumed.
These findings were published Monday in the journal Nature Human Behavior.
Previous to this study, researchers had only dated tobacco use in North America to 3,300 years ago. That evidence was nicotine found in smoking pipes in Alabama.
Archaeologists excavated the remnants of a hunter-gatherer settlement on mudflats in Utah’s Great Salt Lake Desert for the new research. Wind aided in the site’s exposure over time, according to Daron Duke, an archaeologist from the Far Western Anthropological Research Group in Henderson, Nevada.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
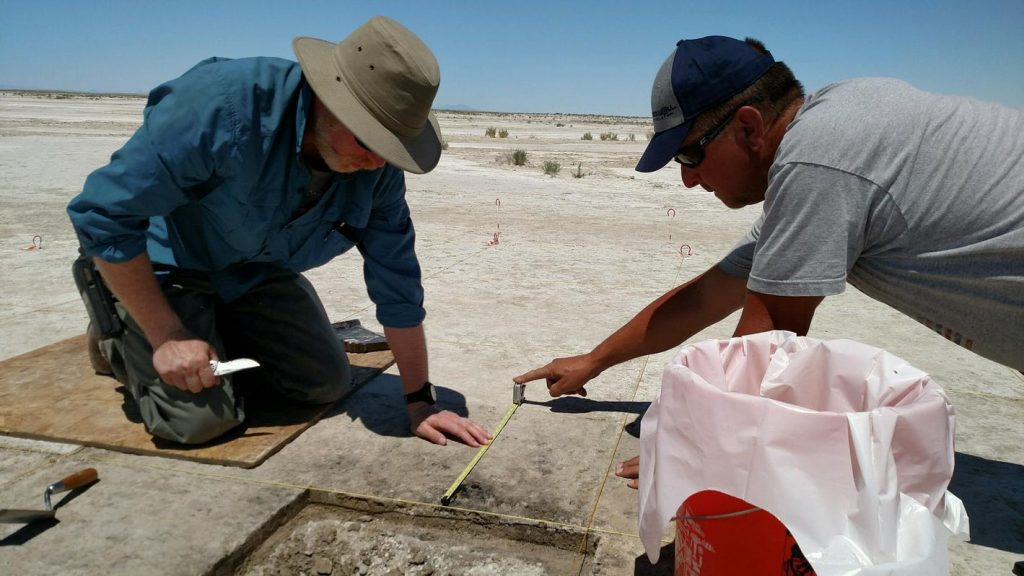

The scientists discovered an intact ancient fireplace surrounded by stone artifacts such as spear points frequently employed in large game hunting. The fireplace also included almost 2,000 bones and bone fragments, primarily from ducks, with cut marks and other evidence indicating that humans cooked and ate there.
The fireplace had burned willow wood, which was probably the finest fuel choice in the region, as it is now in modern neighboring regions. The wood was subsequently tested using carbon dating, which entails measuring the quantity of a radioactive form of carbon with a known rate of decay; the results indicated that the wood was around 12,300 years old.
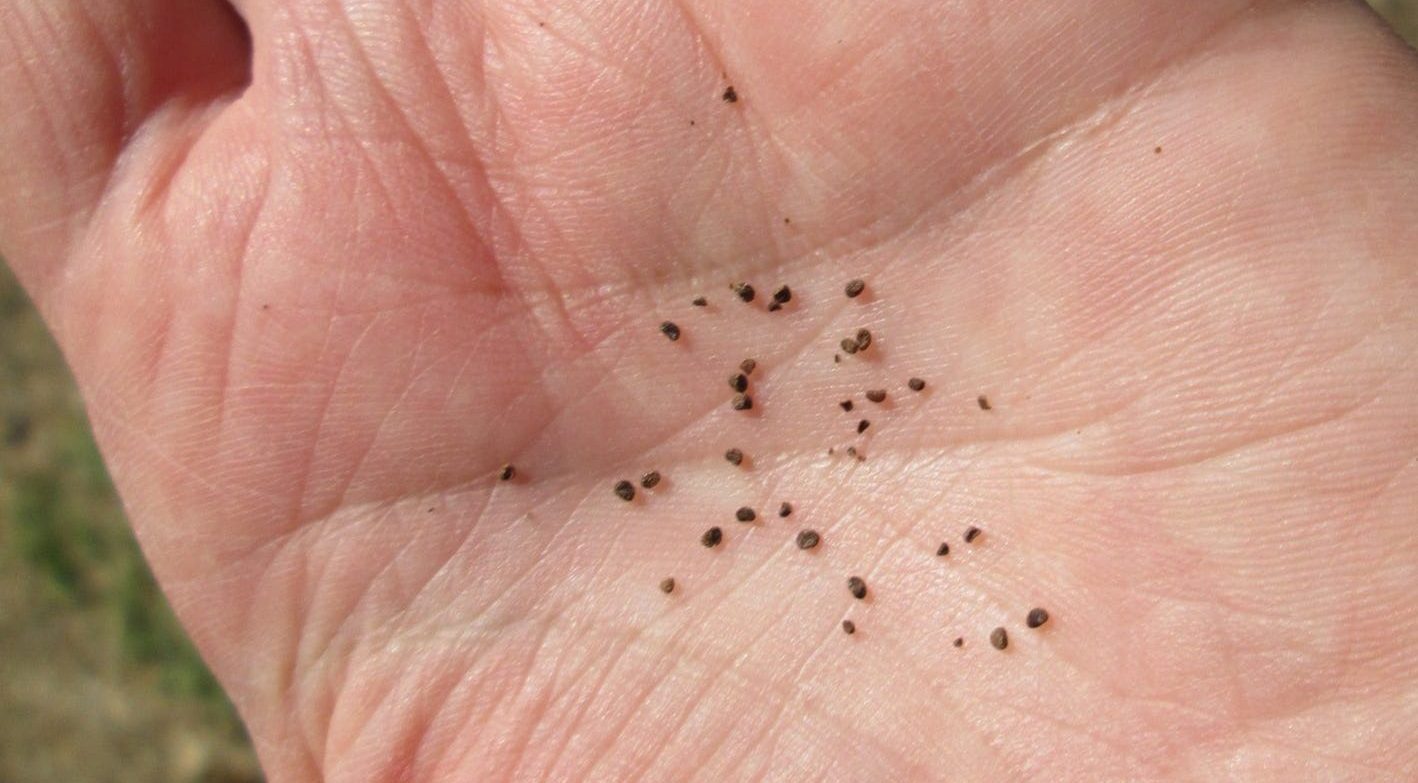
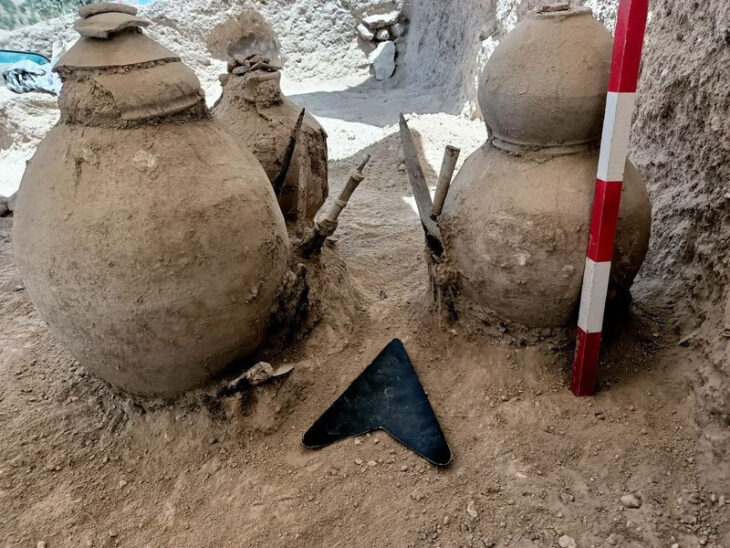
The scientists discovered four charred Nicotiana — tobacco — seeds at the Wishbone hearth site. Using radiocarbon dating on charred wood from the hearth, the researchers estimated humans were using tobacco roughly 12,300 years ago.
This cultural use of tobacco by ancient peoples eventually gave way to domestication, spread to the rest of the world, and spurred modern tobacco use.
Cover Photo: Tobacco seeds in the palm of a human hand. Researchers discovered charred tobacco seeds at the Wishbone site, confirming indigenous cultural use of the tobacco plant. Photo: Tammara Norton