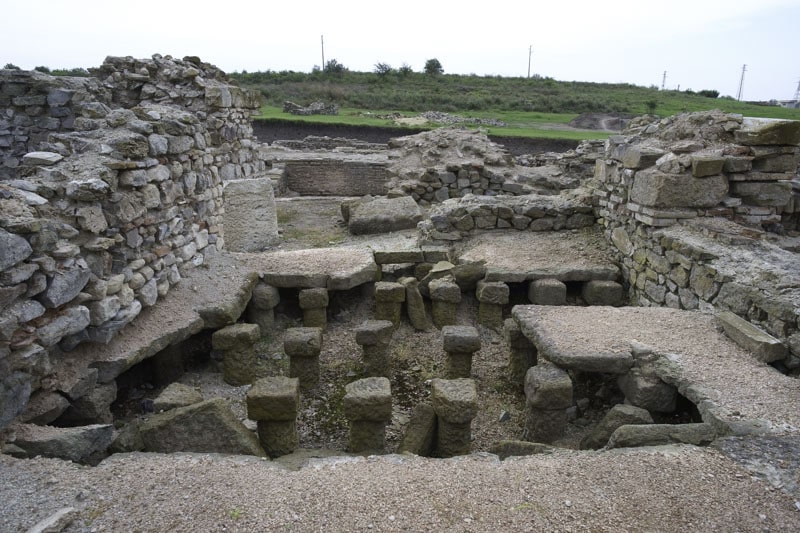
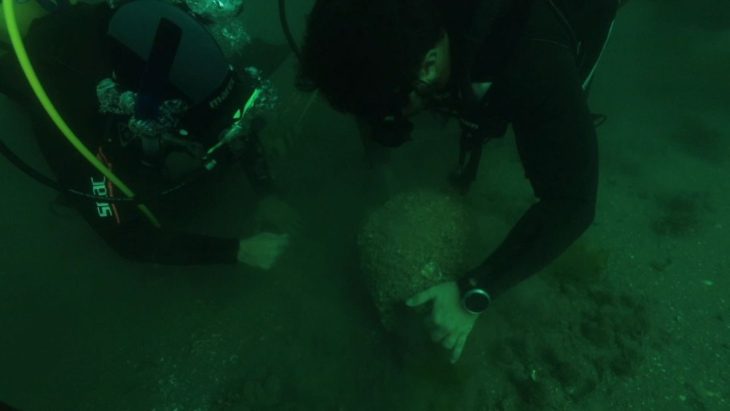
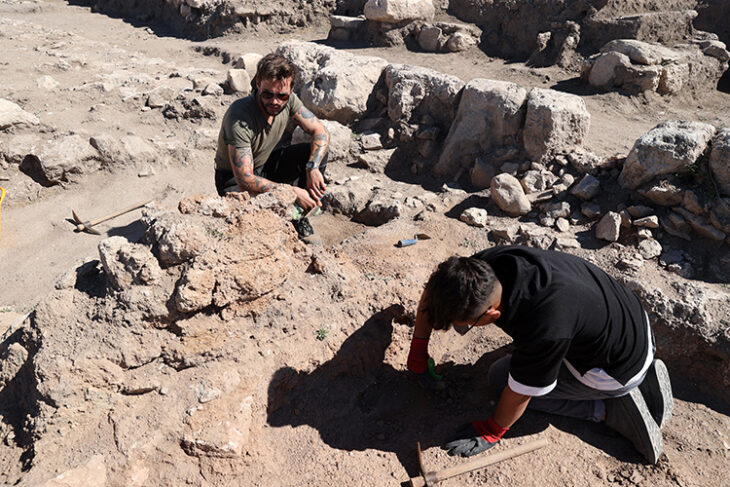
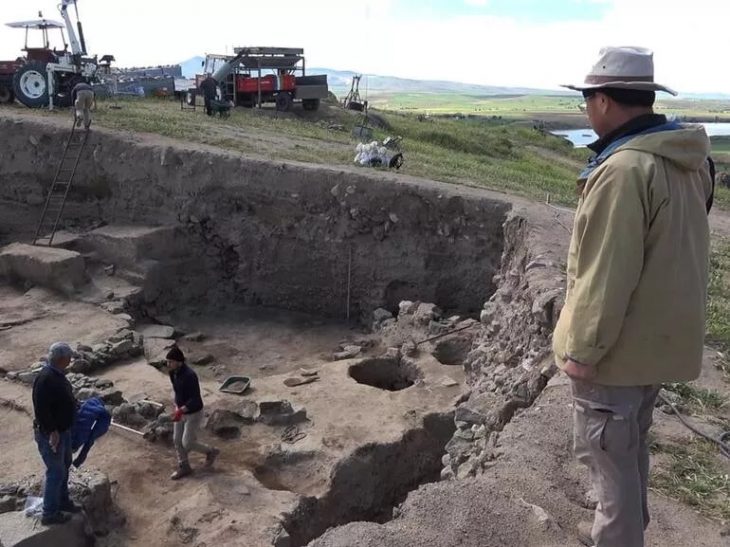
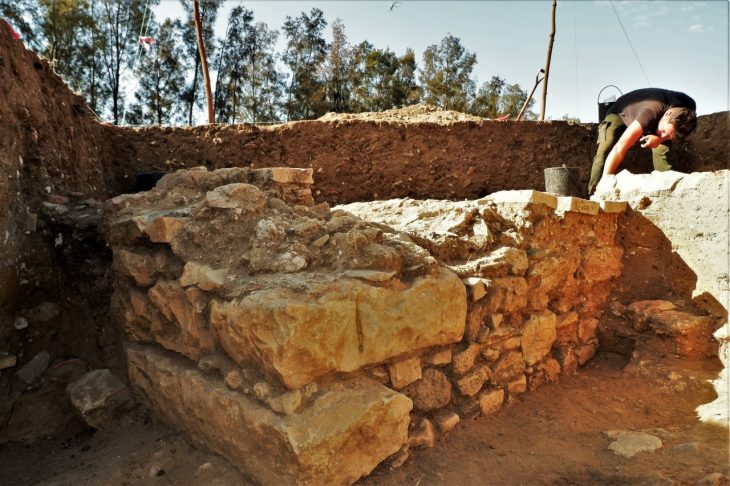
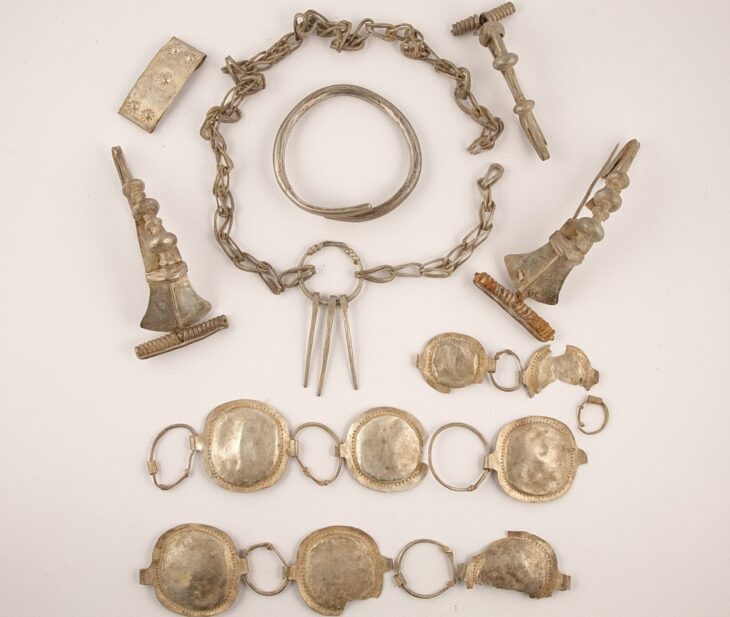
A silver amulet was discovered during excavations of the Deultum-Debelt National Archaeological Reserve, near the village of Debelt in the southeastern Sredets Municipality, in Bulgaria. This recent discovery is the oldest evidence of Christianity on Bulgarian lands.
Deultum was the only colony of free Roman citizens on the territory of today’s Bulgarian lands.
Following the Roman commander Lucius’ conquest of the Southern Black Sea Coast in 72 BC, Emperor Vespasian established the colony of Deultum to the east of the Thracian settlement of Develt or Debelt. On the site of Deultum, there existed an old Thracian settlement prior to the start of the new era. Veterans of the VIII Augustus Legion settled there in the 70s of the first century, during the reign of Roman Emperor Titus Flavius Vespasian.
The Deultum over the next three centuries the town became one of the richest in the surrounding area. The strategic location of Deultum, impressive town planning, and noble inhabitants earned it the nickname Little Rome in Thrace.
Khan Krum took Develt (Deultum) in 812 and drove its people north of the Danube. The town thus became wholly Bulgarian. Historians think that this region has a close connection to Bulgaria’s 864 Christian conversion.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Unearthed during summer excavations in 2023, a silver amulet has garnered attention for its significance. After the restoration and analysis of its inscription, it can now be seen in the museum of the reserve, museum curator Dora Todorova told to BTA.

Initially thought to be a silver ingot, it was later revealed to be an amulet inscribed with the names of archangels Gabriel and Michael, along with the Guardian Christ, following restoration efforts by Silvia Borisova.
“Early Christians were careful not to be recognized and used various symbols to refer to Christ. In this case, the amulet is placed in a grave, near the head of the person buried in it, away from people’s eyes,” explained Todorova. The name of Christ is written on it but the first letter is rotated at 45% and forms the shape of a cross. This feature is known in some very early Christian inscriptions, the curator said.
The interpretation and dating of the amulet were conducted by renowned epigrapher Ch. Assistant Dr. Nikolay Sharankov, in collaboration with the reserve’s team for reading and publishing inscriptions unearthed during excavations.
According to Krasimira Kostova, director of the National Archaeological Reserve ” Deultum” – Debelt, the artifact dates back to the late second or early third century AD, marking a significant milestone in the region’s Christian history.
In his analysis featured in the specialized publication Arheologia Bulgaria, Dr. Sharankov presents a compelling argument for dating the inscription as +ΡЄICTOC with ЄI instead of I. He posits that the inclusion of the cross and the naming of only Archangels Gabriel and Michael strongly suggest the amulet’s connection to a Christian community. Moreover, Sharankov asserts that its dating establishes it as the oldest Christian artifact in Bulgaria, marking the earliest mention of Christ in the region.
According to him, the discovery of such an early Christian monument in Deultum of all places is not unexpected, because the Roman colony was the first settlement known to have had a proven Christian community and a bishop.
Cover Photo: Ancient Bulgaria