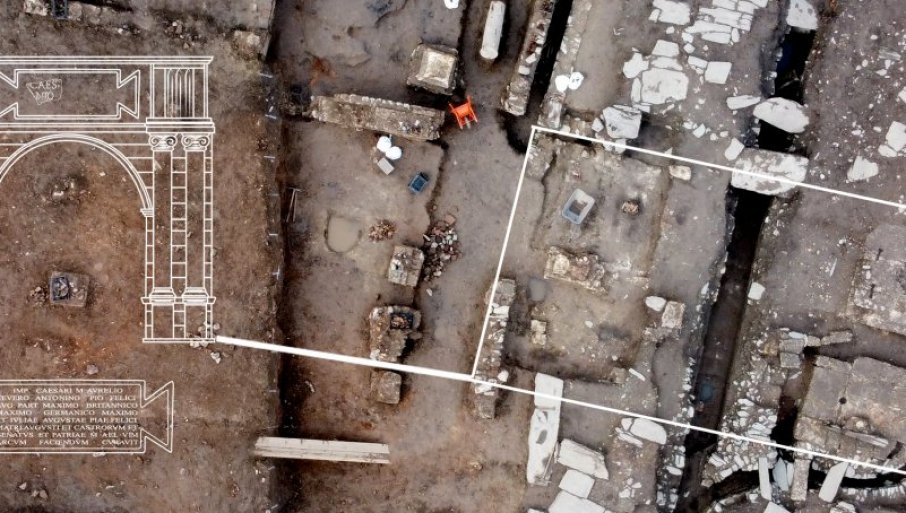
Archaeologists in Serbia have unearthed an ancient Roman triumphal arch dating back to the third century at Viminacium, a Roman city near the town of Kostolac, 70 km (45 miles) east of Belgrade.
Viminacium (Viminacium) or Viminatium, was a major city (provincial capital) and military camp of the Roman province of Moesia (today’s Serbia), and the capital of Moesia Superior.
It included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Albania, northern parts of North Macedonia (Moesia Superior), Northern Bulgaria, Romanian Dobruja, and small parts of Southern Ukraine (Moesia Inferior).
Professor Miomir Korac, one of Serbia’s leading archaeologists, said that the discovery was made during excavations of the main street of Viminacium, the capital of the Roman province of Moesia.
“This is the first such triumphal arch in this area..,” Korac told Reuters on Monday.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

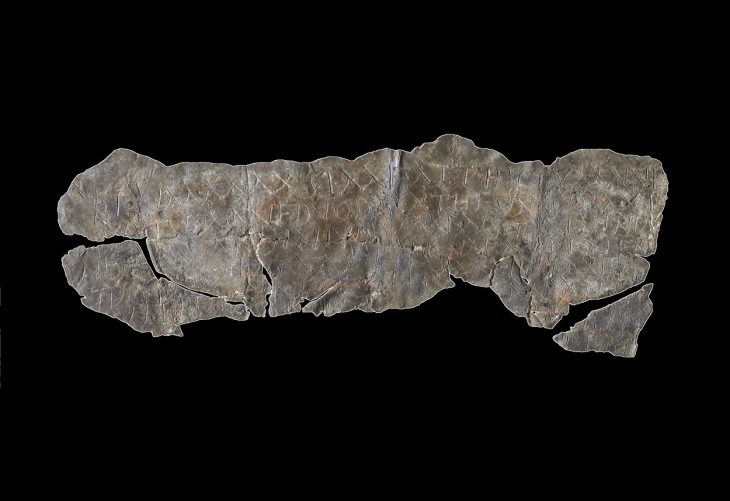
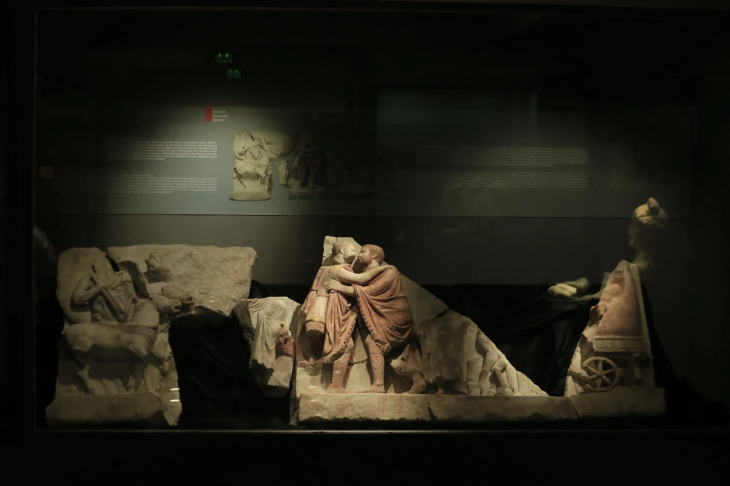
The solution to the riddle – to whom the triumphal gate was dedicated, scientists found when they dug up part of a marble slab with the ruler’s name carved from the almost frozen ground. It was Emperor Caracalla, who grew up in military camps following his father Septimus Severus on campaigns and participated in battles from the age of 15.
Archaeologists, based on the material already found, determined that the triumphal arch was built at the end of the second or the latest at the beginning of the third century AD.
According to historical sources, an extraordinary event took place in the Upper Mesian capital Viminacium: here Marcus Aurelius Antoninus, better known by the nickname Caracalla, was proclaimed Caesar, ruler, and successor of his father Septimius Severus in 195, from whom he took the title of Augustus three years later. The researchers knew that the triumphal arch was built on the occasion of an event of great importance for the fate of the empire, and the plaque with the remains of the dedication to Caracalla confirmed their conclusions.
Since August, the focus of research at Viminacium has been on the urban core.
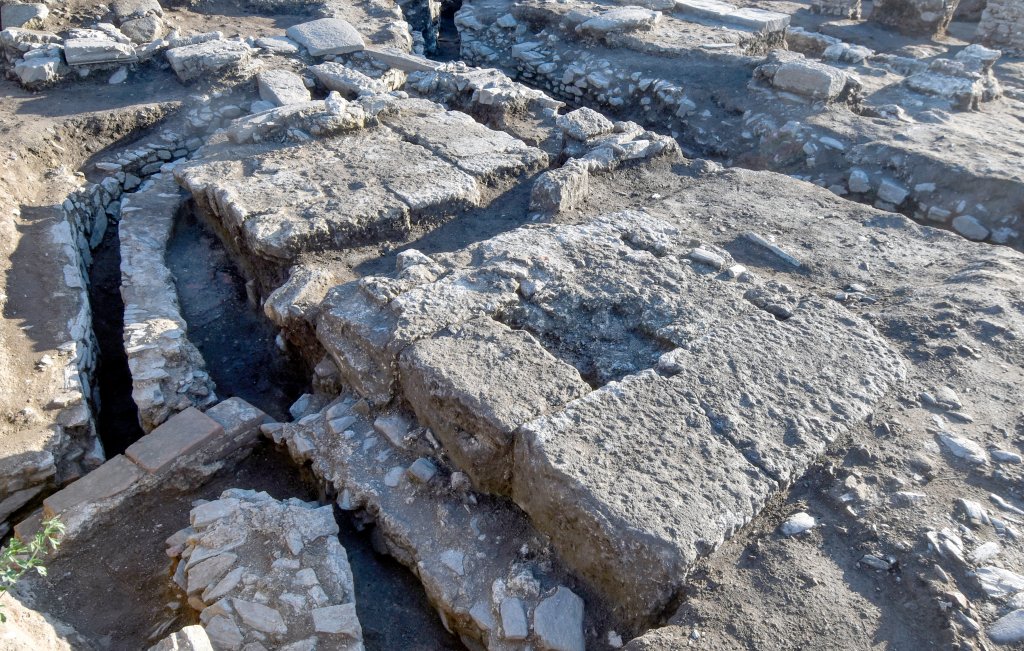

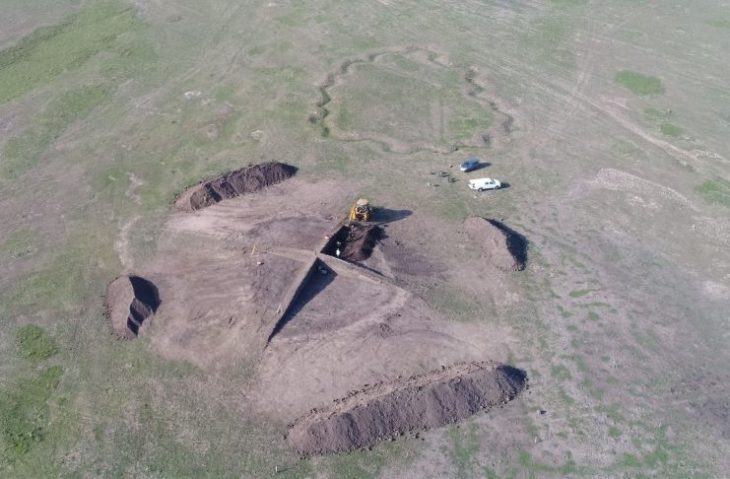
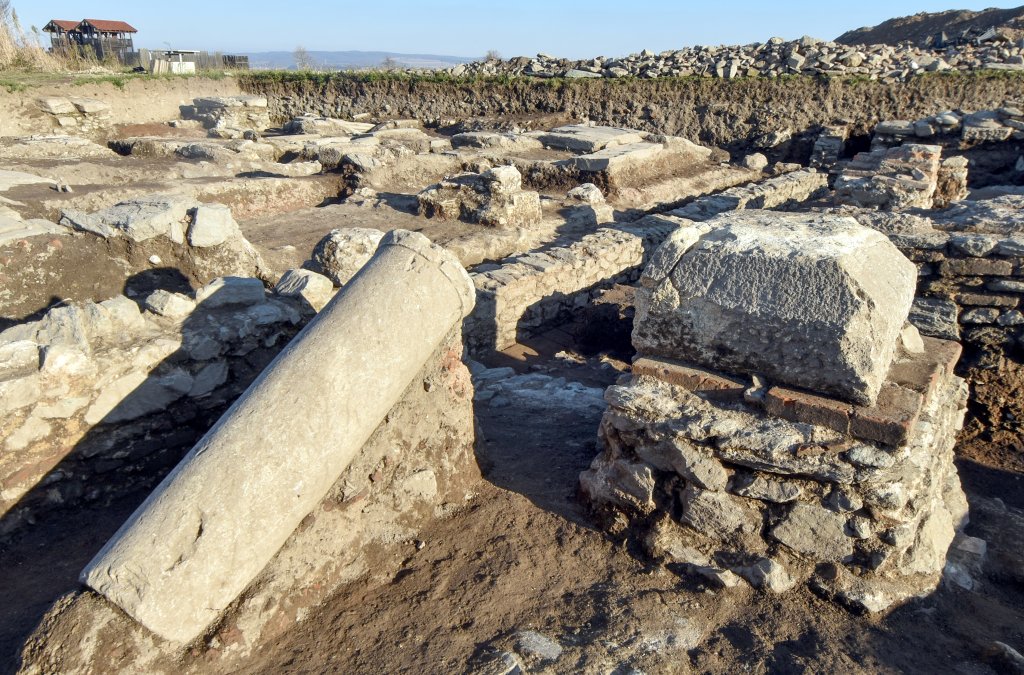
In his statement to the local press, Dr. Ilija Danković said, “The research plan meant that we first excavate the main Viminacium street – Decumanus. We located it and discovered a 10.4-meter-wide street paved with smooth stone then we came to an elaborate sewer network. The excavation confirmed that there were colonnades of columns on both sides of the street.”
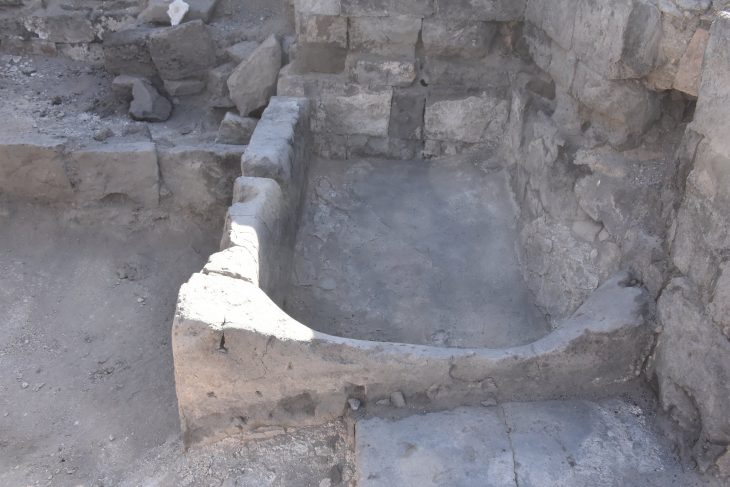
All those archaeological remains were expected until the unusual foundations of some imposing building appeared.
“We were completely surprised when we discovered that one section of the main street of Viminacium was missing the roadway and its substructure. Instead of them, we came across a foundation foot in the shape of a square, built of massive pieces of limestone. We continued our excavations and discovered three more such feet! It became clear that these were the foundations of a tetrapylon, a building on four pillars, with passages on four sides. There was no doubt that it was one of the trademarks of Roman architecture: the triumphal arch or the triumphal arch,” says Dr. Saša Redžić.
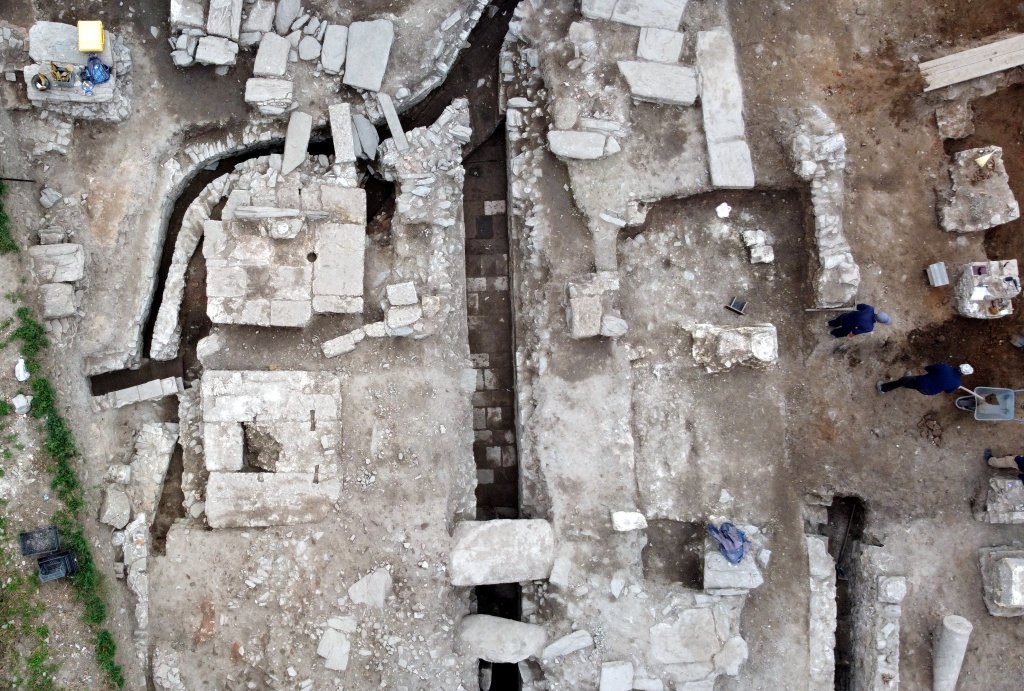

One of the most notable and influential styles of ancient Roman architecture are triumphal arches. The Roman triumphal arch was created by the Romans, who also used their expertise in arch and vault construction to create it. It was intended to honor triumphant generals as well as important public occasions like the establishment of new colonies, the building of a road or bridge, the passing of an imperial family member, or the coronation of a new emperor.
The Viminacium triumphal arch was built in the form of a tetrapylon with a single passage and an inscription field above the arched part. Its basic dimensions are 10.40 by 6.25 meters, which is extremely close to the dimensions of the Arco dei Gavi triumphal arch in Verona, whose height is 12.70 meters.
A fragment of a marble slab with letters reading CAES/ANTO suggested that the arch was dedicated to Emperor Marcus Aurelius Antoninus, known as Caracalla, who reigned from 198 to 217 AD.
Cover Photo: Serbia Archaeological Institute