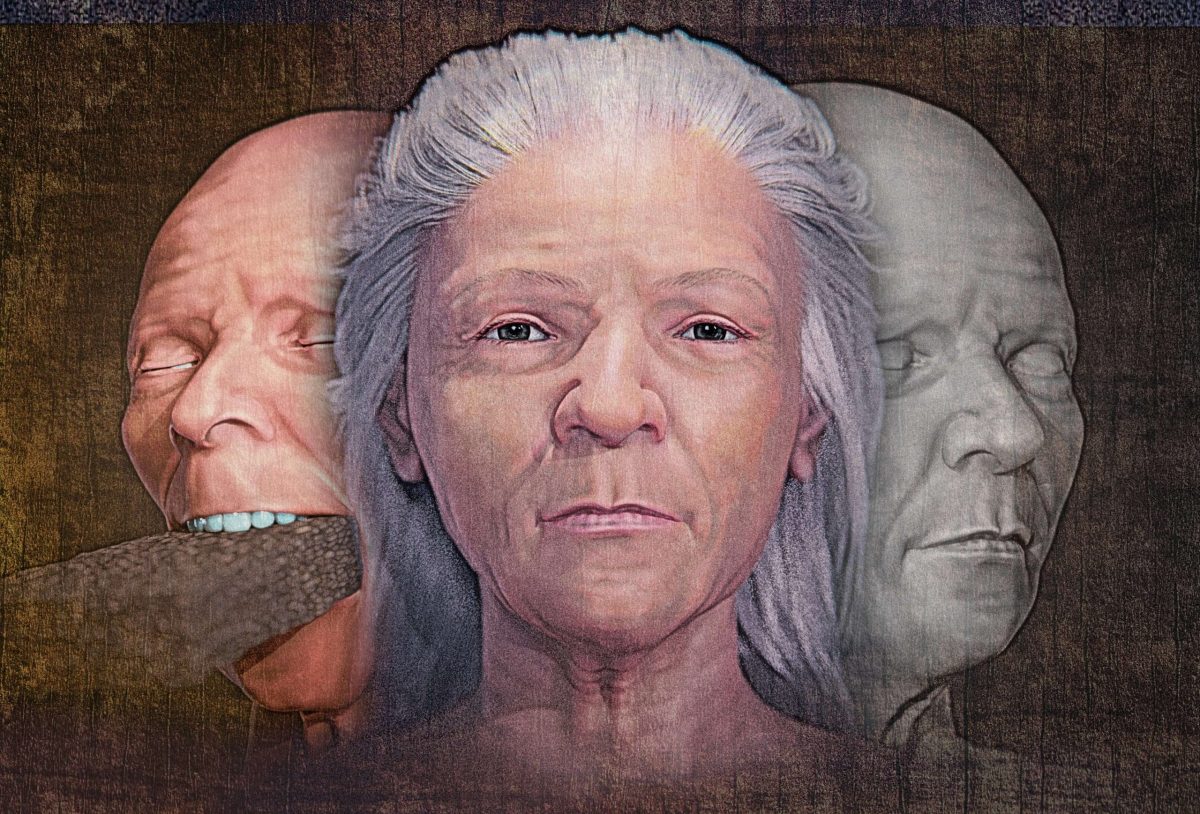
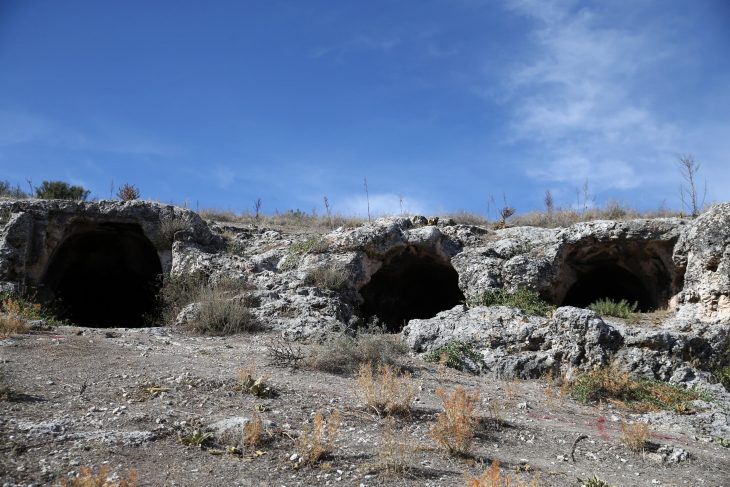
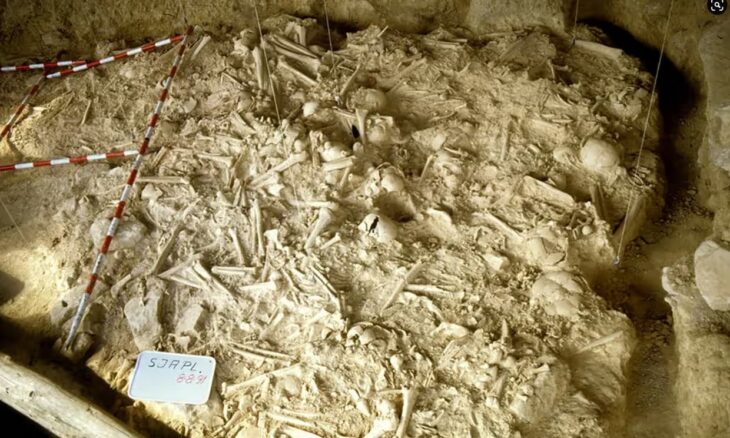
A 16th-century ‘vampire‘ who was buried with a stone brick jammed in her mouth over fears she would feed on corpses underground has had her face reconstructed by scientists.
A facial reconstruction expert reconstructed the features of the female corpse discovered in a mass grave of plague victims on the Venetian island of Lazzaretto Nuovo. Brazilian forensic expert and 3D illustrator Cícero Moraes applied features to the woman, who was unearthed in an archeological dig in 2006.
Incredible new images – made using 3D scans of her ancient skull – reveal a woman with a pointed chin, silver hair, wrinkled skin, and a slightly crooked nose.
Moraes was also able to test the theory of whether it would even be feasible to put a brick in someone’s mouth thanks to this research.
Researchers think the brick was put there shortly after she died by locals who feared she would feed on fellow victims of a plague that swept.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Forensic anthropologist Matteo Borrini led the exploration of the mass grave from the 1576 outbreak of plague. “Vampires don’t exist, but studies show people at the time believed they did,” Morrini said in a statement in 2009, after studying the case for 2 years. “For the first time, we have found evidence of an exorcism against a vampire.”
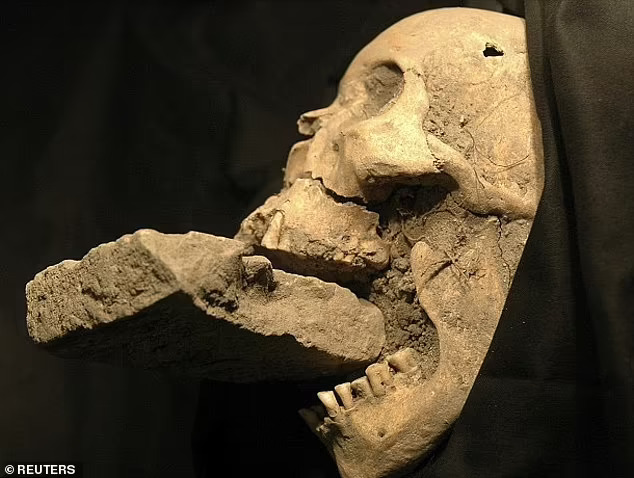

Skeletal evidence already suggests she was 61 years of age at the time of death, and further studies revealed that the skull belonged to a woman of European ancestry. An analysis of her diet shows she mainly ate grains and vegetables, suggesting she was from Europe’s lower class at the time.
Researchers theorize that a gravedigger may have wedged a rock between the corpse’s teeth to prevent the alleged vampire from chewing through her shroud and infecting others with the plague.
During this time in European history, there was a rise in vampire hysteria as villagers started looking for paranormal reasons to blame for the fatal illnesses that were ravaging the continent. It is believed that the vampire theory was disseminated by Italian gravediggers who frequently encountered horrifying decaying bodies when reopening mass burials to accommodate additional corpses.
The idea that these decaying remains were feasting on the blood of their grave-mates was reinforced by the way they frequently looked horribly bloated, with bodily fluids oozing from their mouths and noses. It’s possible that the shrouds covering the corpses’ mouths disintegrated in some instances, giving rise to the theory that vampires gained their strength by consuming these fragments of cloth.
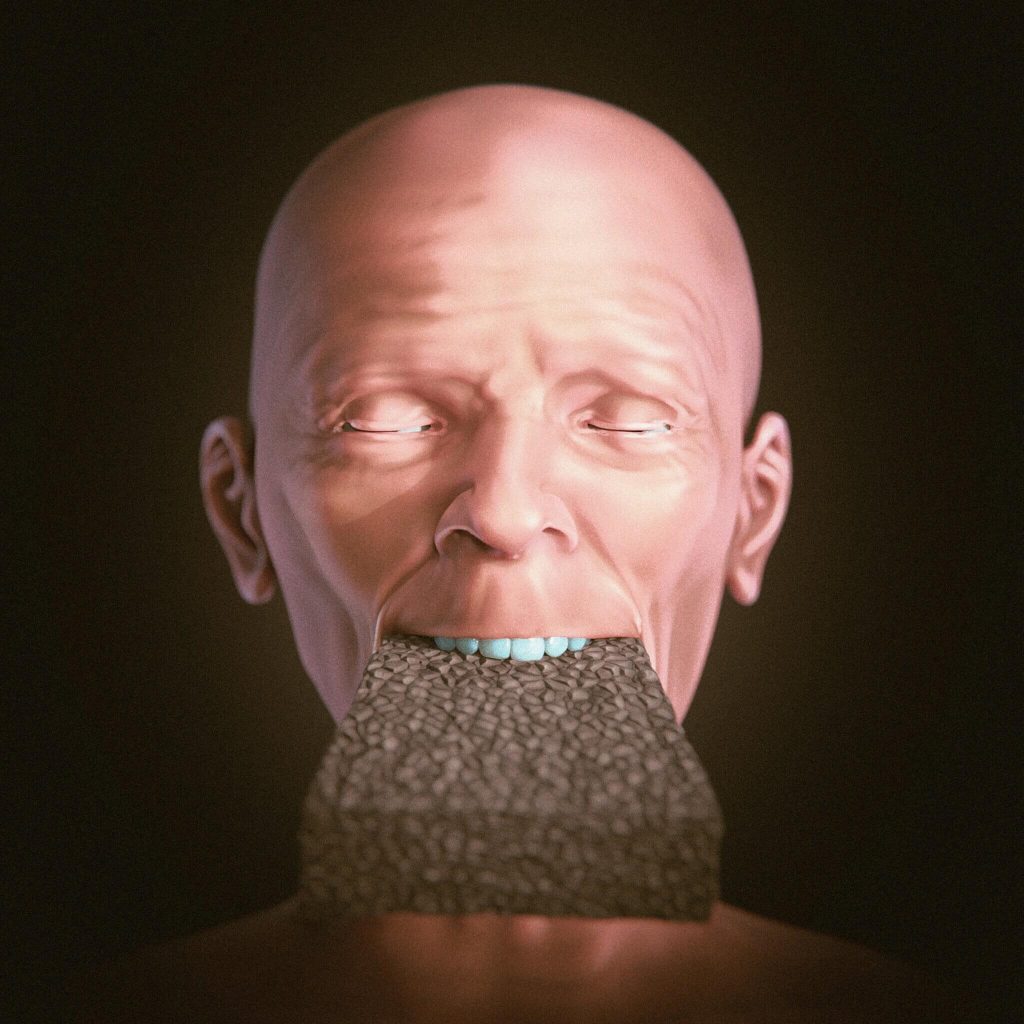
“The researchers found that when they observed the body with the shroud, those responsible for the burial noticed a depression in the mouth region, indicating potential chewing,” study authors write in the journal OrtogOnline.
“By supposedly identifying a vampire, one of the culprits of the plague according to the popular myth of the time, they introduced the stone as an element of protection, preventing it from feeding and also from infecting other people.”
In order to ascertain whether the brick could have been purposefully placed into the woman’s mouth after her death, Moraes replicated the brick using Styrofoam and carried out a number of tests. Their tests revealed that the brick could be wedged into a human mouth without causing damage to the teeth or soft tissue. Compared to the team’s living test subjects, the study authors believe it would have been even easier with the corpse, although it’s still unclear if this was done intentionally or not.
The research is published in the journal OrtogOnline.
Cover Photo: Recreation of the woman’s face using 3D software allowed examination of whether a brick could have been inserted into her mouth. Image Credit: SWNS
















