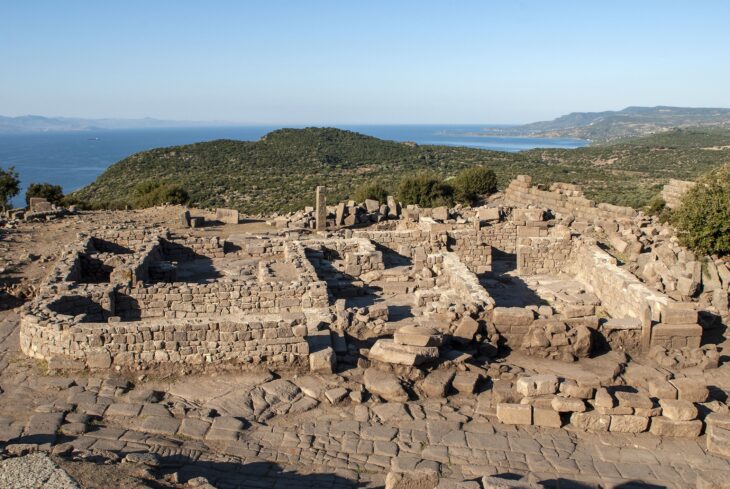
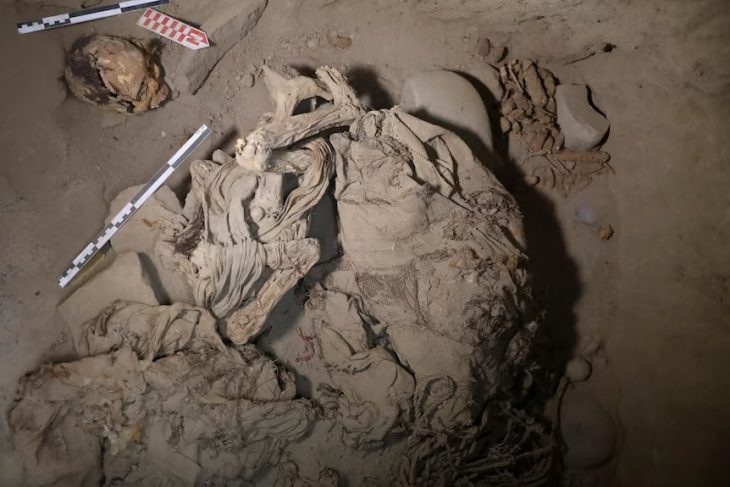
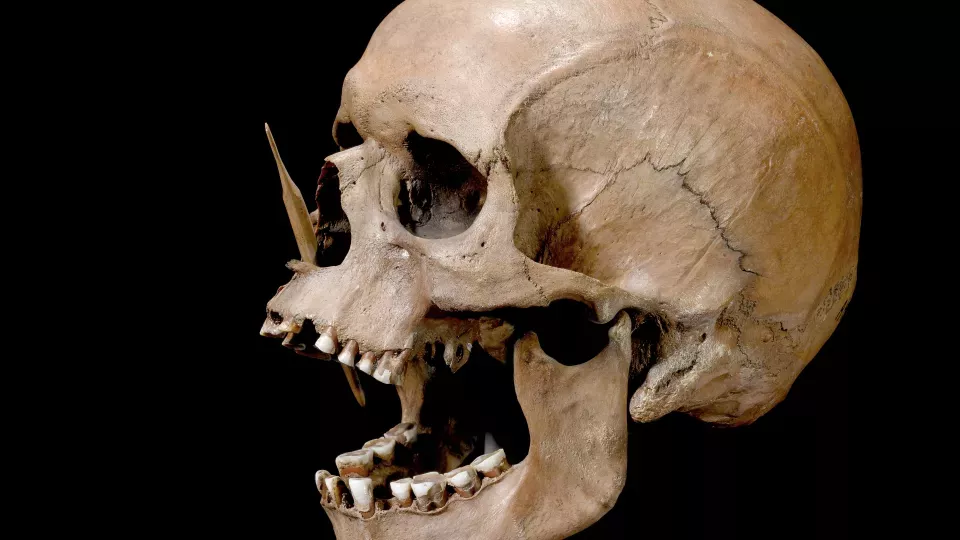
Following the arrival of the first farmers in Scandinavia 5,900 years ago, the hunter-gatherer population was wiped out within a few generations, according to a new study from Lund University in Sweden, among others.
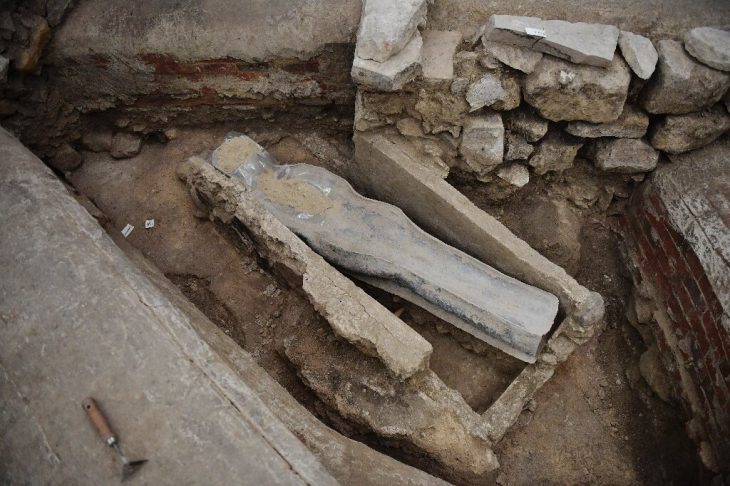
The results, which are contrary to prevailing opinion, are based on DNA analysis of skeletons and teeth found in what is now Denmark.
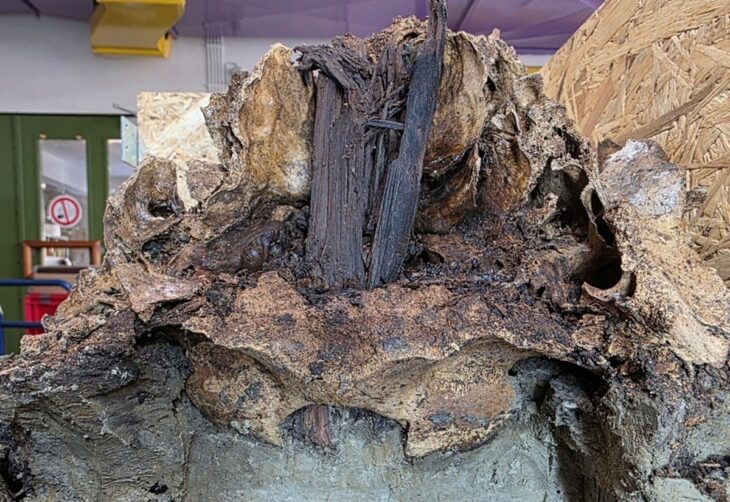
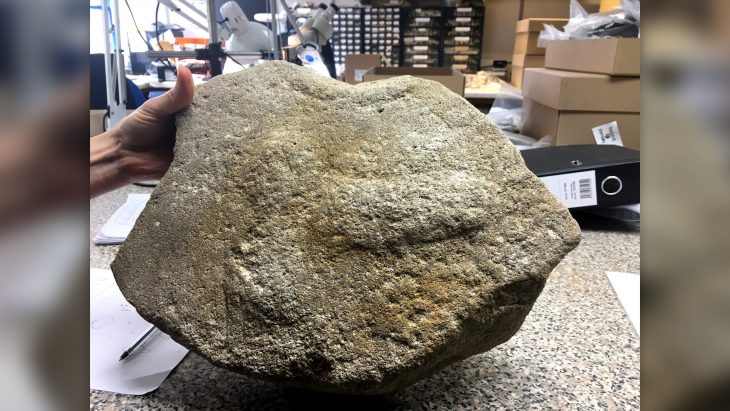
The extensive study has been published as four separate articles in the journal Nature. An international research team, of which Lund University in Sweden is a member, has been able to draw new conclusions about the effects of migration on ancient populations by extracting DNA from skeletal parts and teeth of prehistoric people.
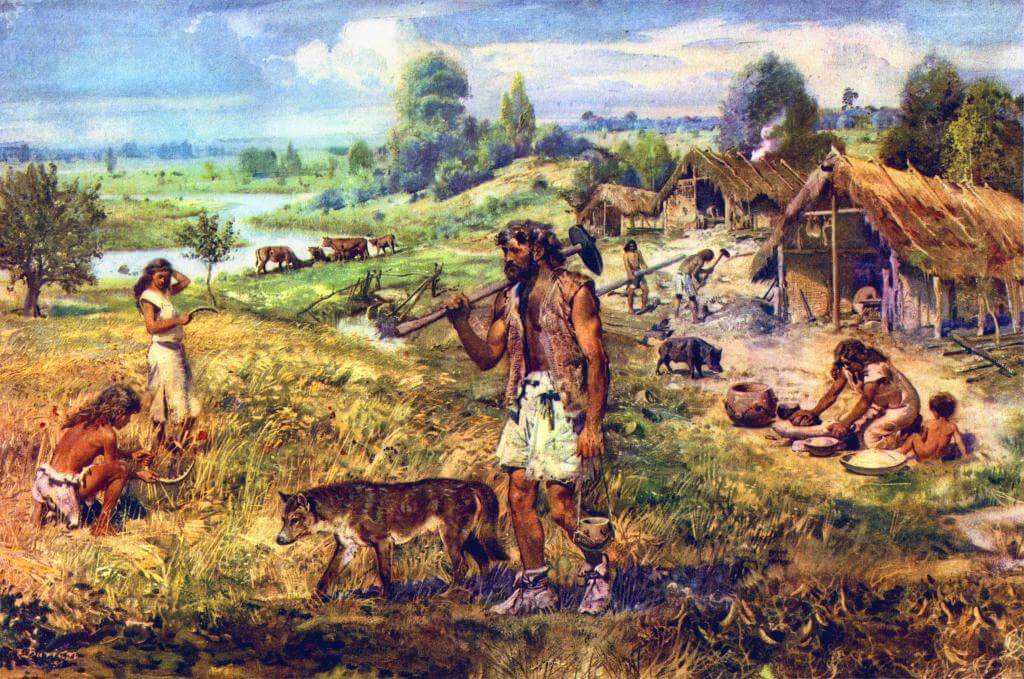
The study shows, among other things, that there have been two almost total population turnovers in Denmark over the past 7,300 years. The first population change happened 5,900 years ago when a farmer population, with a different origin and appearance, drove out the gatherers, hunters and fishers who had previously populated Scandinavia. Within a few generations, almost the entire hunter-gatherer population was wiped out.
“This transition has previously been presented as peaceful. However, our study indicates the opposite. In addition to violent death, it is likely that new pathogens from livestock finished off many gatherers,” says Anne Birgitte Nielsen, geology researcher and head of the Radiocarbon Dating Laboratory at Lund University.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Hefty livestock herders
A thousand years later, about 4,850 years ago, another population change took place when people with genetic roots in Yamnaya – a livestock herding people with origins in southern Russia – came to Scandinavia and wiped out the previous farmer population. Once again, this could have involved both violence and new pathogens. These big-boned people pursued a semi-nomadic life on the steppes, tamed animals, kept domestic cattle and moved over large areas using horses and carts. The people who settled in our climes were a mix between Yamnaya and Eastern European Neolithic people. This genetic profile is dominant in today’s Denmark, whereas the DNA profile of the first farmer population has been essentially erased.
“This time there was also a rapid population turnover, with virtually no descendants from the predecessors. We don’t have as much DNA material from Sweden, but what there is points to a similar course of events. In other words, many Swedes are to a great extent also descendants of these semi-nomads,” says Anne Birgitte Nielsen, who contributed quantitative pollen data which shows how the vegetation changed in connection with the population changes.
Valuable results for medical research
The results do not just overturn previous theories about amorous and peaceful meetings between groups of people. The study also provides a deepened understanding of historical migration flows, and the interpretation of archaeological finds and changes in vegetation and land use found in palaeoecological data.
“Our results help to enhance our knowledge of our heredity and our understanding of the development of certain diseases. Something that in the long term could be beneficial, for example in medical research,” concludes Anne Birgitte Nielsen.
In addition to Lund University, around 40 European, American and Australian higher education institutions and organizations took part in the study.
Cover Photo: An artist’s depiction of ancient Neolithic farmers. Image source.
















