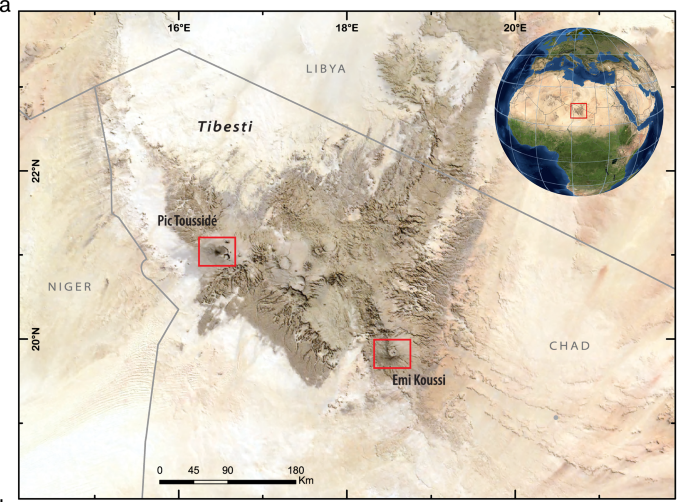
An interdisciplinary research team, led by scientists from the Free University of Berlin and the Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, was able to show how deep lakes could form in the craters of the Tibesti Mountains around 9,500 years ago and persist for over 5,000 years.
In a study published in Nature Communications, researchers have unveiled surprising insights into the climate history of the Central Sahara. During the mid-Holocene, around 7,000 years ago, the Tibesti Mountains — the highest range in the Sahara — experienced extreme rainfall levels, driven not by the well-known West African monsoon, but by moisture-laden winds from the Mediterranean Sea.
This study not only provides insights into the paleohydrological changes between the Tibesti, located in present-day Chad, and the Saharan plains during the North African Humid Period, but also demonstrates the importance of spatially high-resolution paleoclimate simulations.
Deep Lakes in a Desert Heart
Sedimentary records from the craters Trou au Natron and Era Kohor show that these once barren landscapes once hosted deep, freshwater lakes. Trou au Natron reached depths of over 330 meters, while Era Kohor filled to around 130 meters. Such massive bodies of water in the middle of today’s arid Sahara were made possible by a climate system far different from what scientists had previously imagined.
A Mediterranean Connection
For decades, experts assumed the African Humid Period — also known as the Green Sahara — was primarily driven by intensified monsoon rains from the south. But high-resolution climate models reveal a different story: strong orographic uplift in the Tibesti Mountains allowed moisture-rich north-easterly winds from the Mediterranean to release enormous rainfall over the region. This process created precipitation levels at least ten times higher than in the surrounding plains.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Lead author Philipp Hoelzmann from Freie Universität Berlin emphasizes the significance: “Our study demonstrates that the Mediterranean, not just the African monsoon, played a crucial role in sustaining high-altitude lakes in the Sahara.”
Why the Lakes Differed
Interestingly, the two crater lakes did not behave in the same way. Trou au Natron, located in the northwestern Tibesti, was sustained by heavy Mediterranean-fed rainfall. Era Kohor, in the southeastern Tibesti, received much less precipitation due to its leeward position. This explains the dramatic differences in water volumes between the two lakes.
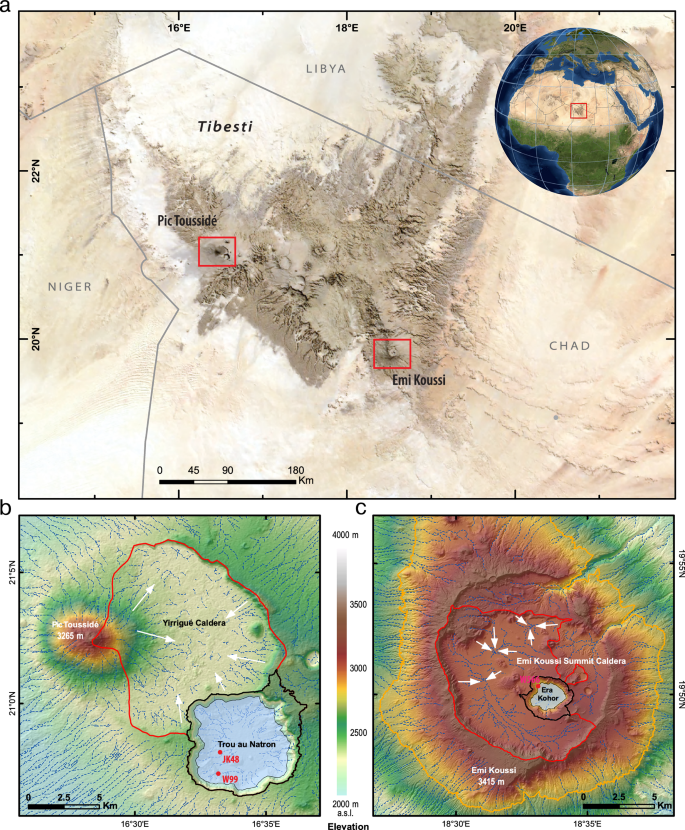
Rethinking Climate Models
The research team combined sediment analysis, satellite-based terrain studies, and advanced 5-kilometer resolution climate simulations to reconstruct the hydrological balance of these ancient lakes. Their results highlight a major shortcoming in current Earth System Models: they smooth out mountainous terrain, underestimating orographic rainfall. As a result, past simulations have failed to capture localized wet zones within the Sahara.
“By resolving the fine-scale topography, we discovered that precipitation in Tibesti was far greater than previously thought,” explains co-author Martin Claussen of the Max Planck Institute for Meteorology. “This has huge implications for both past and future climate scenarios.”
Lessons for the Future
The findings not only reshape our understanding of Sahara’s climate history but also carry warnings for the future. As global warming intensifies, climate models project wetter conditions in the Sahel and southern Sahara. However, without accounting for mountainous orography, these models may miss crucial details about where extreme rainfall — and potentially devastating floods — could occur.
The Sahara’s past is a reminder that deserts are not eternally dry wastelands. Under the right conditions, even the world’s largest hot desert can bloom with lakes and life. As scientists refine climate predictions, the Tibesti Mountains stand as both a historical archive and a warning system for future environmental shifts.
Hoelzmann, P., Claussen, M., Dallmeyer, A. et al. Mid-Holocene extreme precipitation in the Tibesti, Central Sahara. Nat Commun 16, 7426 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-62769-9
Cover Image Credit: Hoelzmann, P., Claussen, M., Dallmeyer, A. et al.