A research team at the University of Cordoba has identified, for the first time, the composition of a Roman perfume more than 2,000 years old.
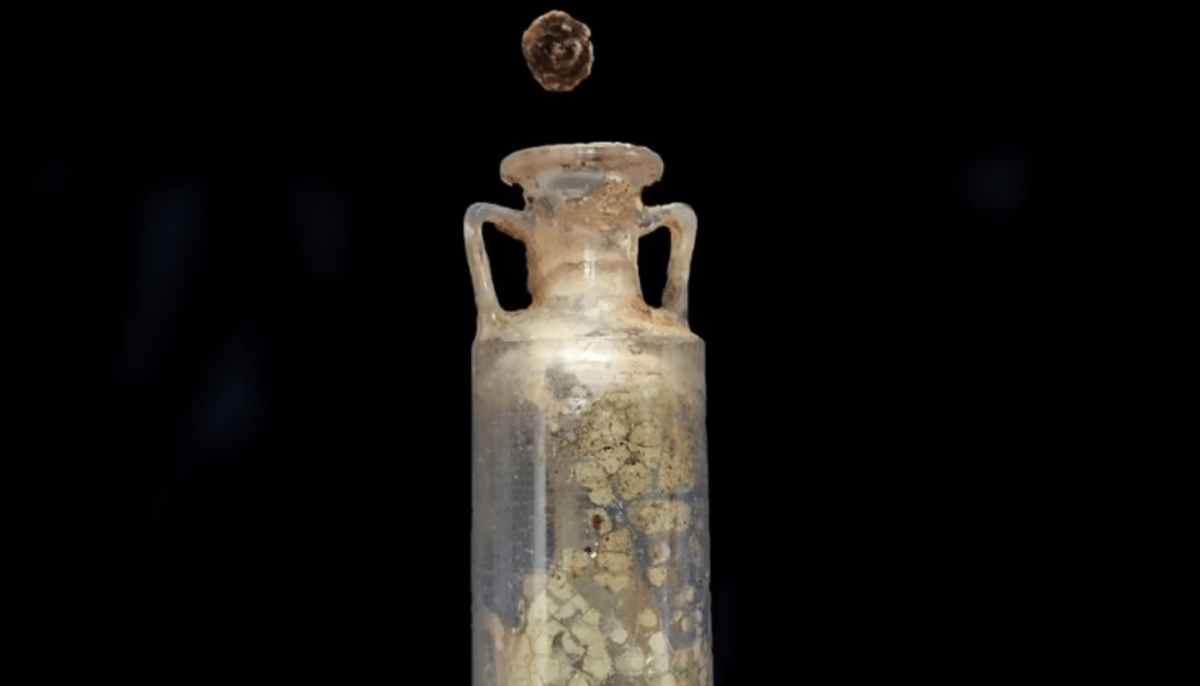
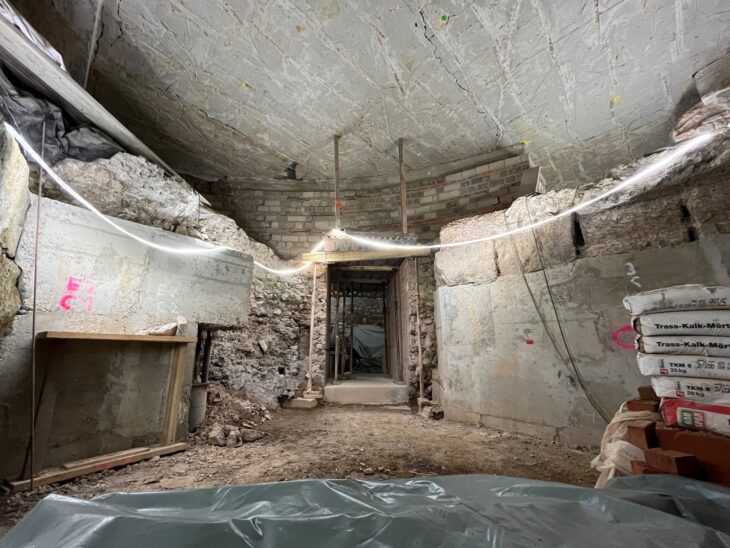
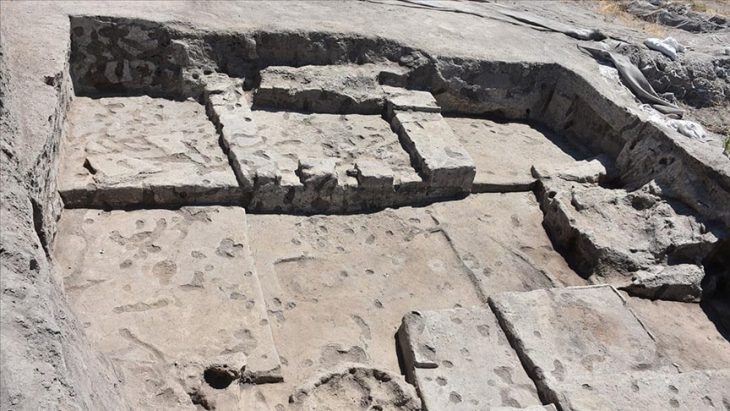
Everything began in 2019 during the renovation of a structure in the Carmona municipality of Seville. Archaeological remains were discovered, and the workers informed the town hall. What was discovered was a mausoleum from 2,000 years ago with eight niches that was “in magnificent condition” because it had never been looted. The remains of six members of a wealthy family were interred in the communal grave. And there were various offerings on them, one of which was a quartz container with “a solid mass inside.” They belonged to the niche of a woman in her 40s.
That bottle, which had been wrapped in a cloth bag of which remains were still left and was accompanied by amber stones, was taken to the laboratory and since then it has been analyzed by a team of researchers.
One of the amphora’s unique features is that it was carved in quartz, a very hard, resistant, and unusual material. At the time, ointments were made of glass, and the researchers claim that by using this other material, they are dealing with an item that was “highly sought-after and expensive.”

In addition to the uniqueness of the receptacle, the truly extraordinary aspect of the find was that it was perfectly sealed, and that the solid residues of the perfume had been preserved inside, which made it possible to carry out this study.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The FQM346 research team at the University of Cordoba, led by Professor of Organic Chemistry José Rafael Ruiz Arrebola, in collaboration with the City of Carmona, has chemically described the components of a perfume dating from the first century AD.
The results were published in the Swiss scientific journal Heritage in an article in which Ruiz Arrebola, the municipal archaeologist of Carmona, Juan Manuel Román; and UCO researchers Daniel Cosano and Fernando Lafontshare the whole technical and scientific process enabling the world to”smell” the bygone Roman Empire.
Ruiz Arrebola stresses that the use of dolomite, a type of carbon, as a stopper, and the bitumen used to seal it, were the key to the magnificent state of preservation of the piece and its contents.
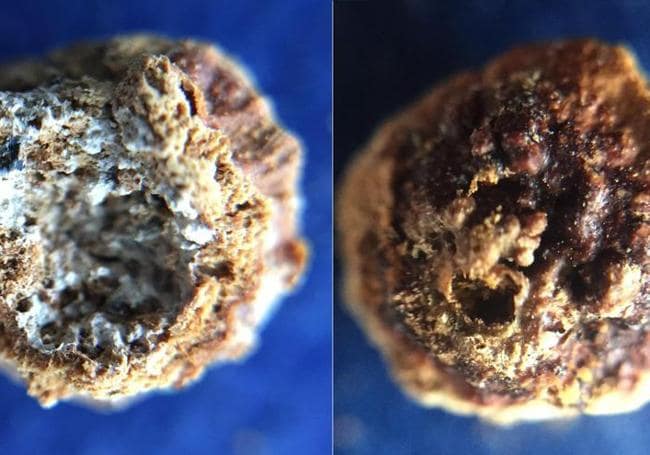
Researchers to ascertain what the perfume was made of, different instrumental techniques were used, such as X-ray diffraction and gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry, among others.
With respect to the perfume, two components have been identified: a base or binder, which allowed for the preservation of the aromas, and the essence itself, these findings according with descriptions by none other than Pliny the Elder. In this case, the base was a vegetable oil; possibly, according to some indications reflected in the analysis, olive oil, although this point could not be confirmed with certainty.
According to the results of chemical analyses carried out by the University of Cordoba, Rome smelled of patchouli, an essential oilobtained from a plant of Indian origin, Pogostemon cablin, widely used in modern perfumery, and whose usein Roman times was not known.
The monumental characteristics of the tomb where it was found and, above all, the material of which the vessel containing it was made, suggest that it was a highly valuable product.
















