Trier, once a significant economic and political center in the northern provinces of the Roman Empire, is set to be the focus of a new research project funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG). With a budget of €340,000, a team from the Rhineland State Museum Trier, Goethe University Frankfurt, and the Leibniz Center for Archaeology will explore the production and distribution of ancient building materials, particularly fired bricks, over the next two years.
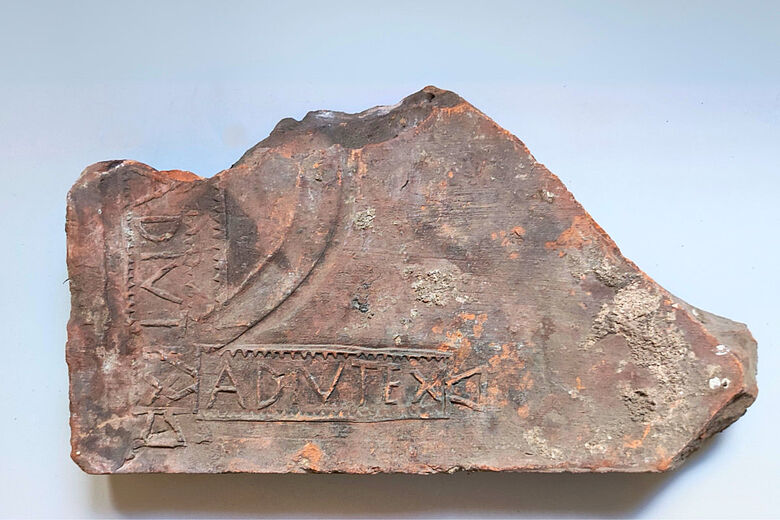
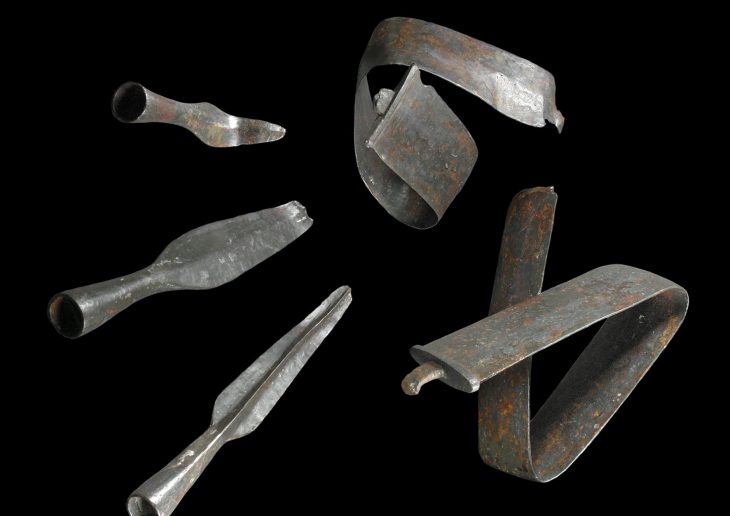
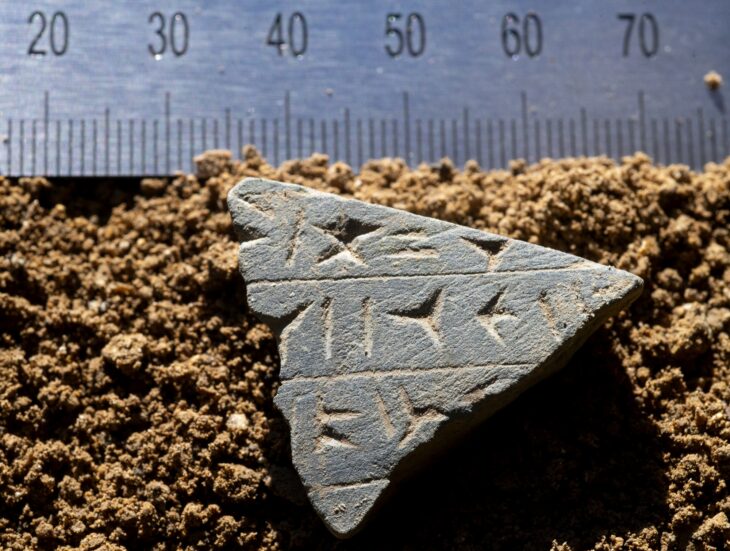
Trier reached its peak in the 4th century AD, when Roman emperors resided in the city, leaving behind monumental structures such as the Imperial Baths and the Basilica of Constantine. Among the building materials used were fired bricks of various sizes for walls, roofs, and heating systems. An estimated 4,000 stamped bricks from Roman times are currently stored in the depots of the Rhineland State Museum Trier, making it one of the largest collections from the northern Roman provinces. However, these artifacts have only been partially studied until now. The research team aims to provide a comprehensive overview of these bricks, shedding light on the brick production as a significant economic sector in the expansion of ancient Trier.
“We assume that most of the stamped bricks date back to late antiquity. This allows us to conduct a thorough analysis of how building ceramics were produced and utilized during this period,” explains Dr. Thomas Schmidts, a lecturer in Roman Archaeology at LEIZA in Mainz. “Thus, the brick stamps are also a key to understanding the economic and social structures of late antiquity,” he adds.

The project will evaluate the spatial distribution of the bricks to trace the architectural development of Augusta Treverorum, the Roman name for Trier, which was referred to as Treveris in late antiquity. Previously unknown state and public construction projects may be identified through this research. Additionally, the researchers plan to quantify the production, transport, and construction processes involved in late antique brick production. For the first time, archaeometric investigations will be conducted on the Trier bricks, analyzing the material properties, specifically the chemical composition of the clay, to provide insights into the raw materials used. This will help identify or confirm individual workshops.
“We are very pleased that our joint application was successful in the competitive DFG process. By combining the outstanding expertise of researchers in provincial Roman archaeology with a broad methodological spectrum, which LEIZA also represents, we can gain increasingly groundbreaking insights,” emphasizes Dr. Alexandra W. Busch, Director General of LEIZA. “The project results will not only expand our knowledge of late antique building ceramics but will also contribute to the reconstruction of Trier’s development as a model study that integrates classical and archaeometric methodologies.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
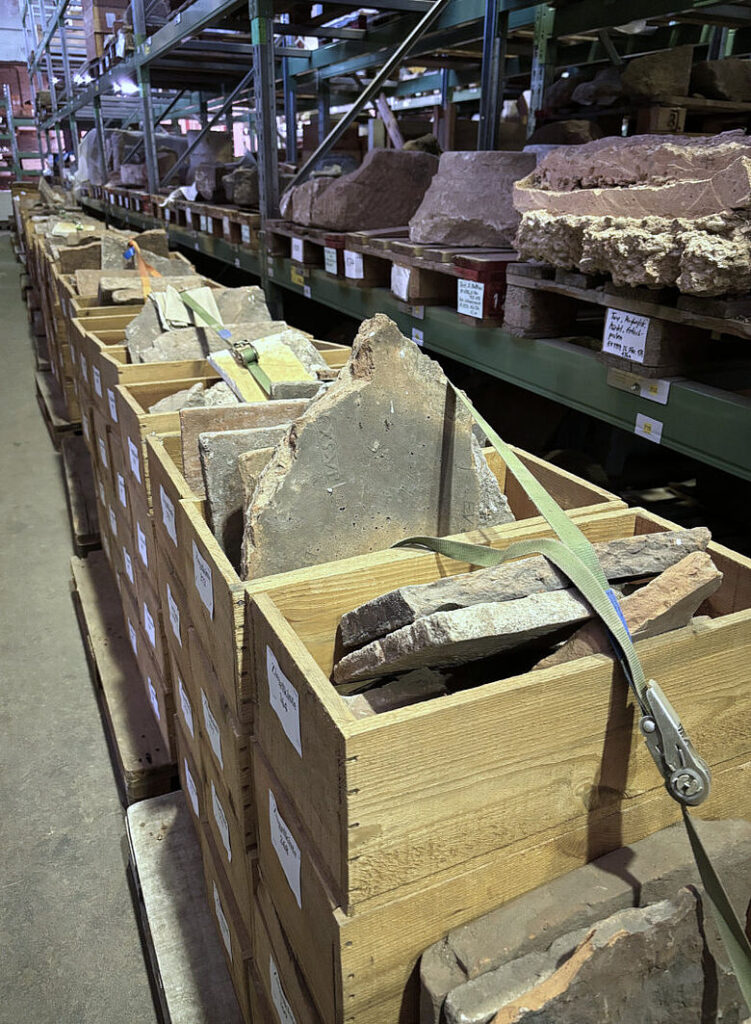

The project, titled “The Roman Brick Stamps from Trier – A Contribution to the Study of the Organization of Ancient Building Ceramic Production and Distribution for the Expansion of a Metropolis in Northern Gaul,” has received funding of €340,000 from the DFG for two years. The applicants include Schmidts, Prof. Dr. Markus Scholz from the Institute of Archaeological Sciences at Goethe University Frankfurt, and Dr. Marcus Reuter, Director of the Rhineland State Museum Trier, which is part of the General Directorate for Cultural Heritage Rhineland-Palatinate (GDKE).
This initiative is also part of the “Research Focus on Roman Archaeology and Maritime Antiquity (FoRuM)” in Rhineland-Palatinate, a strategic alliance between LEIZA, the University of Trier, and GDKE aimed at advancing top-tier research on antiquity.
Cover Image Credit: Fragment of a brick with two stamps, 4th century AD. Credit: Markus Helfert, Goethe University Frankfurt am Main