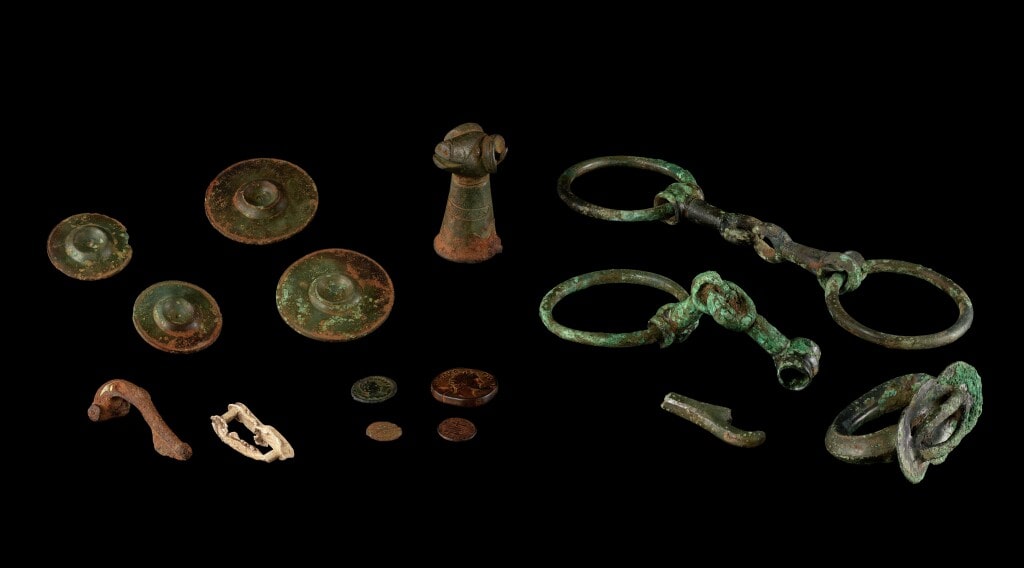
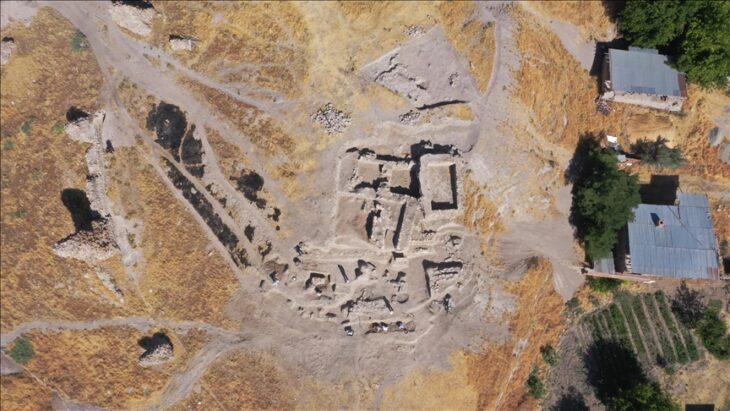
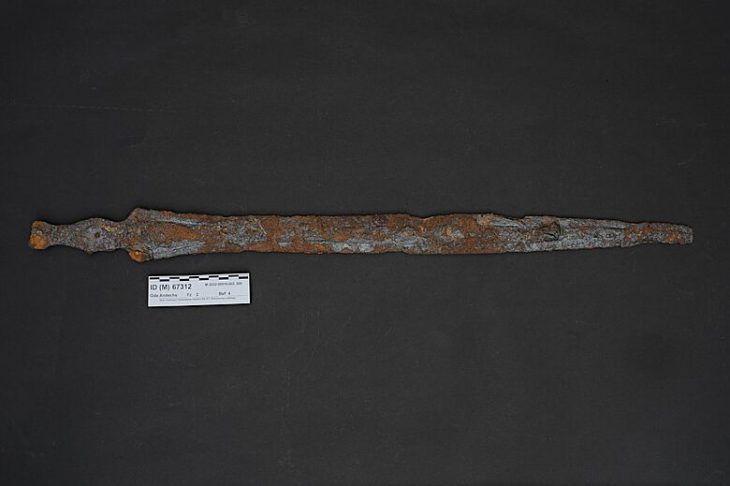
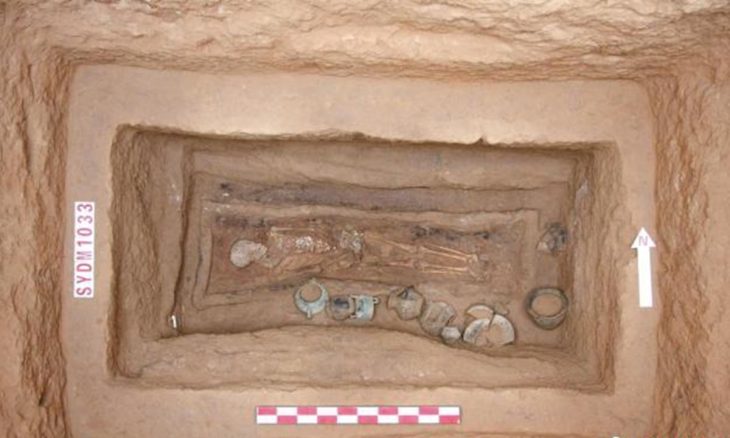
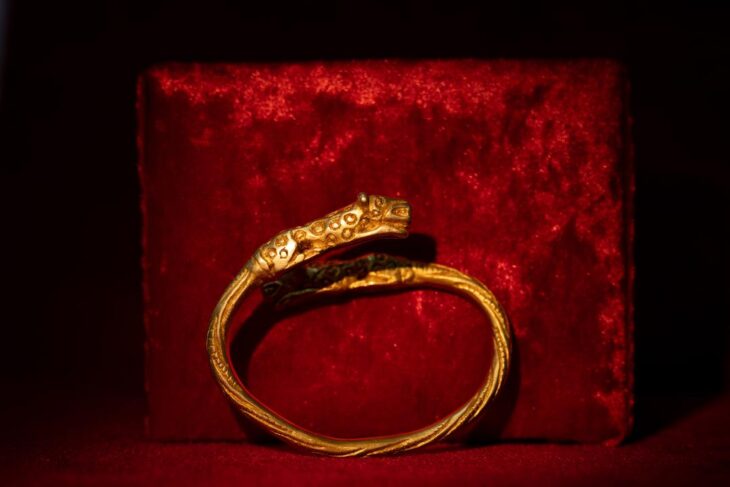
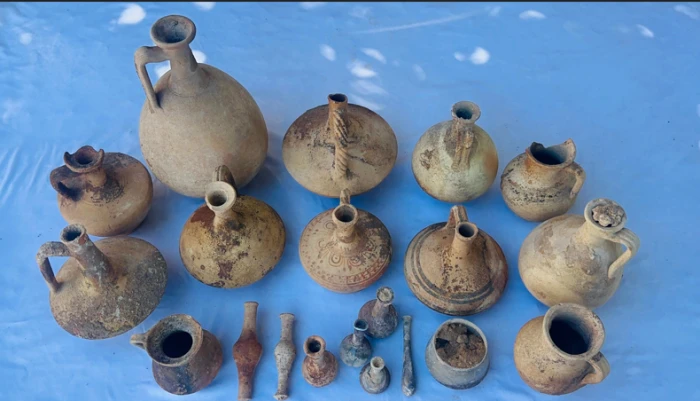
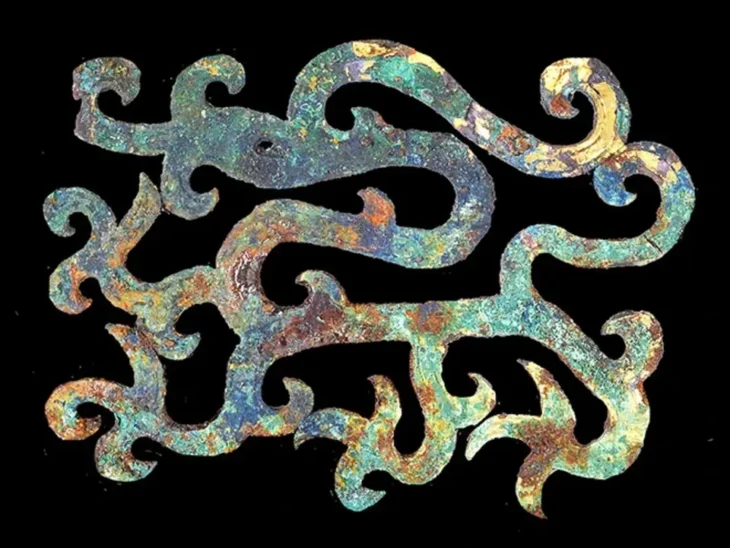
Metal detectorist Ian Porter unearthed sixteen historical artifacts in a boggy field on Anglesey. Among the items found were Iron Age chariot fittings, a metal ram’s head, and a Roman copper ingot, and offer a window into the island’s rich past during the Iron Age and Roman times.
Ian Porter made the discovery on March 4, 2020, while metal detecting in a field under pasture in the Llanfair-Mathafarn-Eithaf Community.
The unusual bronze, copper, and lead artifacts are believed to have been gifted as repeated religious offerings around an ancient sacred spring source during the Late Iron Age and into the Romano-British period.
The additional artifacts, all of Roman date, include a decorated brooch, four coins, and a lead pot repair. A large and complete Roman copper ingot weighing 20.5kg was also discovered, probably smelted copper deriving from the nearby Roman copper mine at Parys Mountain.
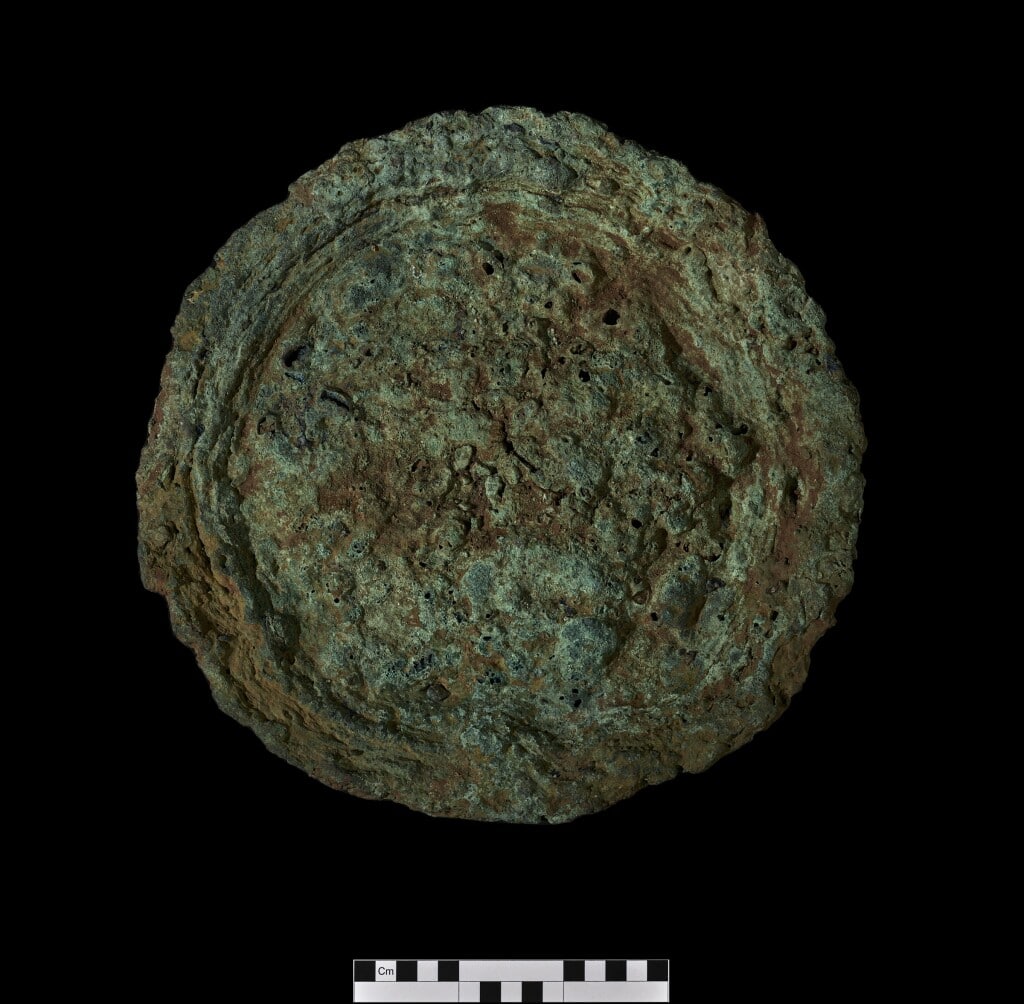

The chariot fittings, cavalry harness pieces, and brooch were all placed around AD 50-120, around the time of, or soon after the invasion of the island by the Roman army in AD 60/61.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The coins and other artifacts suggest a continuing practice of votive gifting around the spring throughout the Roman period, the latest coin in the group being struck around AD 364-378.
Adam Gwilt from Amgueddfa Cymru, Museum Wales, emphasized the role of these finds in understanding ancient religious ceremonies against a backdrop of conflict and change.
Gwilt said: “This culturally mixed artifact group, containing both Iron Age chariot fittings and Roman cavalry fittings, is an important new find for the island.
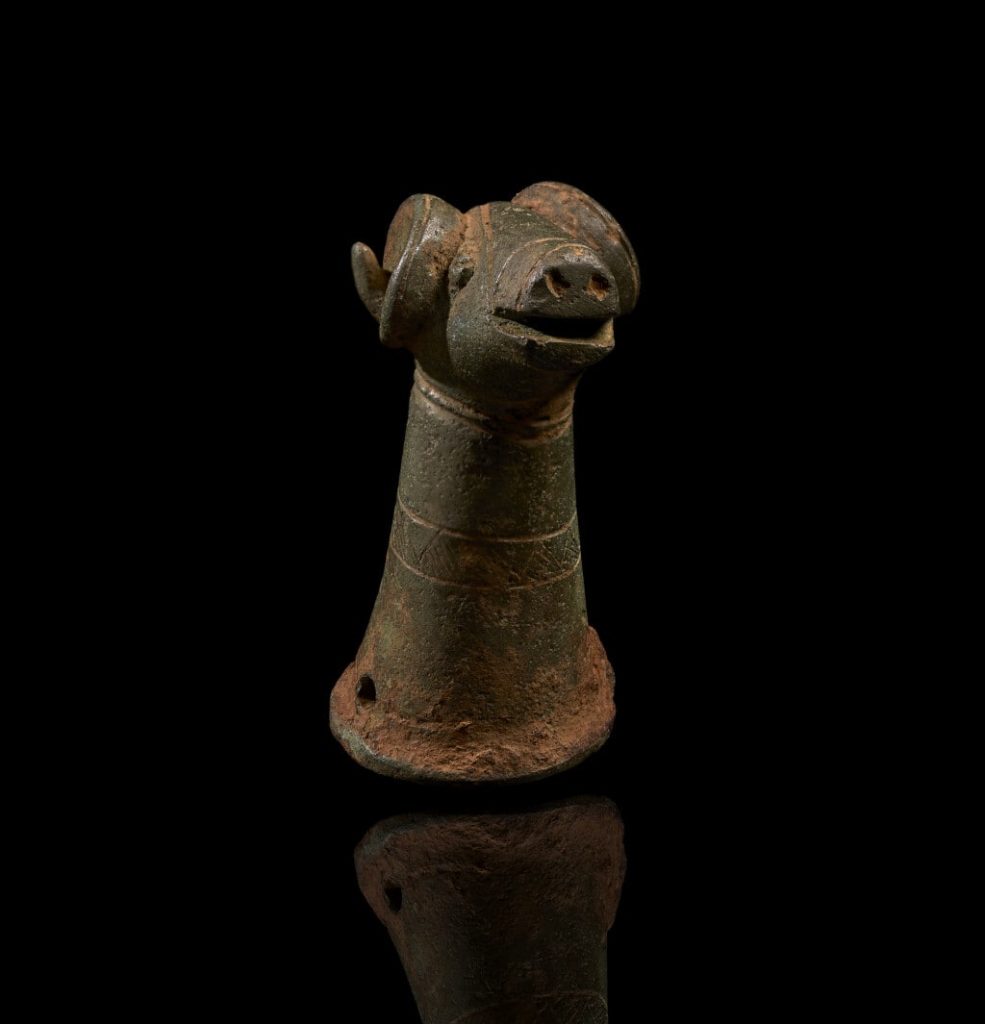

Artifacts were declared treasure by the senior coroner for north-west Wales. They provide unique insights into the cultural and religious practices on Anglesey, an island of significant historical importance during the Roman invasion of Britain.
The presence of Iron Age and Roman artifacts near the sacred spring indicates a blending of cultures and traditions, emphasizing the complex relationship between native inhabitants and Roman invaders. This discovery sheds light on the religious significance of watery sites, which were frequently used for offerings during times of upheaval.
“The ram’s head fitting, probably a vehicle-fitting or staff head is decorated in the late Celtic art style. It is a closely observed and quirky depiction of the ram and a likely future ‘star’ exhibit loved by many for Oriel Môn,” Gwilt added.