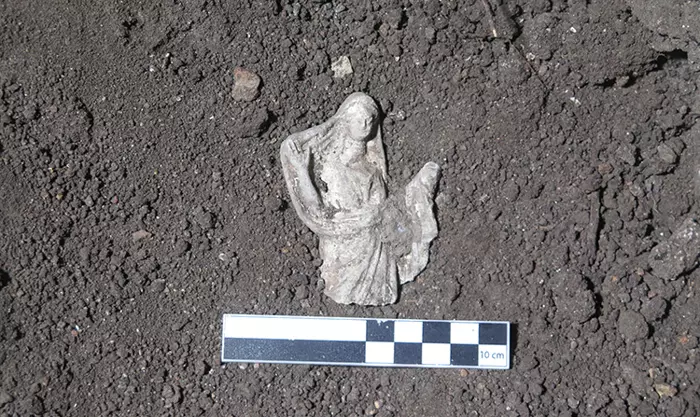
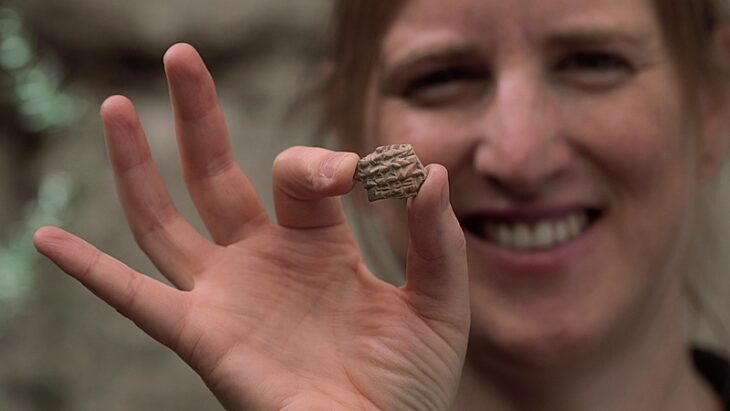Archaeologists working near Jerusalem have uncovered a rare 2,000-year-old oil lamp and a writing stylus dating to the Hasmonean period, offering new evidence of organized Jewish life during the Second Temple era.
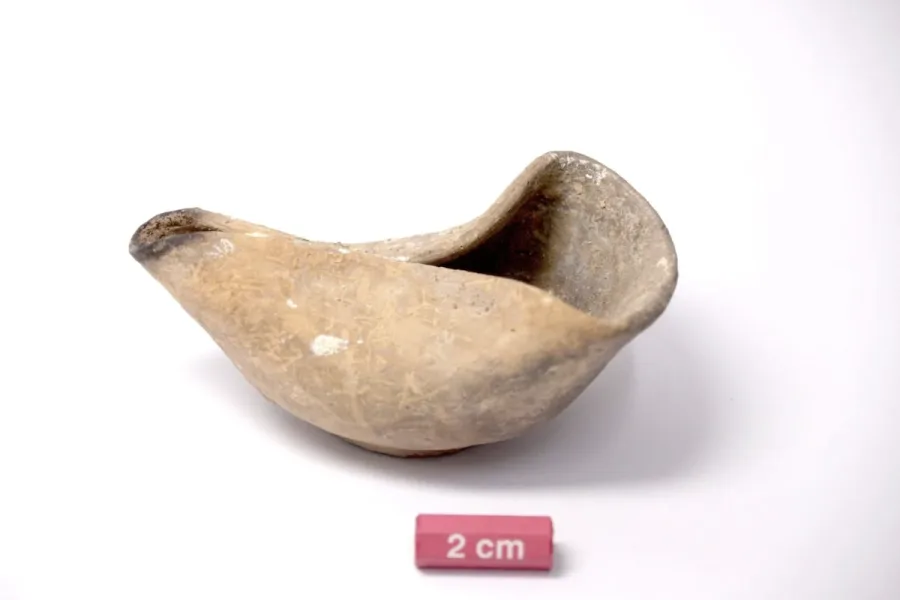
As the first candle of Hanukkah is lit each year, it recalls resilience, continuity, and the enduring power of light. This season, that symbolism took on a tangible form near Jerusalem, where archaeologists uncovered a rare clay oil lamp dating back to the Hasmonean period—nearly two millennia ago. Discovered at the historic site of Nabi Samuel, northwest of the city, the artifact offers compelling evidence of Jewish life during the era of the Second Temple.
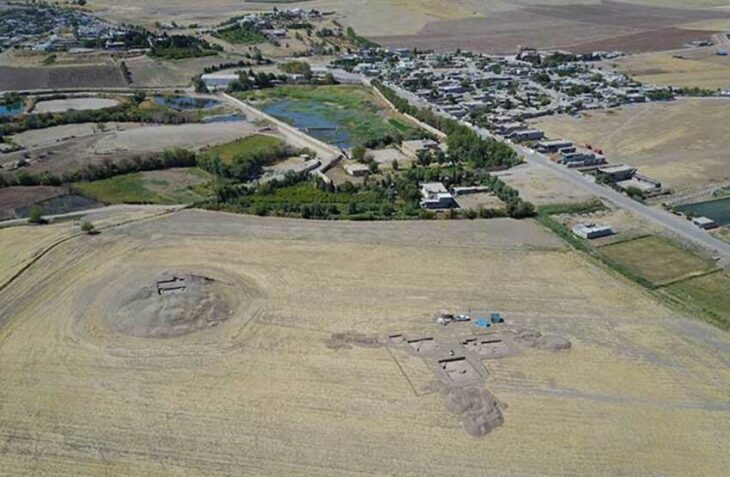
The find emerged during ongoing archaeological work conducted by Israel’s Civil Administration through the Coordination of Government Activities in the Territories (COGAT). Within the organization, a specialized unit known as KAMAT Archaeology is responsible for excavations, documentation, and preservation across Judea and Samaria. Their work at Nabi Samuel has revealed layers of human activity spanning thousands of years, but the newly uncovered Hasmonean lamp stands out for its cultural and symbolic resonance.
A Window into Hasmonean Daily Life
The small clay lamp—once filled with oil and lit with a simple wick—was a household object, likely used to illuminate homes during long evenings. Its discovery near Jerusalem underscores a settled, organized Jewish presence in the region during the Hasmonean dynasty (circa 140–37 BCE), a period marked by political independence and religious revival.
Alongside the lamp, archaeologists also uncovered a stylus, a writing instrument used on wax tablets. This modest tool hints at literacy, administration, and everyday communication—suggesting that life here was not only religiously vibrant but also socially and culturally structured. Together, the artifacts paint a picture of a community engaged in routine tasks, governance, and learning, all within reach of Jerusalem.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Nabi Samuel: A Strategic Hilltop Through the Ages
Rising approximately 885 meters (2,900 feet) above sea level, Nabi Samuel commands sweeping views of the approaches to Jerusalem. Its strategic importance has attracted settlers, soldiers, and worshippers for millennia. Excavations reveal an extraordinary sequence of occupation layers—from the Israelite and Persian periods to the Hasmonean era, and later through the Crusader and Ottoman times.
Among the most prominent remains are the foundations of a massive Crusader fortress and a mosque traditionally associated with the tomb of the biblical prophet Samuel. This dense archaeological tapestry makes Nabi Samuel one of the most significant sites for understanding the political, military, and religious history of the Jerusalem hinterland.
Archaeology as Cultural Memory
The Hasmonean lamp and stylus now join a growing list of discoveries made by KAMAT Archaeology in recent years. Using modern surveying techniques and meticulous documentation, the team aims not only to uncover artifacts but also to preserve them and make their stories accessible to the public.
Benjamin Har-Even, head of KAMAT Archaeology, emphasized the timing of the discovery during Hanukkah. The festival commemorates the endurance of the Jewish people and the rededication of the Temple in Jerusalem. Finding a lamp from the Hasmonean period—an era directly tied to the Hanukkah story—adds a powerful layer of meaning. It is a reminder that the traditions celebrated today are rooted in lived experiences from antiquity.
Light That Crosses Millennia
Small archaeological objects often reveal more about the past than monumental ruins. This unassuming clay lamp, once held in a human hand and lit at dusk, bridges past and present. It transforms abstract history into something intimate and immediate—a flicker of light that once chased away darkness in a home near Jerusalem.
As Hanukkah candles glow anew, this ancient lamp tells a parallel story: of continuity, of daily life shaped by faith, and of a people deeply connected to their land. After 2,000 years beneath the soil, its rediscovery allows history itself to shine—quietly, steadily, and with enduring warmth.
Cover Image Credit: A clay lamp from the Hasmonean period found at Nebi Samuel north of Jerusalem, in a discovery made public on December 15, 2025. COGAT