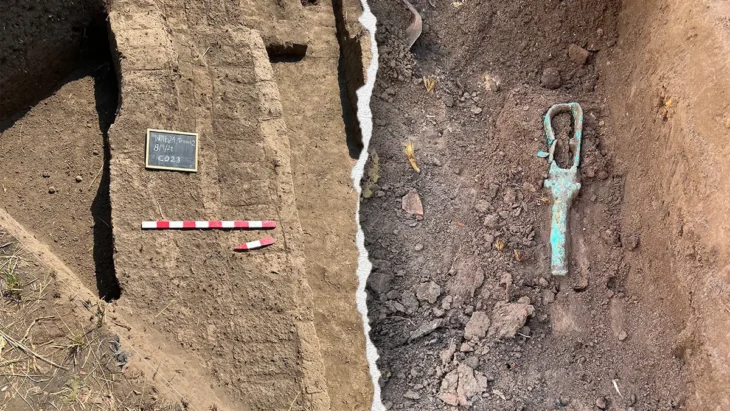
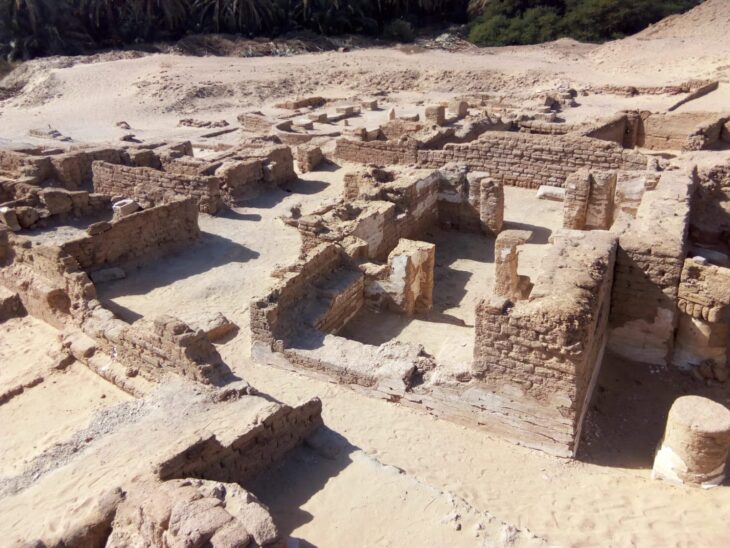
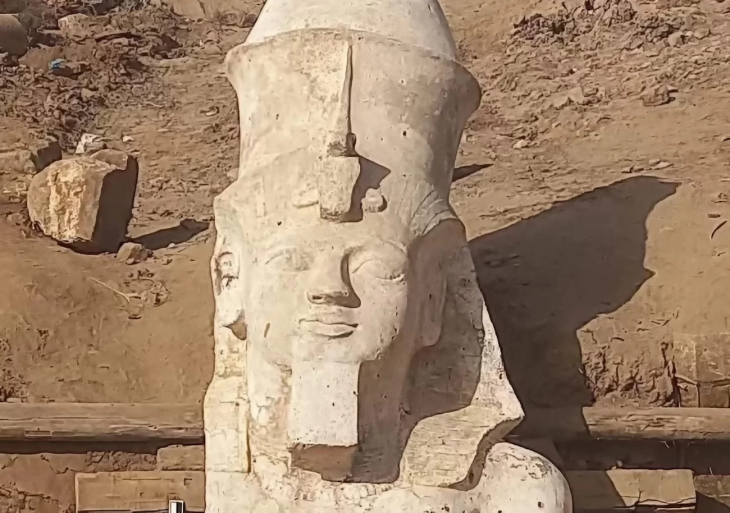
Ramses the Great was the name given to Ramses II, also known as Ramesses or Rameses. He was the third king of the lineage of ancient Egypt, reigning from 1292 to 1190 BCE. His reign was the second-longest in Egyptian history.
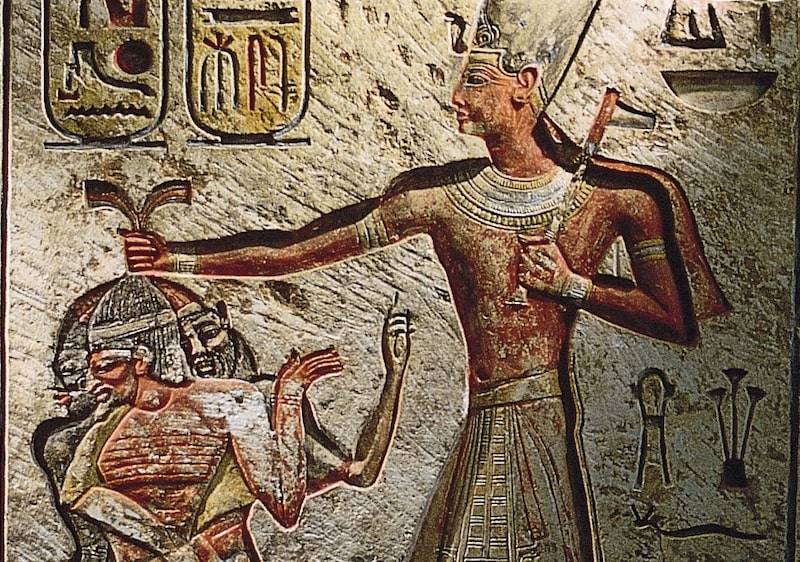
Rameses II (right 19th dynasty), Seti I’s son, was about thirty years old when he became king of Egypt – and reigned for 67 years. He had many wives, including those of his own close relations, and was the father of approximately 111 sons and 51 daughters.
The threat of international invasion against Egypt was always at its highest on the ascension of a new Pharaoh, as was customary in those days. Subject kings no doubt saw it as their responsibility to put a new king in Egypt to the test. Similarly, if the new Pharaoh was to hold peace throughout his reign, he had to make a show of power.
As a result, in his fourth year as pharaoh, Rameses was waging a series of campaigns in Syria against the Hittites and their allies. The Hittites, on the other hand, were a formidable adversary, and the battle lasted twenty years.
In the end, neither side was victorious and the first peace treaty in history was signed. Finally, after several years of conflict, Rameses was forced to sign a treaty with the Hittites. Egypt promised not to attack Hittite territory, and the Hittites agreed not to invade Egyptian territory. They have agreed to form a defense alliance to deter popular adversaries, as well as reciprocal assistance in fighting Syrian rebellions and an extradition treaty.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
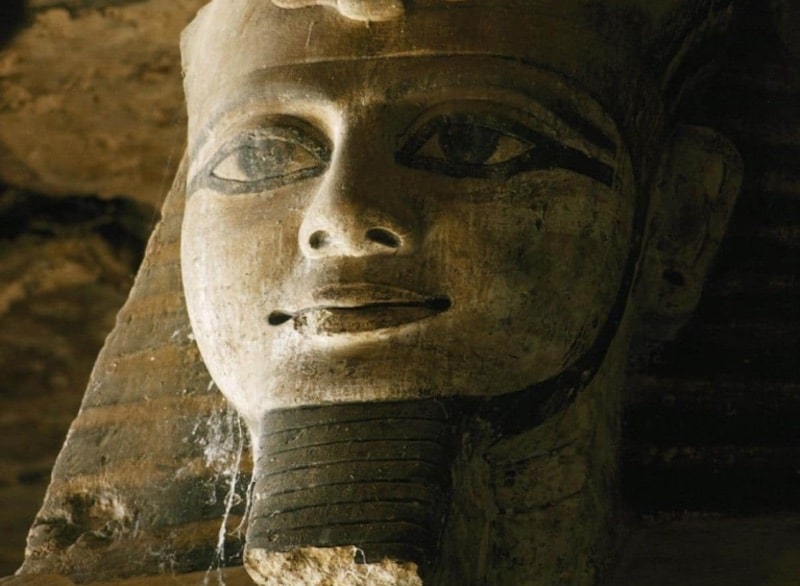

Rameses married the Hittite King’s daughter thirteen years after the treaty was signed, in the thirty-fourth year of his reign. Ueret-ma-a-neferu-Ra was her Egyptian name, which meant “Great One who sees the beauties of Ra.”
He is renowned for his massive construction projects and the numerous monumental sculptures of him that can be seen all over Egypt, in addition to the great wars he waged with the Hittites and Libyans.
One measure of Egypt’s prosperity is the number of temple structures the kings could afford, and on this basis, the reign of Ramses II is most remarkable in Egyptian history. He completed the great hypostyle hall at Karnak (Thebes) and continued work on the temple built by Seti I at Abydos. Ramses also ordered the construction of his father’s funerary temple on the bank of the Nile in Luxor (Thebes) and built another one for himself. The legacy is now known as the Ramesseum.
His greatest works were the rock-cut temple of Abu Simbel, dedicated to Amun, Ra-Harmachis, and Ptah.4 colossal statues of the king rising in front of the temple: its length is 185 feet, its height 90 feet.
His name can be seen on temples and buildings in Egypt, and he often usurped the works of his ancestors by inscribing his own name on sculptures that did not reflect him. The slightest repair to a sanctuary was enough of a reason for him to have his signature engraved on every prominent portion of the structure.
It seems that Ramses II was an admired pharaoh, both during and after his life. His popularity may be due to a combination of the prosperity Egypt enjoyed under his reign, as well as his skill as a propagandist.
Ramses’ personal life is still unknown, possibly due to a lack of records. His first and perhaps favorite queen was Nefertari; the smaller temple at Abu Simbel was dedicated to her.