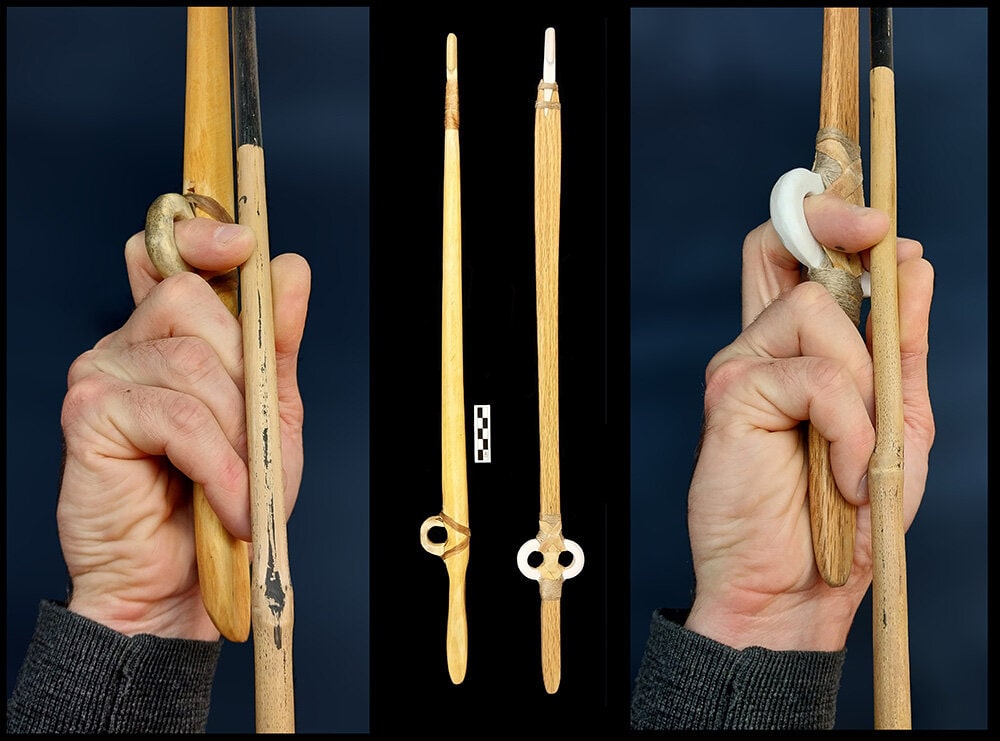
When many researchers looked at an astonishing group of artifacts discovered at French archaeological sites, they presumed they were ornaments or clothing. But Justin Garnett, a doctoral candidate in anthropology at the University of Kansas saw something else.
“They resembled finger loops like those used by some North and South American spearthrowers,” said Garnett.
That observation led to his new article, “Exploring the Possible Function of Paleolithic Open Rings as Spearthrower Finger Loops.” It examines open-ringed objects discovered in the late 19th century at Le Placard, Petit Cloup Barrat, and Cave à Endives. His research hypothesizes that such rings (fabricated from antlers) were finger loops used as part of prehistoric weapon systems. It appears in the Journal of Paleolithic Archaeology.
“If you are familiar with spearthrowers, the shape of it jumps out at you immediately,” said Garnett, who co-wrote the article with Frederic Sellet, KU associate professor of anthropology. “So it was like an ‘aha moment’ when I saw pictures of these objects in a publication. It was hiding in plain sight.”
These particular devices are distinctively shaped like the Greek letter omega, with pointed tabs on either end and an inner opening of approximately 2 centimeters. Since Garnett couldn’t use any of the dozen actual items to test his theory, he built his own.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
He reproduced the open rings in antler, bone, and 3D-printed plastic. These were then hafted to speculatively reconstructed spearthrowers.

“I used the 3D ones to get larger sample sizes of specimens so I could test them for comfort. Like how does shape relate to comfort when you’re using these things? But then for the actual experiment, I used elk antler since I was unable to get reindeer antler, which is the material that the originals were made out of,” he said.
For testing purposes, he employed them to throw darts, which are similar to large arrows or javelins rather than traditional rigid spears.
He said, “Most of these darts are designed to be used as hunting weapons, and their ranges are shorter than ones made to throw long distances because they’re heavy enough to inflict damage. So with hunting-weight darts, I could throw them 50 to 60 meters.”
The finger loop artifacts appear in the European Upper Paleolithic period (a later phase of the Stone Age). It shifts the confirmed presence of the spearthrower back from the Magdalenian or Solutrean to the Badegoulian – which is around roughly 22,000 years before the present.
“People are always interested in when a piece of technology first appears. This pushed back the existence of the spearthrower system by 5,000 to 6,000 years – and this feels significant to me in terms of understanding when things originated,” he said.
So how sure is Garnett that these items are actually finger loops for spear-throwing?
“Well, it’s a fairly simple shape. It could serve a lot of purposes. It might even be a mistake to assume all 12 of them are the same thing just simply because they have the same shape,” he said.
“But on a percentage basis of being right, I’d personally say it’s in the high 90s. They look exactly like what I would expect a spearthrower finger loop to look like if it were made out of antler. And they come out of digs that also produced other parts of spearthrowers. So it is a tidy explanation borne out by the evidence.”
At KU since 2019, Garnett focuses on technological organization around projectile weaponry. He first became interested in this topic when taking an archeology class as a student at the University of Missouri. Since then, he’s taken an active part in the spear-throwing community as an officer in the World Atlatl Association and the Missouri Atlatl Association. (Atlatl means “spearthrower” in the Nahuatl language spoken by the Aztecs.)
“The most misunderstood aspect of prehistoric weapons systems is that they are unsophisticated or poorly designed and crude,” Garnett said. “I think my research has relevance to today’s society because it shows that people all over the world when faced with similar situations do similar things. And prehistoric peoples and technologies were sophisticated and complex in ways we might not initially appreciate.”
Cover Photo: A reconstruction with one loop, and a reconstruction with two, and the ways in which Justin Garnett held them, respectively. Credits: Justin Garnett and Frederic Sellet.