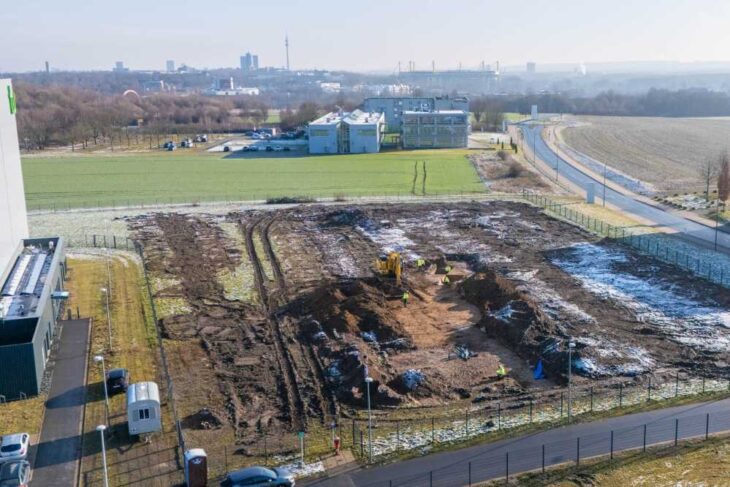
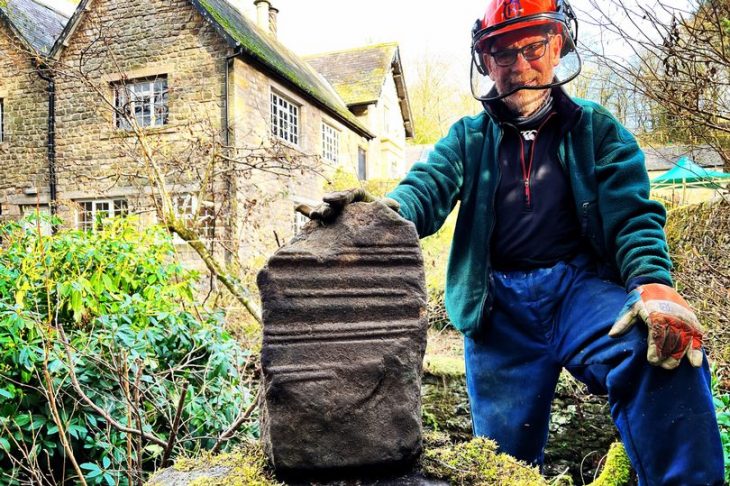
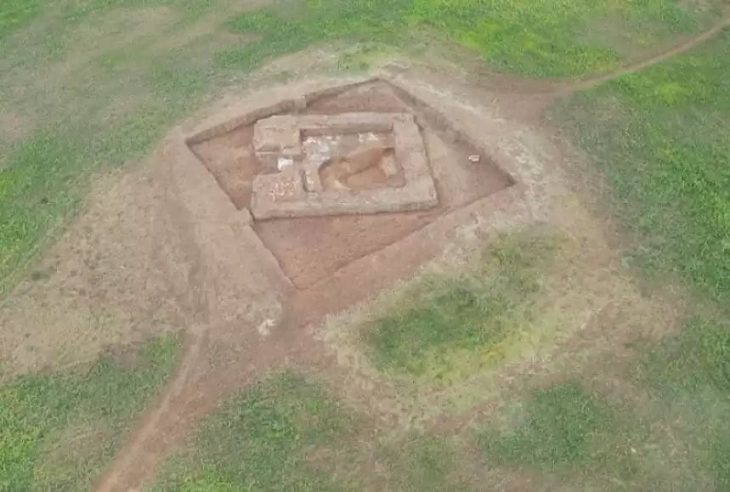
One of four recently discovered shipwrecks near Brunswick Town/Fort Anderson may be the 18th-century Spanish privateer that exploded in 1748 — but coastal erosion threatens these rare finds.
Maritime archaeologists from East Carolina University’s Program in Maritime Studies have uncovered four historic shipwrecks off the coast of North Carolina, including what may be the infamous 1748 Spanish privateer La Fortuna.
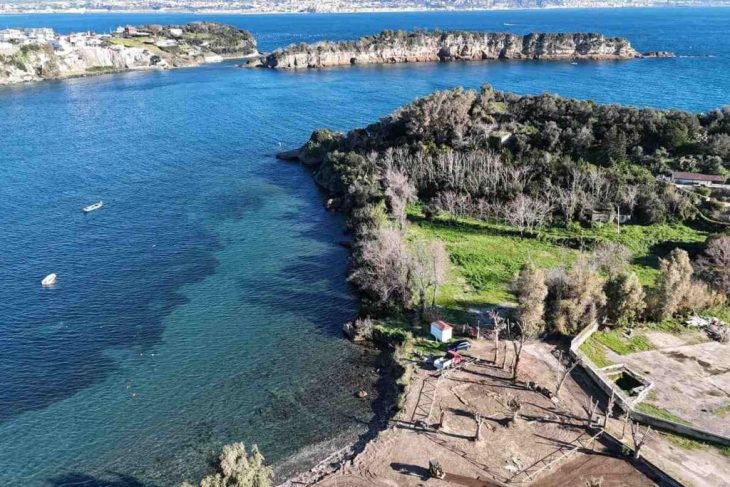
The discovery, made during ECU’s summer field school at the Brunswick Town/Fort Anderson State Historic Site, offers a rare glimpse into the state’s colonial maritime history — but researchers warn that ongoing shoreline erosion could soon destroy these submerged treasures.
A Pirate Ship Lost in Battle
Dr. Jason Raupp, assistant professor in ECU’s Department of History and director of the field project, says one wreck stands out for its historical significance.
“We are extremely excited about these important sites, as each one will help us to better understand the role of BTFA as one of the state’s earliest colonial port towns,” Raupp said. “These submerged colonial waterfront features are incredibly well-preserved and present an excellent opportunity for ECU students to engage in hands-on, collaborative research.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Wood samples from the suspected La Fortuna wreck indicate the use of Monterey or Mexican cypress — trees native to southern California and Central America — suggesting the ship’s construction involved materials from the Spanish Caribbean colonies. The wreck was found near where diver Dennison Breece recovered an 18th-century cannon in 1985, believed to be from La Fortuna.
According to historical accounts, La Fortuna exploded near Brunswick Town’s colonial wharves during a September 1748 attack at the end of King George’s War.
A Student’s Serendipitous Find
Graduate student Cory van Hees was part of the discovery team. While mapping a colonial wharf in the Cape Fear River’s murky waters, he stumbled upon wooden frames barely visible in the clay.
“I didn’t understand what I was looking at in that moment,” van Hees recalled. “Later that day, Dr. Raupp confirmed this was a wreck, which may be La Fortuna. It was kind of overwhelming and a little emotional once it set in.”
Van Hees credits his father’s passion for history and shipwrecks — and ECU’s global reputation in maritime archaeology — for inspiring his career path.
Three More Wrecks Tell a Wider Story
In addition to the possible La Fortuna, ECU archaeologists recorded three other shipwrecks:
A reclaimed vessel likely used for expanding waterfront land.
A colonial flatboat once used to ferry goods between plantations and the port.
An unidentified wreck barely visible above the riverbed.
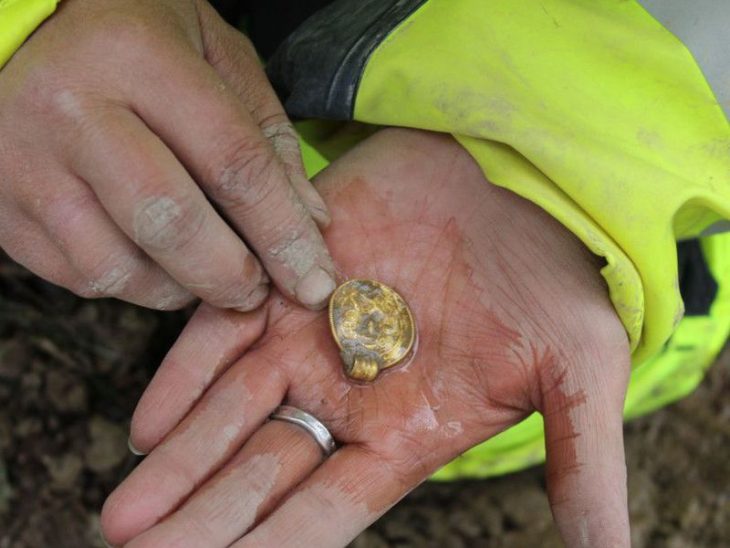
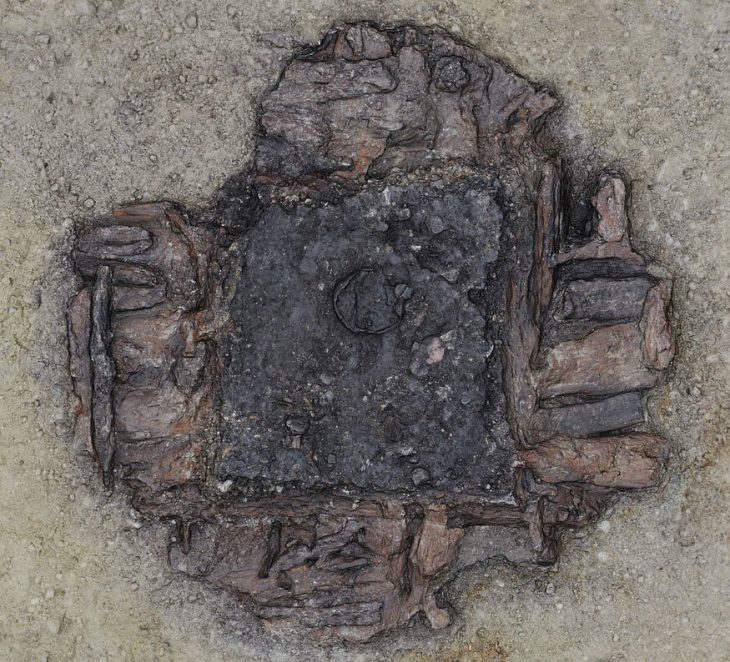
The team also mapped colonial port infrastructure, including two timber-crib wharves, a marsh causeway, and artifacts reflecting trade, daily life, and military conflict.
Erosion: A Race Against Time
While the discoveries are cause for excitement, erosion remains a pressing threat. BTFA’s southern shoreline, unprotected from wave energy and storm surges, is rapidly deteriorating. This summer, the ECU team documented exposed sites and recovered over 40 timbers from the possible La Fortuna before they could be lost.
Remarkably preserved — with visible tool marks from 18th-century shipwrights — the timbers were transferred to the N.C. Office of State Archaeology’s Queen Anne’s Revenge Conservation Laboratory for preservation and study.
“The successful recovery of the possible La Fortuna shipwreck and documentation of heritage at risk within a nationally significant historic site demonstrates the effectiveness of the collaborative efforts of the research team,” Raupp said.
Collaboration for Preservation
The project was made possible through partnerships with the N.C. Department of Natural and Cultural Resources, the Office of State Archaeology, and the Friends of BTFA. Wood species identification was performed by the U.S. Forest Service’s Forest Products Laboratory.
All archaeological sites at BTFA — both land-based and underwater — are protected under state and federal law. ECU holds the necessary permits to conduct fieldwork at the site, with additional surveys planned for the 2025 season.
Preserving North Carolina’s Maritime Heritage
For Raupp and his students, these discoveries offer more than just a glimpse into the past — they’re a reminder of how quickly history can be lost without preservation.
“This work is helping us piece together the story of North Carolina’s colonial maritime heritage,” Raupp said. “But without intervention, erosion could erase these stories forever.”
East Carolina University (ECU)
Cover Image Credit: A large section of the possible La Fortuna shipwreck sits on the beach. Credit: ECU Program in Maritime Studies