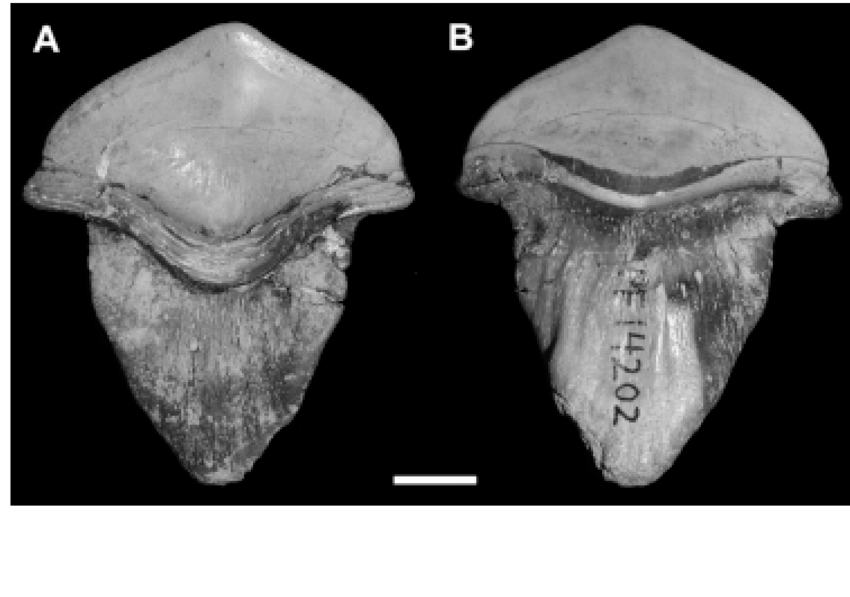
A 290 million-year-old fossil of a shark with petal-shaped teeth has been discovered in China.
Seven well-preserved Petalodus teeth were discovered in the Qianshi limestone in Yangquan City, Shanxi Province, north China.
The study was published in the English edition of the most recent issue of Acta Geologica Sinica. According to the findings, the specimens are characterized by petal-shaped teeth with a spade-like crown and a long, tongue-shaped root.
According to Gai Zhikun of the Chinese Academy of Sciences’ Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology, the shark with petal-shaped teeth is a highly enigmatic and primitive animal that lived between 360 million and 250 million years ago (CAS).
The shark’s tooth fossil is comparable in size to the great white shark’s tooth. According to co-author Lin Xianghong of CAS, it is a prehistoric gigantic shark with a body length of 3 to 5 meters.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
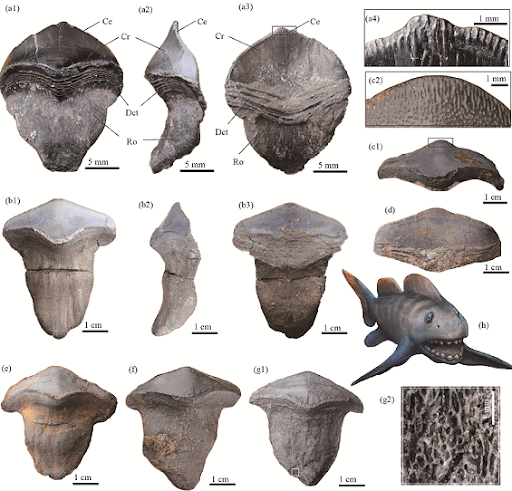
So far, the shark species’ fossil has been discovered in several locations around the Northern Hemisphere.
Shark teeth are among the most widely available fossils. One of the main reasons for this is that shark teeth, like most teeth, are made of dentin, a hard calcified tissue that does not break down easily. In addition, dentin is harder and denser than bone. Also, shark teeth vary depending on the species. Different estimates for different sharks range anywhere from 25,000 to 50,000 teeth lost in a lifetime.
The shark’s fossil has been discovered in China and Japan, showing that it had the ability to move across oceans and was a predator with exceptional swimming abilities, according to the experts.
According to fellow co-author Bai Zhijun of Yangquan City’s Planning and Natural Resources Bureau, “abundant fossil evidence reveals that Yangquan was a warm and translucent shallow sea near the equator more than 200 million years ago, perfect for many sorts of marine life to exist.”