60,000 to 70,000 years ago, our species Homo sapiens walked out of Africa and began to find new homes around the world. Despite the enormous importance of this era, we know surprisingly little about where people were living when they first ventured out into the world, which was between 70,000 and 45,000 years ago.
Homo sapiens walked out of Africa, what happened next? Well, hidden clues can be found in our genes, according to a new study.
A recent multidisciplinary study has by looking at ancient and modern DNA, revealing that the Persian Plateau played a fundamental role as a hub for early Homo sapiens who expanded beyond their African homeland.
Thanks to a combination of genetic, palaeoecological, and archaeological evidence, scientists have uncovered that the region surrounding modern-day Iran likely provided a “home away from home” for around 20,000 years, allowing a significant population of Homo sapiens to build up and thrive before they dispersed across Eurasia and beyond.
Professors Luca Pagani and Michael Petraglia’s team of researchers used a novel approach that combines genetic data with paleoecological models to reveal that the Persian Plateau, located in southwest Asia, emerged as a favorable habitat capable of supporting a significantly larger human population than other areas of western Asia.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
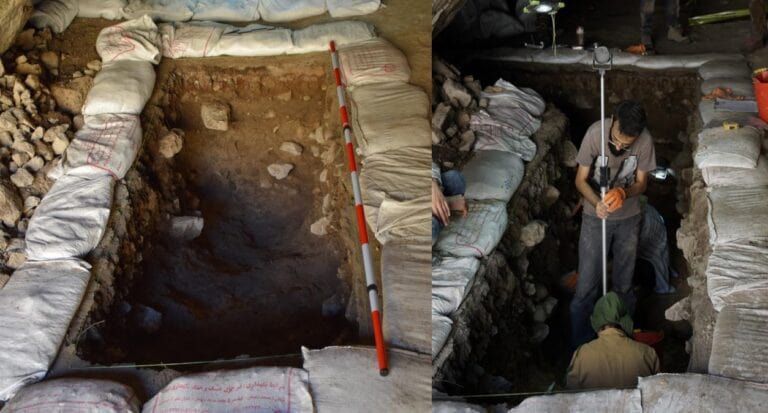

This means that the ancestors of all modern non-Africans spent approximately 20,000 years on the Persian Plateau following their migration out of Africa. In other words, if you have genetic ancestors from Europe, Asia, the Americas, or Oceania, some of them most likely spent significant time in this region.
“We looked at the timing of the movement of Homo sapiens out of Africa and concluded that Iran and the Persian Plateau played a very big role in that,” said Michael Petraglia, an archaeologist from Griffith University and one of the authors of the paper.
Parts of Iran, Turkey, and the Middle East are included in this region, which became a central hub for the initial waves of Homo sapiens’ migration out of Africa. In line with their function as the starting point of our species’ early migrations, the genetic signature found in the populations of the Persian Plateau highlights their long-standing differentiation in the region.

“The discovery elucidates a 20,000-year-long portion of the history of Homo sapiens outside of Africa, a timeframe during which we interacted with Neanderthal populations, and sheds light on the relationships between various Eurasian populations, providing crucial clues for understanding the demographic history of our species across Europe, East Asia, and Oceania,” first study author Leonardo Vallini, of the University of Padova in Italy, said in a statement.
Senior author, Professor Luca Pagani added: “The revelation of the Persian plateau as a hub for early human migration opens new doors for archaeological exploration, enriching our understanding of our species’ journey across continents and highlighting this region’s pivotal role in shaping human history.”
“Our multidisciplinary study provides a more coherent view of the ancient past, offering insights into the critical period between the Out of Africa expansion and the differentiation of Eurasian populations,” said study co-author Professor Michael Petraglia.
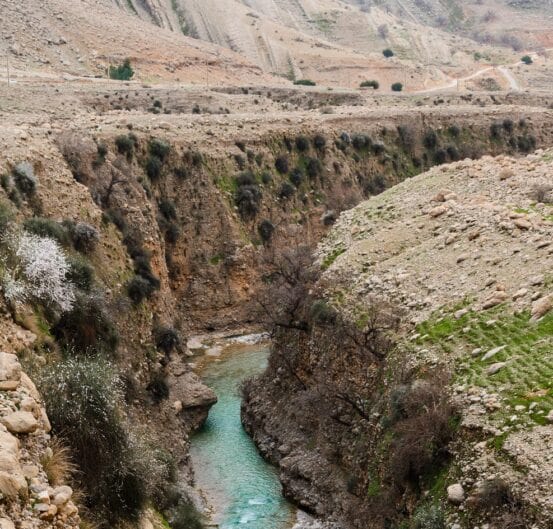

“The Persian plateau emerges as a key region, underlining the need for further archaeological explorations.”
The study is published in the journal Nature Communications.
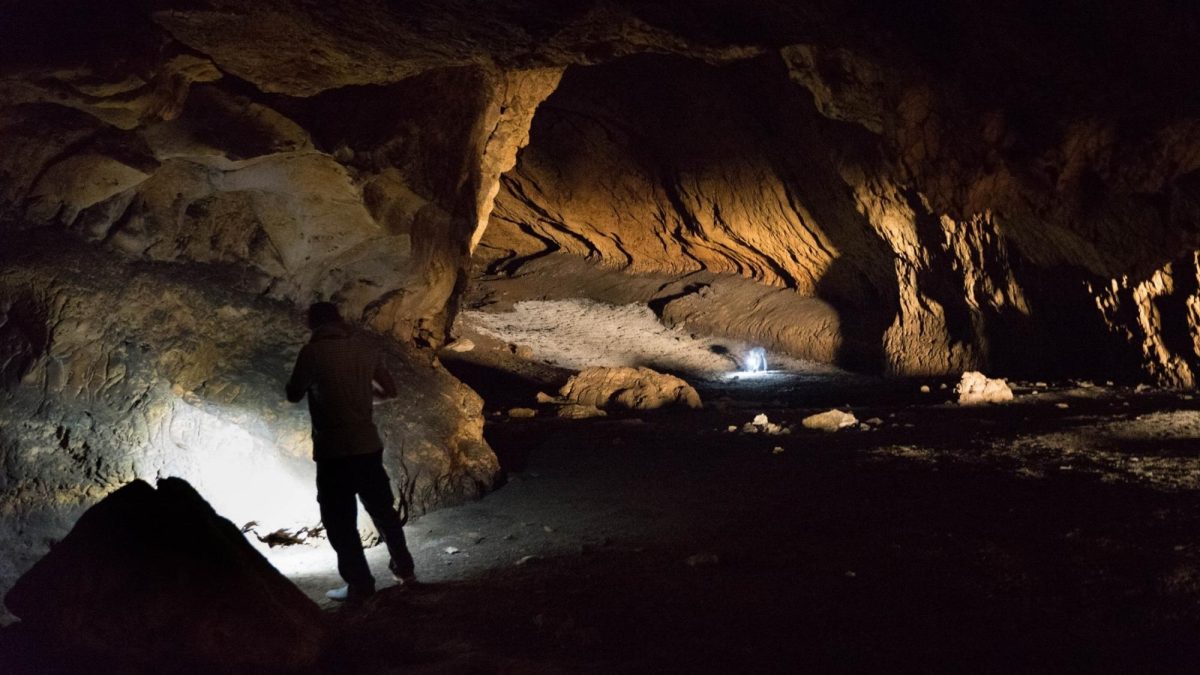
Cover Photo: Pebdeh Cave located in the southern Zagros Mountains. Pebdeh was occupied by hunter-gatherers as early as 42,000 years ago. Photo: Mohammad Javad Shoaee