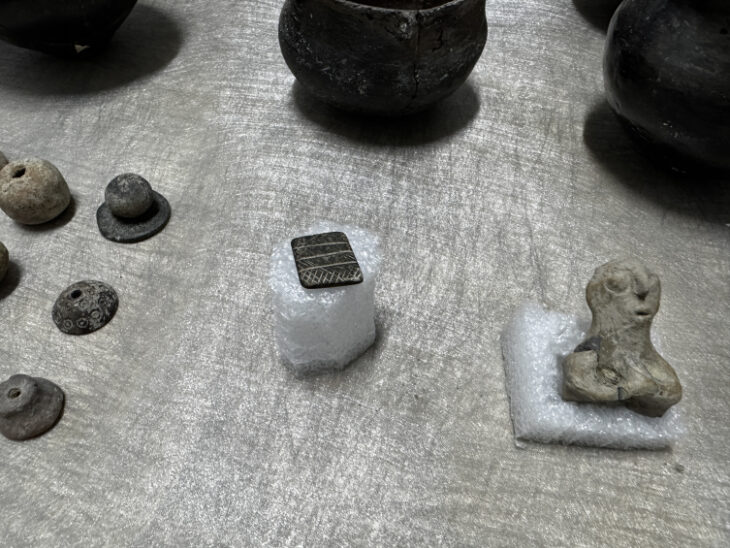
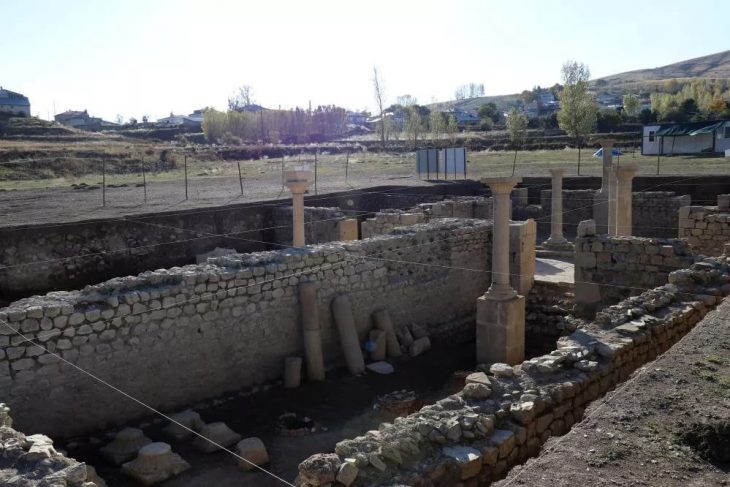
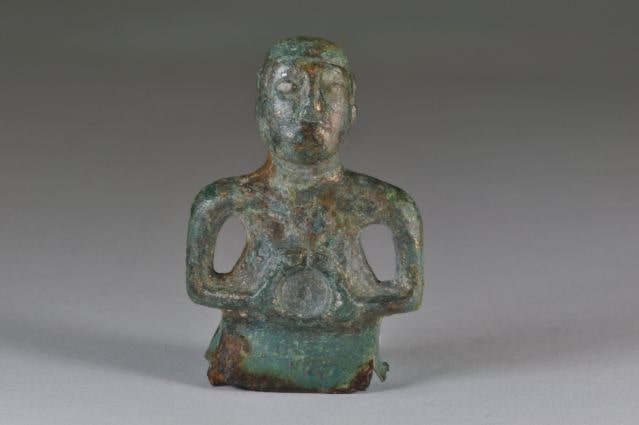
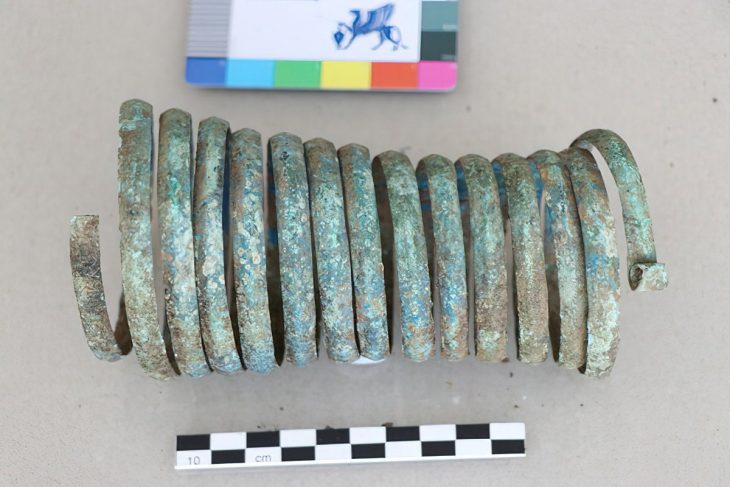
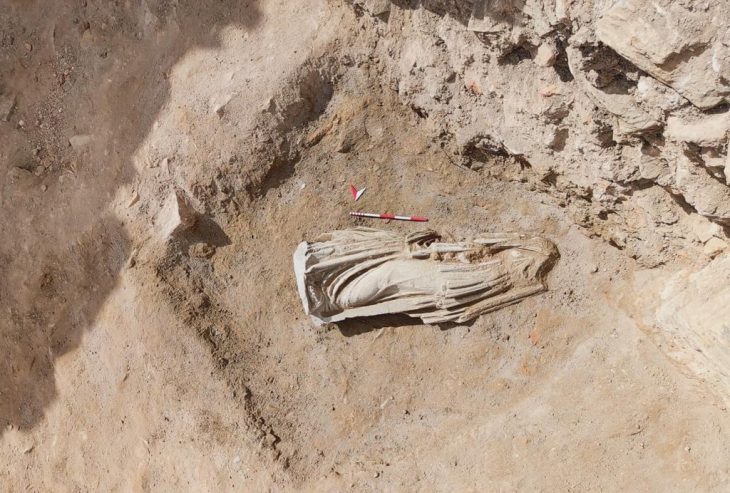
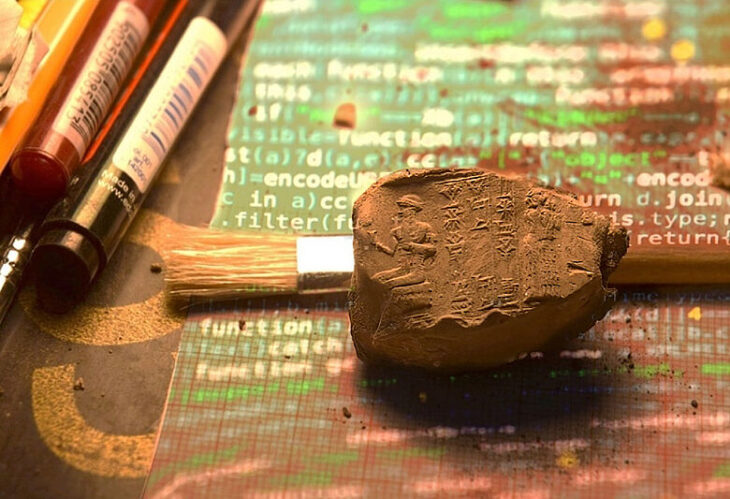
Nearly 10,000 years ago, long before the rise of cities, a community in central Anatolia was already experimenting with new ways of organizing its living space. Excavations at Canhasan 3 Höyük (Höyük: Mound) in Türkiye’s Karaman province revealed one of the earliest known streets of the Neolithic Age, dating back nearly 9,750 years—predating the world-renowned Çatalhöyük by about 750 years.
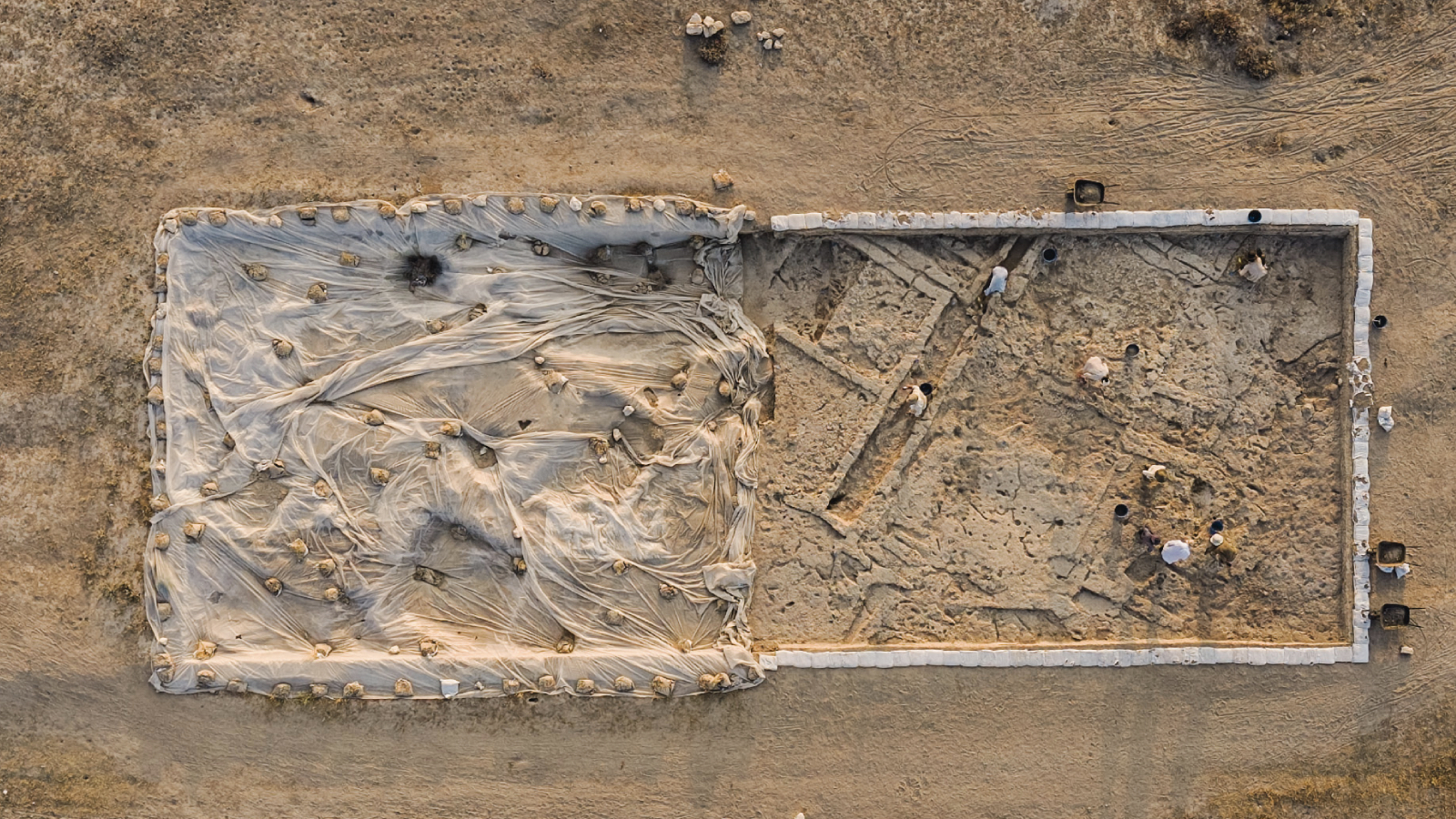
Archaeologists uncovered a carefully planned passage between houses, a rare feature that resembles one of the earliest examples of a street in human history. This finding challenges the long-standing image of Neolithic life as clusters of roof-accessed homes with little external organization, as famously seen at Çatalhöyük. Instead, Canhasan 3 reveals a community that deliberately left space between structures, hinting at early forms of social organization, shared access, and architectural planning nearly a millennium before Çatalhöyük’s peak.
A Rare Example of Early Urban Planning
The excavations, conducted under the Turkish Ministry of Culture and Tourism’s “Heritage for the Future Project”, are led by Assoc. Prof. Adnan Baysal of Ankara University. His team uncovered a passageway separating two houses—suggesting a deliberate attempt at creating communal or functional space, something rarely seen in Neolithic Anatolia.
“This is a major surprise,” Baysal noted. “While Çatalhöyük had tightly clustered houses with roof access, Canhasan 3 shows us a different architectural vision. These gaps between homes may have functioned as passageways, protective corridors for livestock, or even as an early form of a street. Whatever the case, it is extremely rare to see such spatial organization in this period.”
The team also discovered hearths placed differently than those in Çatalhöyük, hinting at diverse cultural practices within Central Anatolia’s Neolithic communities.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
From Neolithic to Bronze Age: A Settlement That Endured
Canhasan is not a single mound but a complex of three mounds (Canhasan 1, 2, and 3), representing continuous human occupation from the Pre-Pottery Neolithic to the Bronze and Iron Ages. Over thousands of years, this small yet fertile region hosted communities that witnessed the birth of agriculture, animal domestication, and permanent architecture.
According to Baysal, the secret of Canhasan’s longevity lies in its abundant water sources and fertile lands. Animal bones found at the site include remains of aurochs (wild cattle), fish, and waterfowl—suggesting a wetland environment that provided rich food resources. Plant remains currently under analysis are expected to reveal more about early farming practices in the region.
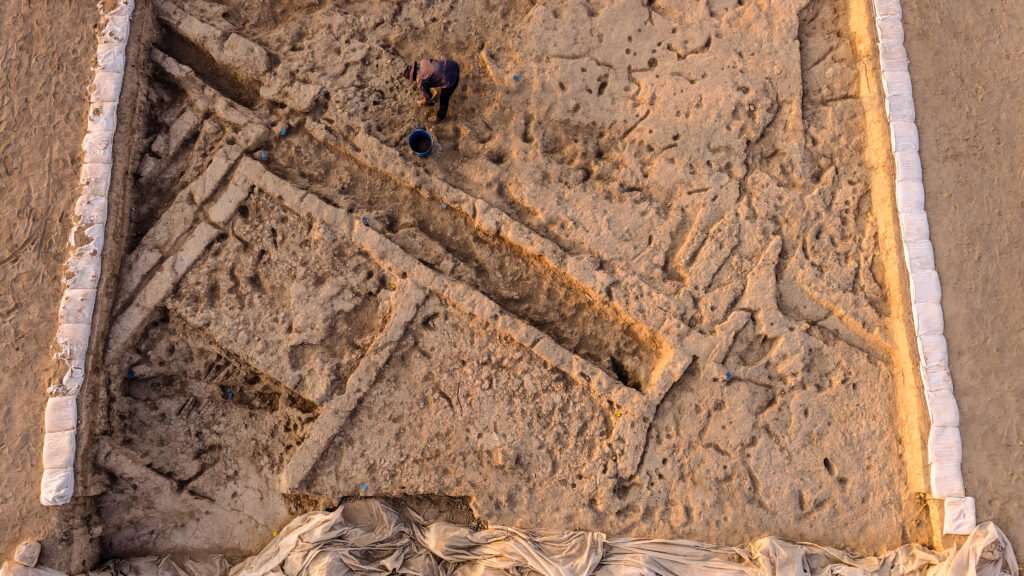

Why the Discovery Matters
The discovery of a street-like space at Canhasan 3 challenges long-held assumptions about early Neolithic settlements. Streets are considered a marker of social complexity and planned urbanism. Finding such an element almost 10,000 years ago pushes back the timeline for these innovations.
Moreover, the contrast with Çatalhöyük—famous for its tightly packed houses without streets—demonstrates that Anatolian Neolithic societies were not uniform. Different communities experimented with different solutions to everyday needs such as movement, protection, and social interaction.
The Global Significance of Canhasan
Although Çatalhöyük has long overshadowed other sites in Central Anatolia, Canhasan 3 is now emerging as a key settlement for understanding the diverse trajectories of early human settlement. Archaeologists argue that Canhasan offers:
Evidence of early spatial planning (possible street formation)
Continuity of occupation over several millennia
Rich environmental data combining geology, botany, and zoology
A link between pre-pottery and pottery Neolithic traditions
This makes Canhasan 3 not only significant for Turkish archaeology but also for the broader study of human social evolution.

A Legacy for the Future
Excavations continue with the hope of uncovering more details about the daily lives of Neolithic people in Canhasan. Researchers aim to understand whether these “streets” were purely functional or whether they carried symbolic or communal importance.
As Baysal explains: “By carefully studying the architecture, artifacts, and ecofacts, we can reconstruct how people lived, farmed, and interacted with their environment. Canhasan 3 allows us to see a unique version of Neolithic life—one that differs from Çatalhöyük yet is just as important for understanding humanity’s shared past.”
With its deep history and groundbreaking discoveries, Canhasan 3 is becoming recognized as a treasure of Anatolia—a place where the earliest experiments in community planning, agriculture, and settlement organization first took root nearly 10,000 years ago.
Cover Image Credit: DHA