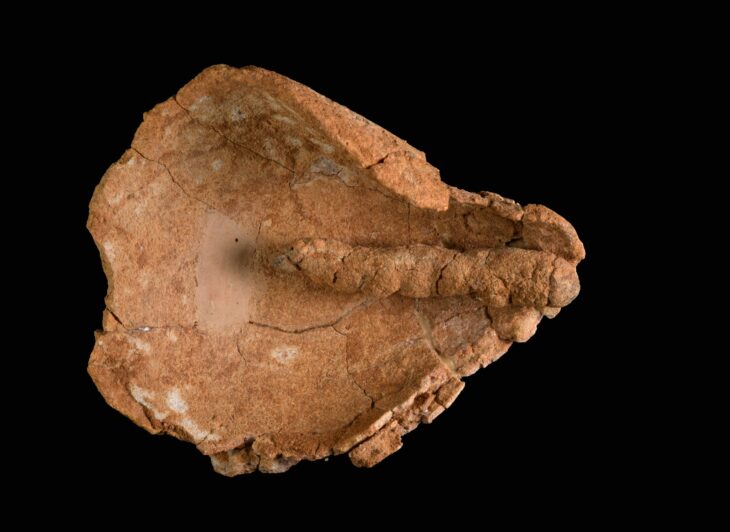
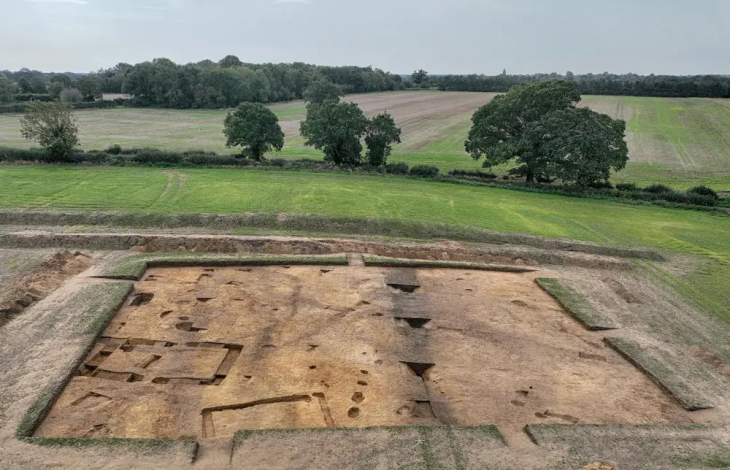
Recent research into obsidian artifacts in Alberta, a province located in western Canada, has unveiled significant evidence of long-distance trade among Indigenous peoples prior to European contact.
This groundbreaking study revisits and updates previous analyses, shedding light on the complex social and economic interactions that existed in the region.
In a statement to CBC, archaeologist Timothy Allan, the report’s author and a member of Ember Archaeology, an archaeology and historic resources consulting firm based in Sherwood Park, Alberta, remarked, ‘The sheer scale of obsidian trade suggests that likely millions of people were in contact with one another.”
The research, which analyzed obsidian sourced from 285 archaeological sites across Alberta’s Eastern Slopes, found that the majority of artifacts originated from Bear Gulch in Idaho, Obsidian Cliff in Wyoming, and two sources in British Columbia: Anahim Peak and Mount Edziza. Notably, Bear Gulch obsidian accounted for 61.8% of the artifacts, indicating a strong preference for this source among Indigenous groups.
The study highlights the relationship between obsidian distribution and communal bison hunting practices, particularly in the southern component of the Eastern Slopes. The findings suggest that obsidian was not only a tool for daily use but also a vital component of trade networks that connected distant communities along river systems.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
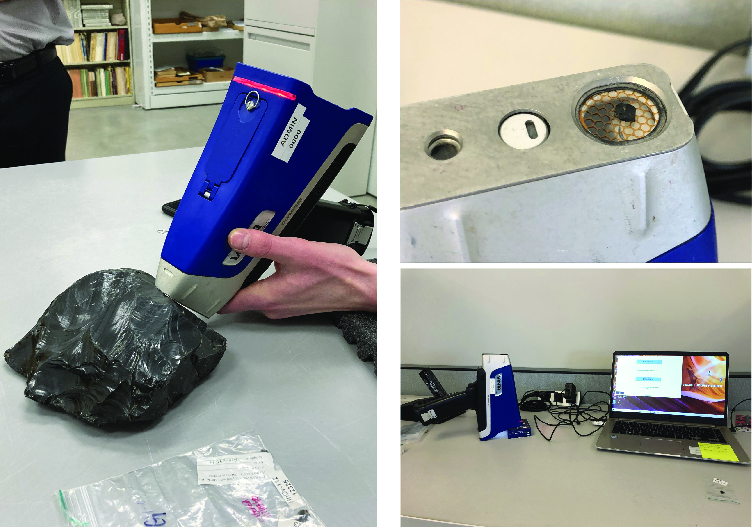

Interestingly, the research indicates that while southern sources of obsidian were frequently found in large quantities, northern sources were less common and often appeared in smaller lithic scatters. This disparity suggests that trade dynamics varied significantly between the northern and southern regions of Alberta.
The presence of obsidian at bison jump sites, where large herds were driven for communal hunting, points to the role these locations played in facilitating trade. The study found that nearly half of the sites containing Bear Gulch obsidian were located within 10 kilometers of a bison jump, underscoring the interconnectedness of hunting and trade.
As the research continues, archaeologists are calling for further analysis of obsidian finds to deepen the understanding of Indigenous trade networks in Alberta. The advent of portable X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analyzers has made it easier for researchers to analyze obsidian artifacts, paving the way for more comprehensive studies.
In conclusion, this research not only enhances our understanding of the economic and social structures of pre-contact Indigenous peoples but also emphasizes the importance of obsidian as a medium of exchange that fostered relationships among diverse groups across the region.
Allan, T. E. (2025, March 14). “Alberta Obsidian Project chronicles: Obsidian research within Alberta’s Eastern Slopes”. Archaeological Survey of Alberta Occasional Paper No. 43
Cover Image Credit: Alberta Obsidian Project