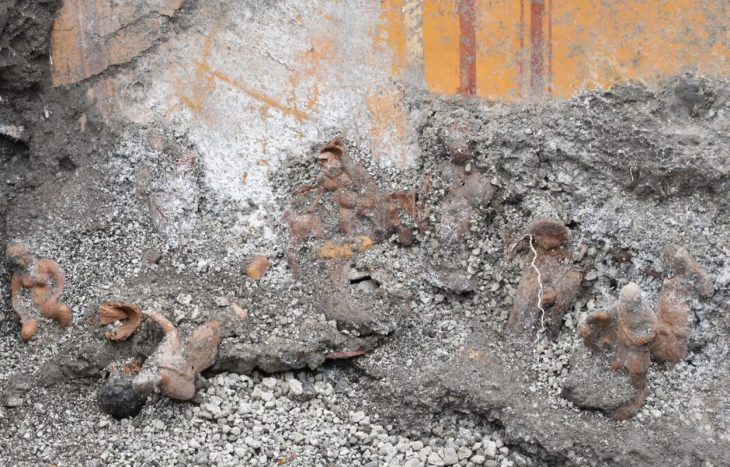
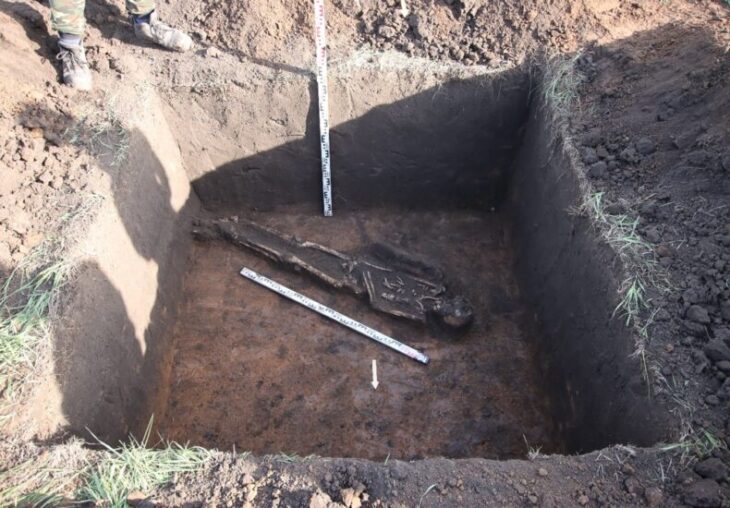
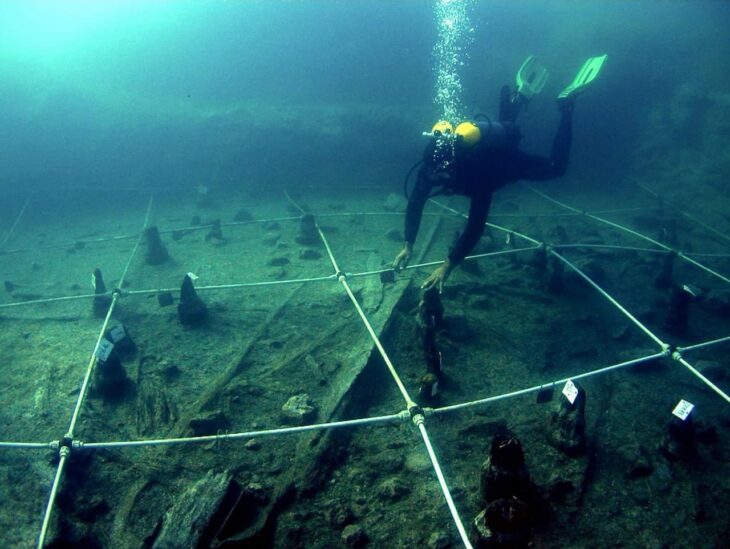
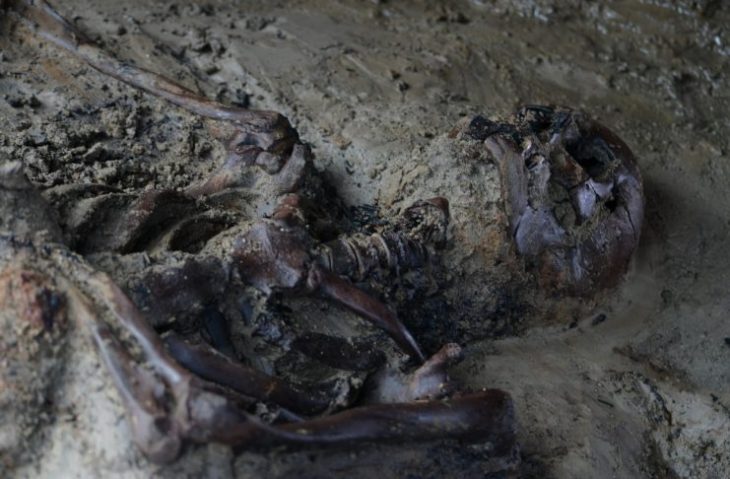
Fourteen bodies were found at Cramond near Edinburgh in 1975. New research suggests that two of the remains of these 14 bodies, also known as ‘bodies in the bog’, may have come from the other side of medieval Scotland.
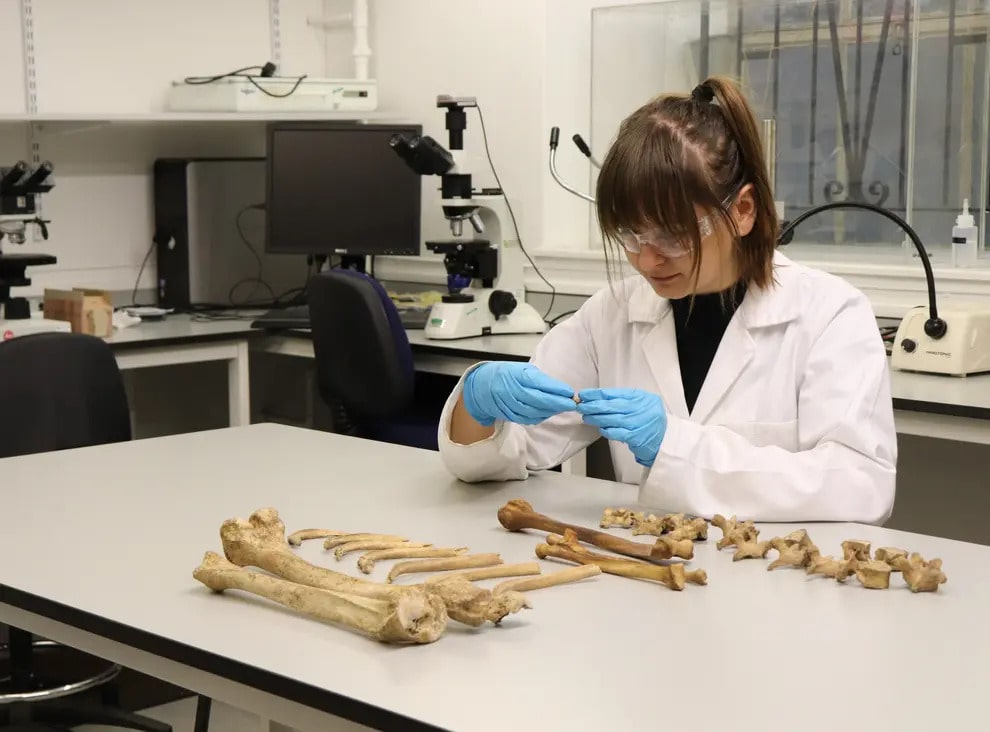
The skeletal remains of nine adults and five infants found in the latrine of what was once a Roman bath house close to Edinburgh have fascinated archaeologists and the public alike.
Discovered in Cramond in 1975 they were originally thought to be victims of the plague or a shipwreck from the 14th century. Then radiocarbon dating showed them to be some 800 years older, dating to the 6th century, or early medieval period.
Bioarchaeological work led by the University of Aberdeen has now discovered that some of the group may have travelled across Scotland to make the Cramond area their home.
Their investigations change our understanding not only of this important site but of the mobility and connections of people across Scotland in the early medieval period, when the country was broadly divided between the Scotti in Dál Riata to the west, the Picts in most of northern Scotland and the Britons in the south.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The researchers examined the bones and teeth of the group unearthed from what was once the latrine of a bathhouse in a Roman fort, leading to them being coined ‘the bodies in the bog’.
Using isotope analyses they were able to look at the diet and origins of each of the adults in the group. Professor Kate Britton, senior author of the study, said they were surprised to discover that despite being buried in close proximity to each other – leading to assumptions that they were one family – some were brought up hundreds of miles apart.
“Food and water consumed during life leave a specific signature in the body which can be traced back to their input source, evidencing diet and mobility patterns,” she added.
“Tooth enamel, particularly from teeth which form between around three and six years of age, act like little time capsules containing chemical information about where a person grew up.
“When we examined the remains, we found six of them to bear chemical signatures consistent with what we would expect from individuals growing up in the area local to Cramond but two – those of a man and a woman – were very different.
“This suggests that they spent their childhoods somewhere else, with the analysis of the female placing her origins on the West coast.”
“The male instead had an isotopic signature more typical of the Southern Uplands, Southern Highlands or Loch Lomond area so it is likely he came to Cramond from an inland area.”
The findings, published in the Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences journal, provide one of the first insights into early medieval population mobility in Scotland.
Dr. Orsolya Czére, post-doctoral researcher and lead author of the study, added: “This is a historically elusive time period, where little may be gleaned about the lives of individuals from primary literary sources. What we do know is that it was a politically and socially tumultuous time.
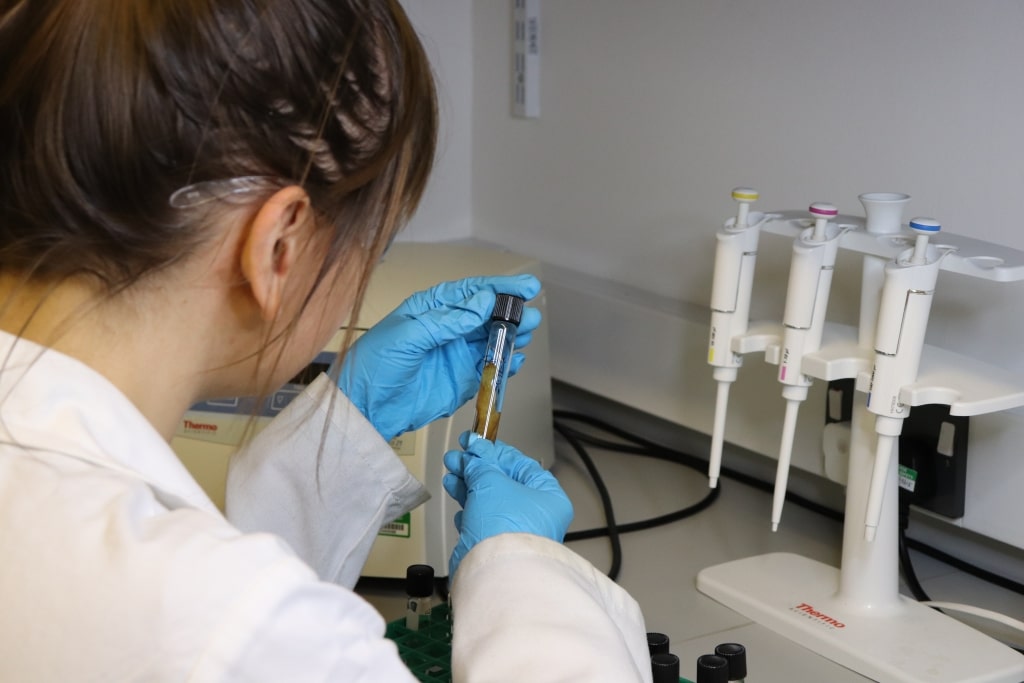

“In Scotland particularly, evidence is scarce and little is known about individual movement patterns and life histories. Bioarchaeological studies like this are key to providing information about personal movement in early medieval Scotland and beyond.
“It is often assumed that travel in this period would have been limited without roads like we have today and given the political divides of the time. The analysis of the burials from Cramond, along with other early medieval burial sites in Scotland, are revealing that it was not unusual to be buried far from where you had originally grown up.
“Previous studies have suggested that those buried here were of high social status, even nobility. What we can say from our new analyses was that these were well-connected individuals, with lives that brought them across the country”
“This is an important step in unravelling how these different populations of early medieval Scotland and Britain interacted.”
Despite evidence for geographical mobility, social tensions may still have been high. Several of the skeletons at Cramond indicate that some of the individuals may have met with violent ends.
Osteoarchaeologist and co-author Dr. Ange Boyle from the University of Edinburgh said: “Detailed osteological analysis of the human remains has determined that a woman and young child deposited in the Roman latrine suffered violent deaths. Blows to the skulls inflicted by a blunt object, possibly the butt end of a spear would have been rapidly fatal. This evidence provides important confirmation that the period in question was characterised by a high level of violence.”
John Lawson, the City of Edinburgh Council archaeologist, co-author and lead archaeologist on the investigations at Cramond, says the new findings further underline the importance of the Cramond site.
“This paper has been the result of fantastic collaboration between ourselves and our co-authors from Aberdeen and Edinburgh Universities. The final results from the isotopic research have confirmed the initial 2015 results giving us archaeological evidence and a window into the movement of elite society in the 6th century.
“In particular it is helping us to support our belief that Cramond during this time was one of Scotland’s key political centres during this important period of turmoil and origins for the state of Scotland. Whilst it has helped us answer some questions about the individuals buried in the former Roman Fort’s Bathhouse, it has also raised more. We hope to continue to work together to bring more findings to publication as these have a significant impact on what is known about the history of Scotland and Northern Britain during the Dark Ages.”
The study was funded by Edinburgh City Council and the University of Aberdeen and research by Professor Britton and Dr. Czere is supported by the Leverhulme Trust and AHRC respectively.