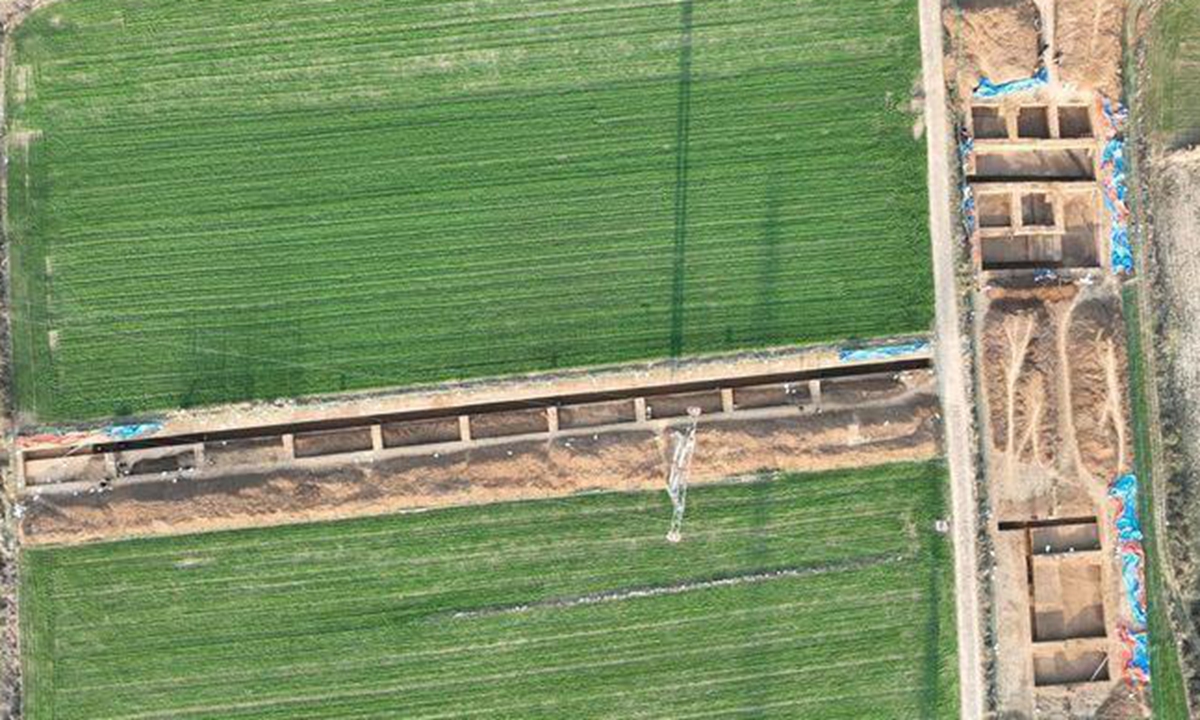
Recently discovered evidence from the Changqing district of Jinan, located in East China’s Shandong Province, reveals that the origins of the Great Wall can be traced back 300 years earlier than previously thought.
The excavations in the Changqing district of Jinan, located in East China’s Shandong Province, have uncovered that the earliest known sections of the Great Wall date back to the late Western Zhou Dynasty (1046 BC-771 BC) and the early Spring and Autumn Period (770 BC-476 BC). This discovery pushes the timeline for the construction of the Great Wall back by approximately 300 years, as reported by Jinan Daily.
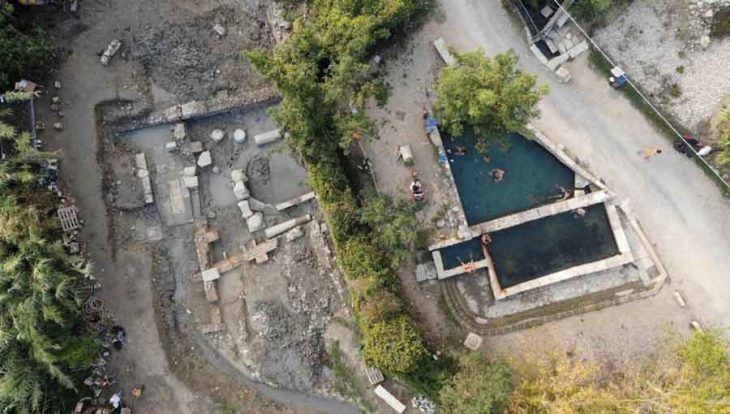
The excavation, conducted from May to December 2024, spanned an area of 1,100 square meters in Guangli village. This marks the first proactive excavation of the Great Wall of Qi State, following earlier surveys and investigations.
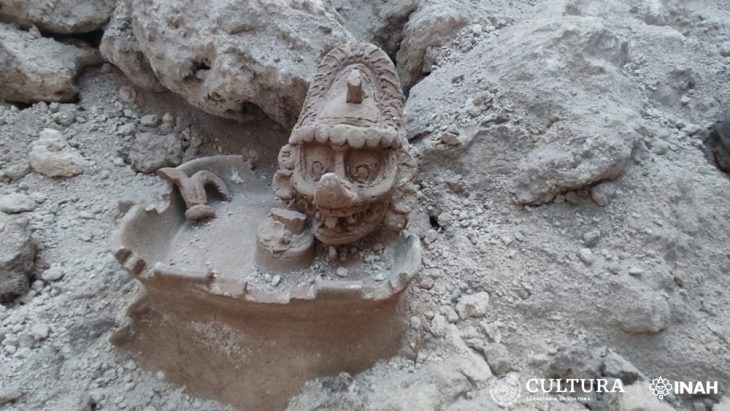
Archaeologists utilized a multidisciplinary approach, collecting not only traditional artifacts but also specimens such as plant silica and animal bones. They gathered samples for optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) and carbon-14 dating, resulting in a wealth of archaeological findings.
The Great Wall of Qi is a significant component of the UNESCO World Heritage-listed Great Wall. As the earliest and longest of China’s Great Walls, it extends a total of 641 kilometers.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Zhang Su, the project leader from the Shandong Provincial Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology, explained that the excavation revealed substantial evidence of multiple construction phases. The team unearthed large rammed-earth structures, roads, slopes, residential foundations, trenches, ash pits, and walls from various stages of the wall’s development.
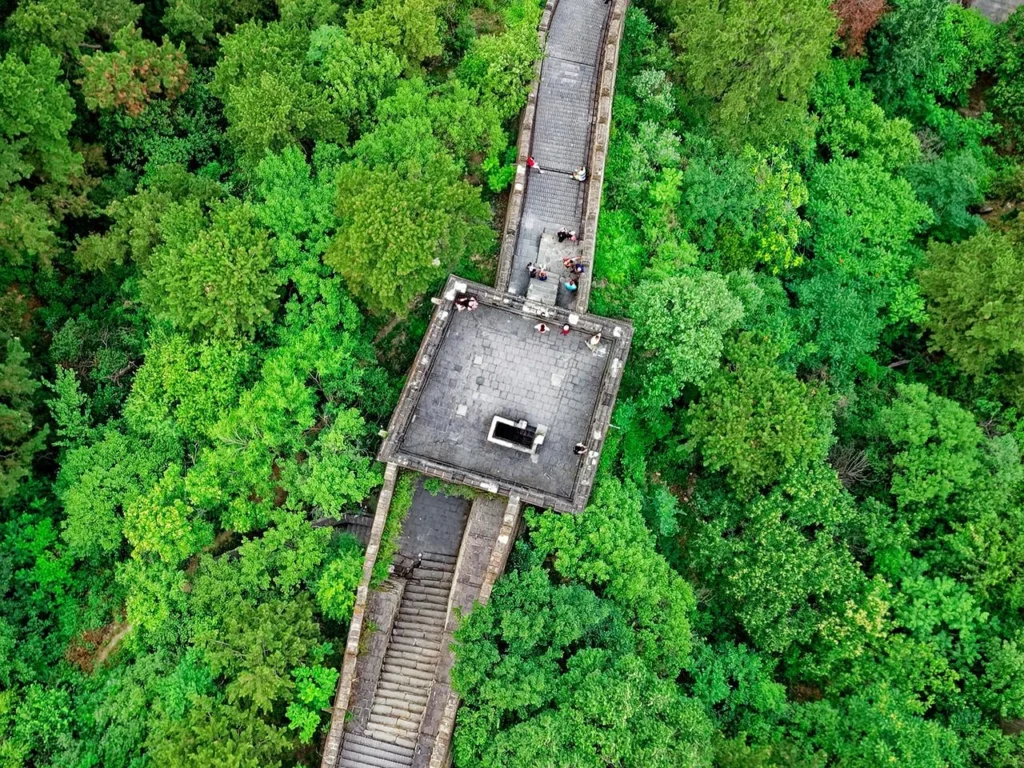

According to Zhang, the walls can be categorized into two main phases: early and late. The earlier walls, dating back to the Spring and Autumn Period, are approximately 10 meters wide and may have been constructed as early as the Zhou Dynasty (1046 BC-256 BC). The later sections primarily belong to the Warring States Period (475 BC-221 BC).
The third phase of the walls is the best preserved, showcasing the most advanced construction techniques and measuring over 30 meters in width. This section was likely built during the peak of the Qi State in the Warring States Period.
“This archaeological discovery pushes the construction date of the Great Wall back to the Western Zhou period, establishing it as the earliest known Great Wall in China,” Liu Zheng, a member of the Chinese Society of Cultural Relics, stated to the Global Times on Sunday. “It marks a significant breakthrough in Great Wall archaeology and is a milestone in clarifying the origins and development of research on China’s Great Wall.”
In addition to the walls, two residences from the Zhou Dynasty were discovered beneath the early walls in the northern excavation area. These homes, characterized by square foundations with rounded corners, are typical of the semi-subterranean dwellings of that era. This suggests that prior to the wall’s construction, the area may have been part of a small settlement, potentially linked to river defense, Zhang noted.
The archaeological team, led by Zhang, also uncovered an ancient settlement known as Pingyin City, which is mentioned in historical texts. This site is located about 1.5 kilometers north of the Great Wall.
“The layout, location, and associated infrastructure of the Great Wall of Qi reflect the advanced military planning and strategic responses of the Qi State to external threats. Its close connection to Pingyin indicates that the wall served not only as a defensive structure but also played a strategic role in controlling key transportation routes,” Zhang remarked.
This discovery not only reshapes our understanding of the Great Wall’s history but also highlights the advanced military strategies of the Qi State, emphasizing the wall’s dual role as both a defensive structure and a crucial element in controlling trade and transportation routes in ancient China.
Cover Image Credit: Jinan Daily