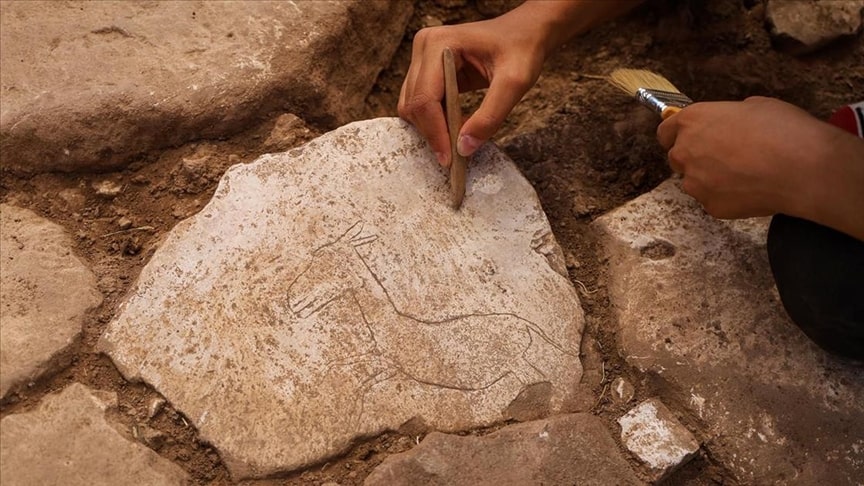
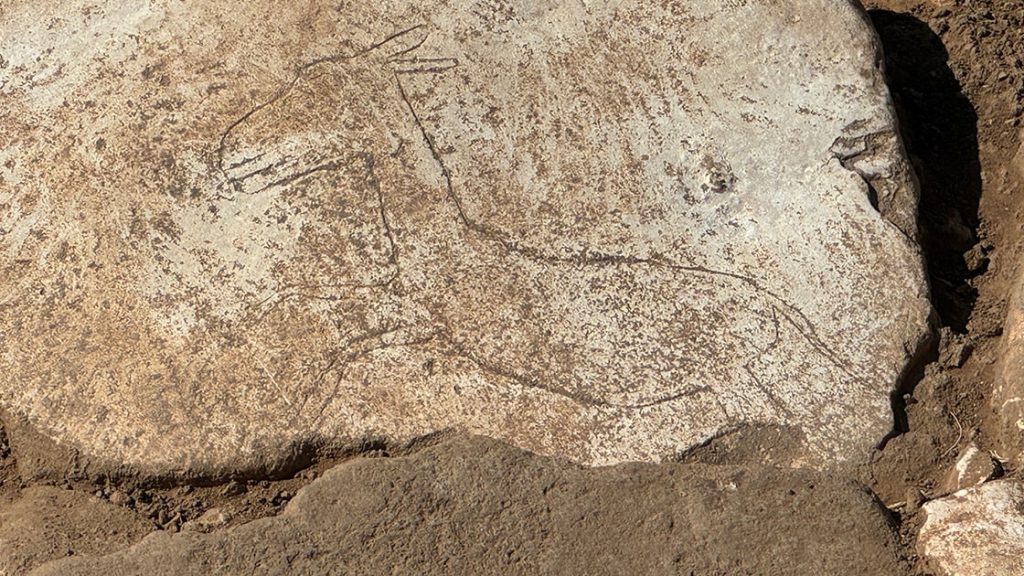
The figure of a running wild donkey carved on a stone was discovered during excavations at Karahan Tepe, a Pre-Pottery Neolithic site located in Şanlıurfa, southeast Türkiye.
Karahan Tepe is one of the Pre Pottery Neolithic Sites emerging in what is known as the Taş Tepeler Region of Southeast Turkey in the province of Şanlıurfa. Located just 23 miles (37 km) southeast of Göbekli Tepe, Karahantepe is part of the Taş Tepeler (Stone Hills) project.
Taş Tepeler simply means stone hills and is an apt description of a region producing numerous sites characterized by T-shaped anthropomorphic pillars of the type that first came to prominence at Göbekli Tepe.
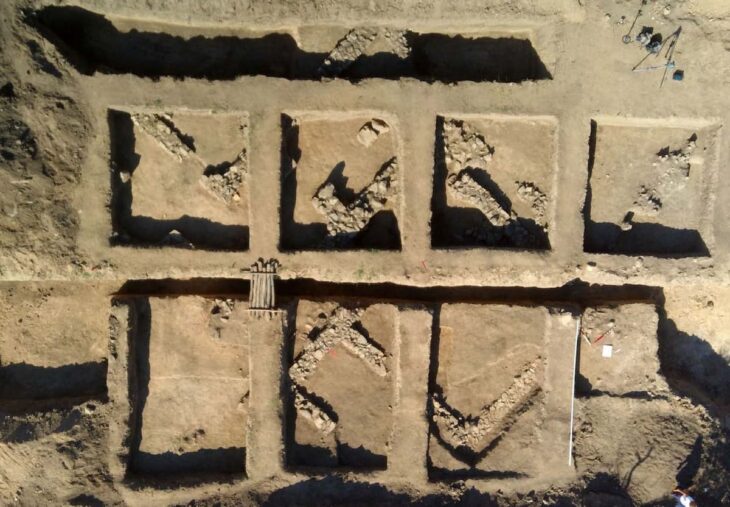
2024 excavations continue in Karahan Tepe, where more than 250 obelisks in the ‘T’ shape were found. In this context, a depiction of a running wild donkey figure was uncovered on one of the stones paved on the floor.
Karahan Tepe Excavation Head Prof. Dr. Necmi Karul told AA correspondent that excavation works are continuing at 10 points including Karahan Tepe within the scope of the Taş Tepeler (Stone Hills) Project.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Stating that they have been working on other public buildings and huts around the central public building in Karahan Tepe this year and that they started to open one of them a few weeks ago, Karul said:
‘The building is sunken into the ground and has a wattle and daub roof system over a short stone wall. We understand that the floor was paved with large flat stones. Some of these stone pavements were used as grinding stones and on one of them we came across a wild donkey motif. There are animals that are decisive in the iconography of this period. We divide them into 2 categories. The first one is the animals whose eeriness is emphasised, and we see these especially on the obelisks. Another group consists of birds and the most consumed animals, among which the gazelle is the most popular. Wild donkeys are also among the other consumed animals. We can say that these animals were the animals that people were around, consumed and lived with during this period, compared to the scary ones. Similarly, this wild donkey is a figure placed in a base with grinding stones and carved in motion. In this respect, we have encountered some figures on building bases in Göbeklitepe before, but this is the first time we have encountered such a moving wild donkey motif. This is a find that will contribute a little more to our understanding of the animal iconography and the relationship between man and his environment.’
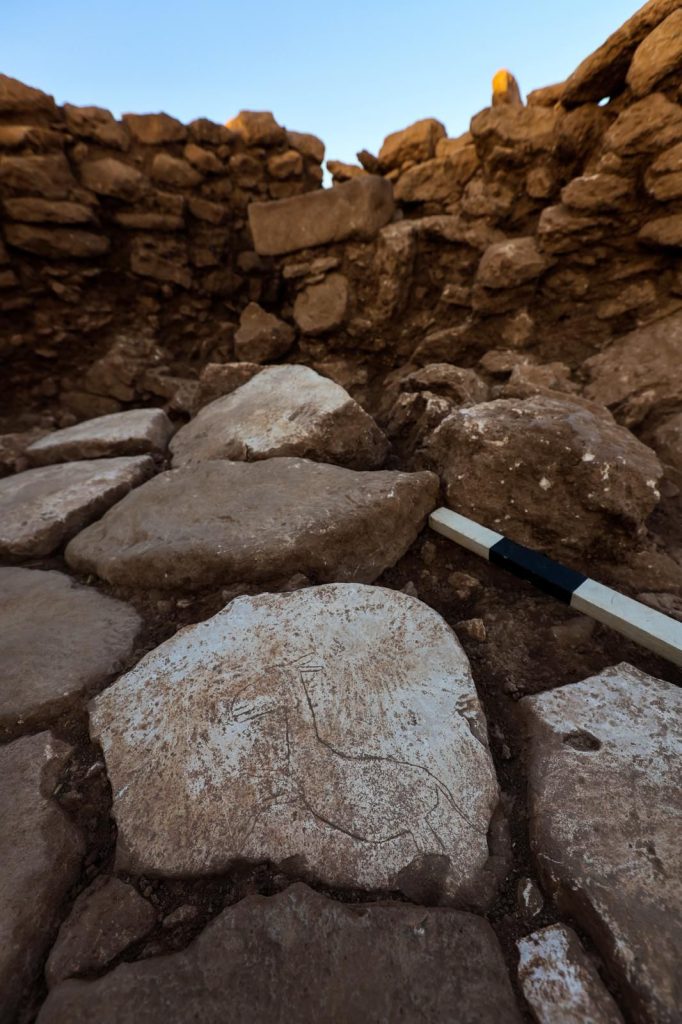

Stating that the structures they are currently working on are places dating back to 11 thousand years ago, Karul pointed out that the presence of grinding stones in them indicates that daily life activities were also carried out here.
Stating that the presence of such animal depictions or obelisks in these places also proves that there are symbolic aspects, Karul said:
‘The donkey figure found is a figure of about 20 centimeters in length placed right next to the grinding stone, but the fact that it is mobile rather than its dimensions and that it is depicted in proportion to the stone on which it is carved, is again an indicator of the skill of the artists of this period. This is the first example we have encountered as a figure on the floors of buildings in Karahan Tepe. This, of course, shows that there may be similar ones. We have not yet reached the floor levels of many of the huts mentioned here. We are deepening them in different structures. There are other places where we will reach those levels.’
Mehmet Nuri Ersoy, Minister of Culture and Tourism, shared on his social media account that Karahan Tepe sheds light on the depths of history as one of the most important settlements of the Neolithic Age and that the Stone Hills project continues to shed light on world history.
Cover Image: Minister of Culture and Tourism